Australia's Marine Fauna Under Siege: The Impact Of Invasive Seaweed

Table of Contents
Identifying Invasive Seaweed Species in Australian Waters
Several invasive seaweed species are wreaking havoc in Australian waters, significantly impacting native marine life and habitats. Two of the most notorious culprits are Caulerpa taxifolia and Undaria pinnatifida.
-
Caulerpa taxifolia: This aggressive seaweed, originally from the Mediterranean, has spread rapidly along the Australian coast, primarily through ballast water discharged from ships and accidental introductions from aquaculture activities. Its rapid growth rate and potent allelopathic chemicals (chemicals that inhibit the growth of other organisms) allow it to outcompete native species. [Insert high-quality image of Caulerpa taxifolia with alt text: "Caulerpa taxifolia invasive seaweed"].
-
Undaria pinnatifida: Known as wakame, this Asian seaweed is commonly used in food. Its introduction to Australia, likely through aquaculture and shipping, has led to widespread infestations along temperate coastlines. Its fast growth and ability to thrive in various conditions make it a formidable competitor to native species. [Insert high-quality image of Undaria pinnatifida with alt text: "Undaria pinnatifida invasive seaweed"].
Effective seaweed identification is crucial for early detection and management. Citizen scientists play a vital role in reporting suspected invasive species, aiding in the rapid response necessary to contain their spread. Understanding the pathways of introduction—ballast water, aquaculture practices, and even recreational boating—is key to preventing future infestations.
The Ecological Impact of Invasive Seaweed on Australian Marine Life
The ecological consequences of invasive seaweed are far-reaching and devastating. These non-native species disrupt the intricate balance of the marine ecosystem, triggering a cascade of negative impacts.
Habitat Loss and Degradation
Invasive seaweed species like Caulerpa taxifolia and Undaria pinnatifida aggressively overgrow native seagrass beds and kelp forests, smothering these vital habitats. This leads to:
- Reduced habitat for fish nurseries, impacting the reproduction and survival of many fish species.
- Displacement of native algae, reducing biodiversity and disrupting the food web.
- Loss of foraging grounds for sea turtles and other herbivorous marine animals.
Impacts on Biodiversity
The competitive nature of invasive seaweed drastically reduces biodiversity. They outcompete native species for resources such as sunlight, nutrients, and space, resulting in:
- Reduced species richness, leading to a less resilient ecosystem.
- Disruption of food webs, affecting predator-prey relationships and overall ecosystem stability.
- Increased vulnerability to other threats like pollution and climate change.
Impacts on Marine Fauna
Direct impacts on marine animals are also significant. Some species experience:
- Sea turtle entanglement in dense seaweed mats.
- Reduced sea urchin populations due to habitat loss and competition.
- Decreased fish stocks as their food sources and habitats are destroyed.
Economic Consequences of Invasive Seaweed in Australia
The invasion of non-native seaweed carries substantial economic implications for Australia. The impacts are felt across various industries:
- Fisheries: Declines in fish populations due to habitat loss and competition directly affect the fishing industry, leading to reduced catches and economic losses.
- Tourism: Degraded marine environments, characterized by smothering seaweed, negatively impact tourism, particularly in areas dependent on the aesthetic appeal of healthy reefs and coastlines.
- Aquaculture: Invasive seaweed can foul aquaculture facilities, increasing operational costs and reducing yields.
The costs associated with management and control efforts, including manual removal, chemical treatments, and research, further add to the economic burden. Quantifying these losses accurately is challenging, but the overall impact is undeniable and significant.
Management and Control Strategies for Invasive Seaweed
Combating invasive seaweed requires a multifaceted approach employing various management strategies:
- Manual Removal: This labor-intensive method involves physically removing the seaweed, but it's often only effective for small, localized infestations.
- Chemical Treatments: Herbicides can be used, but their application needs careful consideration to minimize impacts on non-target species and the wider environment.
