Analyzing The Great Decoupling: Trends, Impacts, And Future Predictions
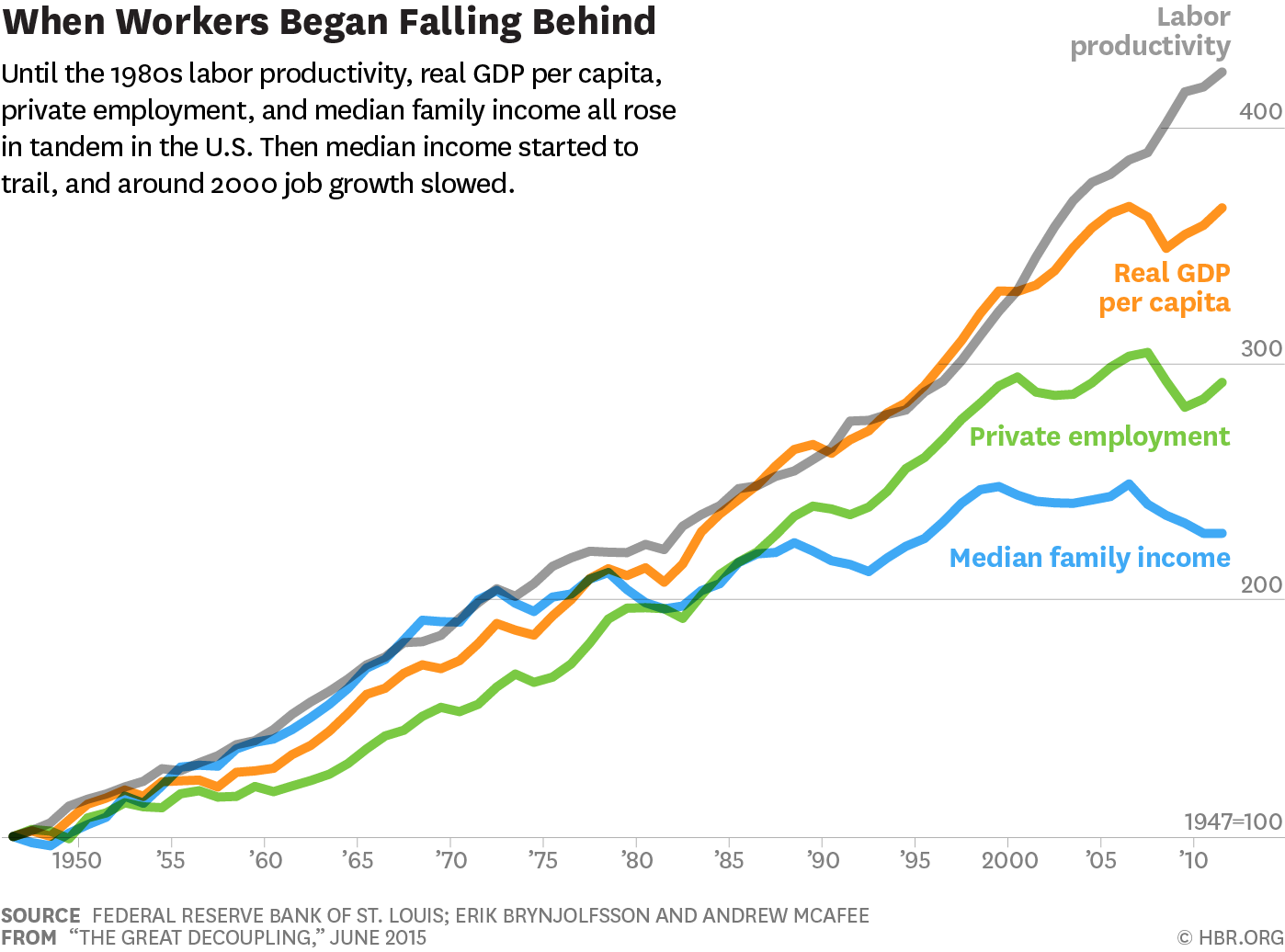
Table of Contents
Defining the Great Decoupling:
The Great Decoupling refers to the ongoing process of decreasing economic interdependence between nations. It signifies a move away from the highly integrated global supply chains and free-flowing capital that defined globalization for decades. Instead, we are seeing a rise in regionalization, with countries prioritizing domestic production and seeking to reduce their reliance on foreign partners. This shift is driven by a confluence of factors, including escalating geopolitical risks, concerns over supply chain resilience, and a growing desire for greater national economic autonomy. Keywords associated with this phenomenon include economic decoupling, geopolitical risks, and supply chain resilience. This article aims to analyze the trends driving this decoupling, examine its impacts on various sectors, and offer predictions for the future.
Trends Driving the Great Decoupling
Geopolitical Tensions and Trade Wars
Escalating trade disputes, sanctions, and political conflicts are major catalysts for the Great Decoupling. The increasing use of protectionist policies and trade barriers disrupts established global trade flows and encourages nations to focus on self-sufficiency.
- Examples: The US-China trade war, with its tariffs and counter-tariffs, significantly disrupted global supply chains. Sanctions imposed on Russia following its invasion of Ukraine have further highlighted the fragility of interconnected global systems.
