Analyzing Trump's Proposal: Can Tariffs Substitute Income Taxes?
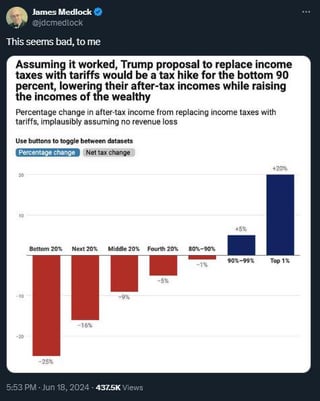
Table of Contents
The Economic Theory Behind Tariffs and Taxation
Revenue Generation Through Tariffs
Tariffs, essentially taxes on imported goods, generate revenue for the government. When goods enter a country, importers pay a percentage of the goods' value (ad valorem tariff) or a fixed amount per unit (specific tariff) to customs authorities. This revenue contributes to the government's overall budget. However, this revenue stream is significantly more volatile and limited compared to income tax.
- Limitations of Tariff Revenue Generation: Tariff revenue is heavily dependent on the volume of imports and the specific tariff rates imposed. Fluctuations in global trade and retaliatory tariffs from other countries can severely impact revenue generation.
- Dependence on Trade Volume and Import Levels: If import levels decrease due to economic slowdowns or trade disputes, tariff revenue will decline accordingly.
- Retaliatory Tariffs Impacting Revenue: Imposing high tariffs often triggers retaliatory measures from other countries, leading to reduced exports and potentially offsetting any gains in tariff revenue.
The Principles of Income Taxation
Income tax, in contrast, forms a far more stable and significant portion of government revenue. It's levied on individuals' and corporations' income, typically following a progressive system where higher earners pay a larger percentage of their income in taxes. This progressive nature is designed to fund essential government services and redistribute wealth.
- Contrasting Tax Bases: The tax base differs significantly: income tax is levied on earned income, while tariffs target imported goods. This impacts the distribution of the tax burden.
- Distribution of the Tax Burden: Income tax aims for progressive taxation, while tariffs can be regressive, disproportionately affecting low-income households who spend a larger portion of their income on imported goods.
- Administrative Complexities: While both systems have administrative complexities, income tax collection involves significantly more intricate processes, including deductions, exemptions, and auditing.
Comparing Tariffs and Income Taxes: A Critical Analysis
Economic Impact of Replacing Income Taxes with Tariffs
Replacing income taxes with tariffs would have profound macroeconomic effects. Such a drastic shift would likely trigger significant economic instability.
- Inflation: Increased prices on imported goods (due to higher tariffs) would fuel inflation, impacting consumer purchasing power.
- Decreased Consumer Spending: Higher prices on goods, coupled with uncertainty in the market, could significantly decrease consumer spending, leading to an economic slowdown.
- Impact on Specific Industries: Certain industries heavily reliant on imported goods would suffer, leading to job losses and potential business failures.
- Potential for Trade Wars: High tariffs provoke retaliatory measures from other countries, potentially escalating into damaging trade wars.
Distributional Effects: Who Bears the Burden?
The impact of a tariff-based tax system wouldn't be evenly distributed.
- Effect on Consumers: Consumers would face higher prices on imported goods, decreasing their disposable income, disproportionately affecting lower-income households.
- Effect on Producers: Domestic producers of goods that compete with imports might benefit initially, but retaliatory tariffs could negate these advantages.
- Effect on Importers: Importers would face significantly higher costs, potentially impacting their profitability and employment levels. The burden of higher tariffs would largely fall on importers and, ultimately, consumers. This suggests a regressive tax structure.
Practical Challenges and Political Considerations
Feasibility of Complete Substitution
It's practically impossible to generate enough revenue from tariffs to entirely replace income taxes.
- Current Revenue Comparison: Current tariff revenue represents only a small fraction of total US government revenue compared to income tax.
- Political Obstacles: Implementing such a radical change would face immense political opposition, particularly from those affected by higher prices and reduced economic activity.
- International Reactions: Heavy reliance on tariffs would almost certainly provoke strong international reactions and retaliatory measures, harming US export industries.
International Trade Relations and Retaliation
Over-reliance on tariffs poses significant risks to international trade relations.
- Trade Wars: High tariffs inevitably lead to retaliatory measures from trading partners, triggering trade wars that damage global economic growth.
- Reduced Exports: Retaliatory tariffs would likely reduce US exports, potentially harming key industries and creating job losses.
- Damage to International Relationships: Escalating trade conflicts can damage diplomatic relationships, creating further economic and geopolitical instability.
Conclusion
Replacing income taxes with tariffs is an unrealistic and economically damaging proposal. The limitations of tariff revenue, the potential for inflation and decreased consumer spending, and the risk of devastating trade wars outweigh any potential benefits. Trump's proposal demonstrates a fundamental misunderstanding of the complexities of tax policy and international trade. The reliance on tariffs as a primary revenue source is impractical and likely detrimental to the long-term health of the US economy. We encourage readers to further research the economic impact of tariffs and actively participate in discussions surrounding alternative tax policies and a more sustainable approach to international trade, moving away from harmful policies based on "Trump tariffs" and exploring more balanced and effective solutions for tariff policy and tax reform.

Featured Posts
-
 Investigating The Connection Household Plastics Chemical Exposure And Heart Disease Deaths
May 01, 2025
Investigating The Connection Household Plastics Chemical Exposure And Heart Disease Deaths
May 01, 2025 -
 Frances Convincing Win Sets Up Ireland Six Nations Clash
May 01, 2025
Frances Convincing Win Sets Up Ireland Six Nations Clash
May 01, 2025 -
 Baitulmal Sarawak Salurkan Bantuan Rm 36 45 Juta Kepada Penerima Asnaf Mac 2025
May 01, 2025
Baitulmal Sarawak Salurkan Bantuan Rm 36 45 Juta Kepada Penerima Asnaf Mac 2025
May 01, 2025 -
 Onderzoek Naar Steekincident In Van Mesdagkliniek Verdachte Malek F
May 01, 2025
Onderzoek Naar Steekincident In Van Mesdagkliniek Verdachte Malek F
May 01, 2025 -
 Shrimp Ramen Stir Fry A Delicious Asian Inspired Dish
May 01, 2025
Shrimp Ramen Stir Fry A Delicious Asian Inspired Dish
May 01, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Judge And Goldschmidts Performances Secure A Win For The Yankees
May 01, 2025
Judge And Goldschmidts Performances Secure A Win For The Yankees
May 01, 2025 -
 Yankees Judge And Cardinals Goldschmidt Lead In Crucial Series Victory
May 01, 2025
Yankees Judge And Cardinals Goldschmidt Lead In Crucial Series Victory
May 01, 2025 -
 Ovechkin I Ego Rekord V N Kh L Reaktsiya Zakharovoy
May 01, 2025
Ovechkin I Ego Rekord V N Kh L Reaktsiya Zakharovoy
May 01, 2025 -
 Zakharova Pozdravila Ovechkina S Rekordom N Kh L
May 01, 2025
Zakharova Pozdravila Ovechkina S Rekordom N Kh L
May 01, 2025 -
 Key Facts About Wayne Gretzky A Concise Overview
May 01, 2025
Key Facts About Wayne Gretzky A Concise Overview
May 01, 2025