- Biological Control: This involves introducing natural predators or pathogens of the invasive seaweed, a promising but complex approach requiring extensive research and careful risk assessment.
Early detection and rapid response are paramount. Citizen science initiatives, where members of the public participate in monitoring and reporting, play a critical role in identifying and managing emerging infestations. Ongoing research into new and improved control techniques is crucial for developing sustainable and effective solutions.
Conclusion: Protecting Australia's Marine Fauna – Combating Invasive Seaweed
Invasive seaweed poses a significant and escalating threat to Australia's unique and valuable marine ecosystems. The ecological consequences, including biodiversity loss and habitat degradation, are severe, coupled with substantial economic impacts on vital industries. Effective management requires a concerted effort involving government agencies, researchers, and the community. By understanding the invasive seaweed species present, their ecological impact, and available control methods, we can collectively work towards protecting Australia's rich marine fauna. Learn more about invasive seaweed identification and participate in citizen science initiatives to aid in early detection and reporting. Together, we can safeguard Australia’s marine environment for future generations. Visit [link to relevant Australian organization] for more information on invasive seaweed management and how you can help.

Featured Posts
-
 Alcaraz Vs Musetti A Monte Carlo Masters Showdown In 2025
May 30, 2025
Alcaraz Vs Musetti A Monte Carlo Masters Showdown In 2025
May 30, 2025 -
 Wybory Prezydenckie 2025 Czy Strategia Mentzena Zdziwi Wyborcow
May 30, 2025
Wybory Prezydenckie 2025 Czy Strategia Mentzena Zdziwi Wyborcow
May 30, 2025 -
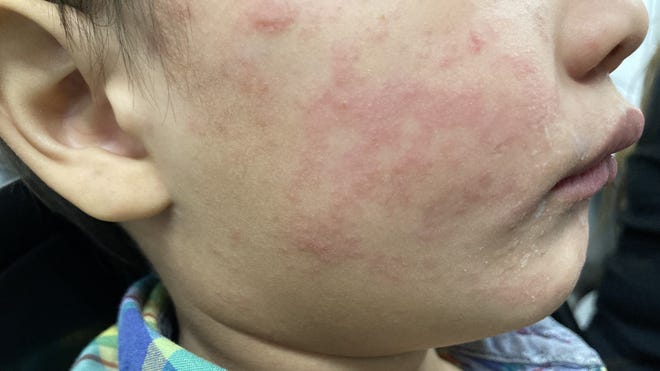 Texas Sees Spike In Measles Cases Unrelated To Current Outbreak
May 30, 2025
Texas Sees Spike In Measles Cases Unrelated To Current Outbreak
May 30, 2025 -
 Gare Du Nord Perturbations Importantes Du Trafic Toute La Journee Apres Decouverte D Une Bombe
May 30, 2025
Gare Du Nord Perturbations Importantes Du Trafic Toute La Journee Apres Decouverte D Une Bombe
May 30, 2025 -
 Rajinikanths Tribute To Ilaiyaraajas London Symphony Performance
May 30, 2025
Rajinikanths Tribute To Ilaiyaraajas London Symphony Performance
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Dont Miss Out 30 Off Lavish Hotels This Spring
May 31, 2025
Dont Miss Out 30 Off Lavish Hotels This Spring
May 31, 2025 -
 Up To 30 Off Lavish Spring Hotel Bookings
May 31, 2025
Up To 30 Off Lavish Spring Hotel Bookings
May 31, 2025 -
 Book Now And Save 30 Off Lavish Spring Hotel Stays
May 31, 2025
Book Now And Save 30 Off Lavish Spring Hotel Stays
May 31, 2025 -
 Spring Hotel Sale Get 30 Off Your Lavish Stay
May 31, 2025
Spring Hotel Sale Get 30 Off Your Lavish Stay
May 31, 2025 -
 Luxury Hotel Spring Sale 30 Discount
May 31, 2025
Luxury Hotel Spring Sale 30 Discount
May 31, 2025
