$9 Billion Budget Boost: Australia's Opposition's Economic Plan
Table of Contents
Australia's political landscape is buzzing with the opposition's newly unveiled $9 billion economic plan, promising significant changes to the nation's financial trajectory. This detailed analysis explores the core components of this ambitious proposal, examining its potential benefits and drawbacks for the Australian economy. We'll dissect the key policy areas, assess their feasibility, and consider their broader implications for Australian businesses and citizens.
Key Promises of the $9 Billion Budget Boost
The opposition's $9 billion economic plan centers around several key areas aimed at boosting economic growth and improving the lives of Australians. These include significant investments in healthcare, infrastructure, education, and targeted tax cuts designed to stimulate the economy.
Increased Funding for Healthcare
A substantial portion of the $9 billion is earmarked for improvements to Australia's healthcare system. This includes:
- Increased hospital funding: Allocating additional resources to alleviate pressure on public hospitals and reduce waiting lists.
- Improved Medicare benefits: Expanding access to essential medical services and reducing out-of-pocket expenses for patients.
- Investment in preventative healthcare: Focusing on early intervention and public health initiatives to improve overall health outcomes and reduce long-term healthcare costs.
These improvements are projected to lead to reduced waiting times, improved health outcomes for Australians, and a stronger, better-equipped healthcare workforce. However, challenges remain. Critics question the cost-effectiveness of some proposals and raise concerns about the long-term sustainability of increased healthcare spending without corresponding revenue increases. The opposition needs to clearly articulate how these initiatives will be funded sustainably.
Investment in Infrastructure and Job Creation
A significant portion of the $9 billion is dedicated to infrastructure projects designed to create jobs and stimulate economic activity. The plan includes:
- Road upgrades and expansions: Improving transport links across the country, facilitating trade and reducing congestion.
- Rail network improvements: Investing in upgrading existing rail lines and constructing new ones, boosting inter-city connectivity and freight transport efficiency.
- Renewable energy projects: Investing in renewable energy infrastructure, creating jobs in the green energy sector and contributing to Australia's climate goals.
The opposition projects the creation of tens of thousands of jobs across various sectors. This infrastructure investment is anticipated to have a significant economic multiplier effect, benefiting regional communities and driving broader economic growth. However, potential concerns include potential environmental impacts of some projects, and the possibility of project delays affecting the timeline and budget. Thorough environmental impact assessments and robust project management will be critical to the success of this initiative.
Tax Cuts and Economic Stimulus Measures
The plan also includes targeted tax cuts aimed at stimulating consumer spending and business investment. These include:
- Targeted income tax cuts for low and middle-income earners: Boosting disposable income for families and individuals, driving consumer demand.
- Temporary corporate tax reductions: Incentivizing business investment and job creation.
The opposition argues that these tax cuts will inject much-needed capital into the economy, leading to increased consumer spending and business investment. However, critics express concern about the potential impact on income inequality and government revenue. The effectiveness of such stimulus measures also depends on various macroeconomic factors and the overall consumer sentiment. A thorough analysis considering different economic scenarios is necessary to gauge the plan's efficacy.
Funding for Education and Skills Development
Investing in education and skills development is another key component of the $9 billion plan. This involves:
- Increased funding for vocational training: Addressing skills shortages and equipping Australians with the skills needed for the modern workforce.
- Investment in higher education: Supporting research and innovation and enhancing the quality of tertiary education.
- Improved early childhood education: Laying a strong foundation for future learning and development.
The goal is to create a more skilled workforce, increase workforce participation, and boost national productivity. The success of this initiative, however, depends on effective program design and equitable funding distribution across different educational sectors. Potential criticisms center on the effectiveness of specific programs and their ability to address existing skills gaps efficiently.
Funding Sources and Economic Sustainability
The success of the $9 billion budget boost hinges on its funding and long-term economic viability.
Government Revenue Projections
The opposition has yet to fully detail how the $9 billion will be funded. Proposals may include:
- Increased taxes on high-income earners or corporations: Generating additional revenue to support the increased spending.
- Targeted spending cuts in less-efficient areas: Reallocating existing government funds to prioritize the initiatives outlined in the plan.