- Impact: These actions have led to increased uncertainty and volatility in global markets, prompting businesses to reconsider their reliance on international trade. Keywords associated with this trend include trade wars, sanctions, protectionism, and geopolitical instability.
Technological Rivalry and National Security Concerns
Technological competition, particularly in areas like 5G technology and semiconductors, is another key driver of decoupling. Nations are increasingly prioritizing the development of domestic technological capabilities to reduce their reliance on foreign technologies and address national security concerns.
- Examples: Governments are investing heavily in domestic semiconductor production to reduce dependence on foreign suppliers. Restrictions on technology transfers and data localization policies further contribute to economic separation.
- Impact: This technological decoupling can lead to fragmentation of technological innovation and potentially slower technological advancement across the globe. Keywords include technological decoupling, national security, semiconductor industry, and 5G technology.
Supply Chain Diversification and Regionalization
Businesses are actively diversifying their supply chains to mitigate risks associated with geopolitical instability and supply chain disruptions. This is leading to a shift towards regional production hubs and a reduction in reliance on globalized supply chains.
- Examples: Companies are relocating production facilities closer to their target markets (nearshoring) or back to their home countries (reshoring). The growth of regional trade agreements further supports this trend.
- Impact: While enhancing supply chain resilience, this shift also increases logistics and transportation costs, impacting overall efficiency and potentially increasing prices for consumers. Relevant keywords here include supply chain resilience, nearshoring, reshoring, and regional trade agreements.
Impacts of the Great Decoupling
Economic Impacts
The Great Decoupling has significant economic consequences. It may lead to a slower rate of global economic growth, increased inflation due to supply chain bottlenecks, and altered patterns of foreign direct investment (FDI).
- Potential Impacts: Some economists predict slower global growth as trade barriers rise and investment flows shift. Inflationary pressures may increase due to disruptions in global supply chains. The patterns of FDI could change dramatically, with more investment directed towards domestic markets.
- Keywords: global economic growth, inflation, foreign direct investment, and economic recession.
Social and Political Impacts
Beyond economic consequences, the Great Decoupling can have profound social and political impacts. Increased economic nationalism could lead to social inequality, impacting job markets and potentially causing social unrest. International cooperation may weaken as countries prioritize national interests.
- Potential Impacts: Job losses in certain sectors could increase social inequality. Nationalistic sentiments might rise, potentially exacerbating political polarization and hindering international cooperation. Protectionist policies may become more common.
- Keywords: social inequality, nationalism, international cooperation, and political polarization.
Future Predictions and Scenarios
Potential Scenarios for the Future
Several scenarios are possible regarding the future of the Great Decoupling. These range from a complete fragmentation of the global economy to a partial decoupling or even a return to greater interdependence, albeit with significant structural changes.
- Scenario Analysis: A complete decoupling would lead to significantly slower global growth and potential regional conflicts. A partial decoupling would involve greater regionalization, but with some degree of continued global trade. A return to greater globalization is less likely in the near future but might occur with significant changes in global governance and international cooperation.
- Keywords: future of globalization, economic fragmentation, globalization 2.0, and geopolitical forecasting.
Strategies for Navigating the Great Decoupling
Businesses and governments need strategies to adapt to the changing global landscape. Businesses should prioritize supply chain diversification, regionalization, and enhanced risk management. Governments need to foster domestic industries, negotiate new trade agreements, and invest in infrastructure.
- Business Strategies: Diversify supply chains, explore nearshoring/reshoring options, improve risk management practices.
- Government Strategies: Invest in domestic industries, negotiate new regional trade deals, enhance infrastructure development, and encourage international cooperation where possible.
- Keywords: risk management, supply chain management, economic policy, and international relations.
Analyzing the Great Decoupling: Key Takeaways and Future Outlook
The Great Decoupling presents a complex and uncertain future for the global economy. The trends discussed highlight the significant shifts occurring in global trade, technology, and geopolitical relations. Understanding these impacts and adapting to the changing landscape is paramount for businesses and governments alike. Further analysis of the Great Decoupling is crucial, and staying informed on the latest trends in economic decoupling is essential for navigating this transformative period. Understanding the complexities of the Great Decoupling is paramount for a successful future in this evolving global environment.

Featured Posts
-
 Draisaitl Reaches 100 Points Oilers Defeat Islanders In Ot Thriller
May 09, 2025
Draisaitl Reaches 100 Points Oilers Defeat Islanders In Ot Thriller
May 09, 2025 -
 Draisaitls Hart Trophy Finalist Status Highlights Exceptional Oilers Season
May 09, 2025
Draisaitls Hart Trophy Finalist Status Highlights Exceptional Oilers Season
May 09, 2025 -
 Cheveux A Donner A Dijon Trouver Un Centre De Collecte
May 09, 2025
Cheveux A Donner A Dijon Trouver Un Centre De Collecte
May 09, 2025 -
 Nottingham Hospital Data Breach Over 90 Nhs Staff Accessed Victim Records
May 09, 2025
Nottingham Hospital Data Breach Over 90 Nhs Staff Accessed Victim Records
May 09, 2025 -
 Harry Styles Devastated Reaction To Poor Snl Impression
May 09, 2025
Harry Styles Devastated Reaction To Poor Snl Impression
May 09, 2025