The feasibility and sustainability of these funding mechanisms will be crucial. Any significant tax increases could impact economic activity and investment. Similarly, spending cuts could have unintended consequences, affecting other essential government programs. A transparent and detailed breakdown of funding sources is essential for public scrutiny and to ensure the long-term sustainability of the plan.
Long-Term Economic Impact Assessment
The opposition projects positive long-term economic impacts from this plan, including:
- Increased GDP growth: Stimulating economic activity and creating a more robust economy.
- Higher employment rates: Generating jobs across various sectors through infrastructure projects and economic stimulus.
- Reduced budget deficits (in the long term): Increased economic activity leading to higher tax revenue.
However, independent economic forecasts will be necessary to assess the accuracy of these projections. Unforeseen economic shocks or ineffective policy implementation could significantly alter the outcomes. A comprehensive, independent analysis accounting for various economic scenarios is crucial for a realistic assessment of the long-term impact.
Conclusion
The opposition's $9 billion budget boost represents a bold attempt to address key economic challenges facing Australia. The plan's focus on healthcare, infrastructure, education, and targeted tax cuts aims to stimulate growth, create jobs, and improve the lives of Australians. However, the success of this plan hinges on the feasibility of its funding mechanisms and the effective implementation of its various components. Careful consideration of both the potential benefits and risks is crucial for a thorough understanding of its impact on the Australian economy.
Call to Action: To stay informed about the ongoing debate surrounding Australia's economic future and the implications of this $9 billion budget boost, continue to follow our in-depth analyses and stay tuned for further updates. Learn more about the details of this significant economic plan and its potential effect on your community.

Featured Posts
-
 Remembering Priscilla Pointer A Legacy Of Acting And Mentorship
May 02, 2025
Remembering Priscilla Pointer A Legacy Of Acting And Mentorship
May 02, 2025 -
 Wizarding World Holiday Marathon On Syfy Your Complete Guide
May 02, 2025
Wizarding World Holiday Marathon On Syfy Your Complete Guide
May 02, 2025 -
 Christina Aguileras Transformed Look A Photoshop Controversy
May 02, 2025
Christina Aguileras Transformed Look A Photoshop Controversy
May 02, 2025 -
 Analyzing The Bank Of Canadas Response To Trump Tariffs In April
May 02, 2025
Analyzing The Bank Of Canadas Response To Trump Tariffs In April
May 02, 2025 -
 Unlocking The Potential Saudi Arabias Liberalised Abs Market
May 02, 2025
Unlocking The Potential Saudi Arabias Liberalised Abs Market
May 02, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Fortnites In Game Store Practices Face Another Legal Challenge
May 03, 2025
Fortnites In Game Store Practices Face Another Legal Challenge
May 03, 2025 -
 Improving Workplace Productivity Through Effective Mental Health Policies
May 03, 2025
Improving Workplace Productivity Through Effective Mental Health Policies
May 03, 2025 -
 The Walking Deads Negan In Fortnite Jeffrey Dean Morgan Speaks
May 03, 2025
The Walking Deads Negan In Fortnite Jeffrey Dean Morgan Speaks
May 03, 2025 -
 Highly Demanded Fortnite Skins Re Released In Item Shop
May 03, 2025
Highly Demanded Fortnite Skins Re Released In Item Shop
May 03, 2025 -
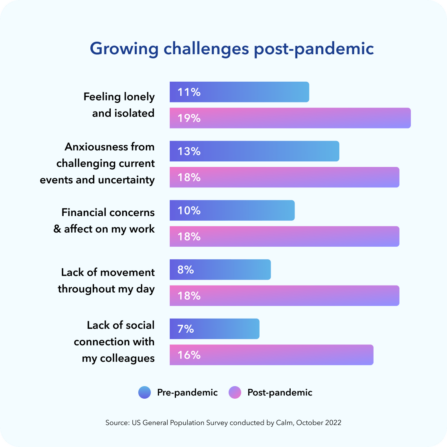 Mental Health Policy A Foundation For Workplace Productivity
May 03, 2025
Mental Health Policy A Foundation For Workplace Productivity
May 03, 2025
