Bank Of Canada Interest Rate Cuts: The Impact Of Tariffs On Employment And Economic Outlook
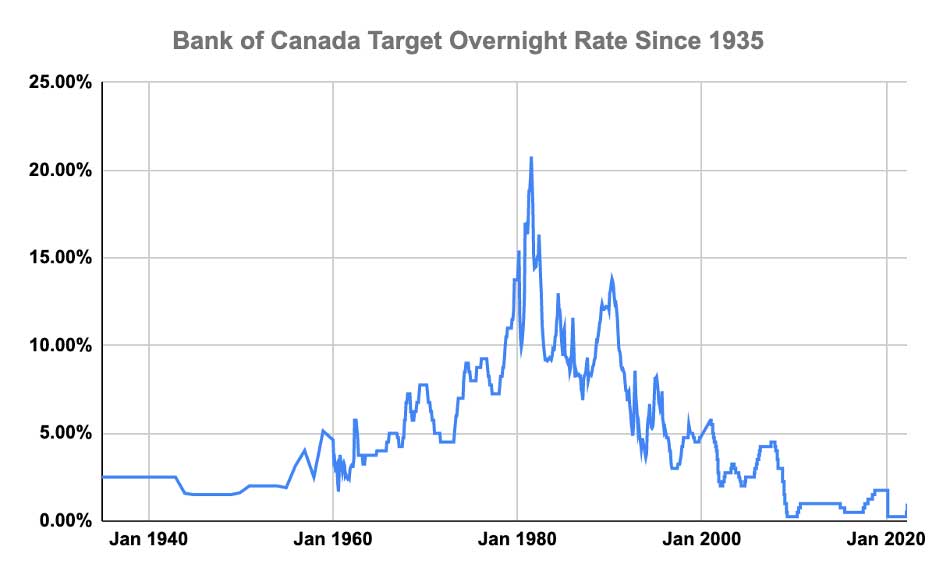
Table of Contents
Tariffs and their Impact on Canadian Employment
Tariffs, essentially taxes on imported or exported goods, have far-reaching consequences for the Canadian economy. Their impact is multifaceted, significantly affecting employment across various sectors.
Reduced Exports and Job Losses
Tariffs imposed by other countries on Canadian goods directly hinder our export market. This leads to reduced demand for Canadian products and, consequently, job losses. The "tariff impact" is keenly felt in sectors heavily reliant on exports.
- Manufacturing: Reduced demand for Canadian manufactured goods, particularly in automotive and resource sectors, can lead to factory closures and significant job losses in Canada.
- Agriculture: Tariffs on Canadian agricultural products, such as wheat, canola, and dairy, can severely impact farmers and related industries, leading to decreased production and employment decline.
- Forestry: The forestry sector is also vulnerable, with reduced demand for lumber and other wood products resulting in job losses in logging, milling, and related industries.
Data from [Insert Source if available – e.g., Statistics Canada] shows [Insert Statistic if available – e.g., X% decline in exports leading to Y job losses in the manufacturing sector]. The consequences of this "job losses Canada" trend are far-reaching, impacting not only workers but also communities dependent on these industries.
Increased Import Costs and Inflation
Tariffs on imported goods directly increase prices for businesses and consumers. This increase in "import costs" fuels "inflation Canada," impacting purchasing power and potentially triggering a decrease in consumer spending and business investment.
- Increased prices for raw materials and intermediate goods increase production costs for businesses, leading to reduced profitability and potentially layoffs.
- Higher prices for consumer goods, particularly essentials like food and energy, disproportionately affect low- and middle-income households, reducing their disposable income and further dampening consumer demand.
- This ripple effect impacts various sectors, including retail, hospitality, and services, as reduced consumer spending translates into lower demand for their products and services.
Supply Chain Disruptions
Tariffs contribute to uncertainty and disruptions in global supply chains. Canadian businesses face challenges in obtaining necessary materials and goods, leading to production delays, increased "input costs," and potential job losses.
- Industries heavily reliant on imported components, such as the automotive and electronics sectors, are particularly vulnerable to supply chain disruptions caused by tariffs. Increased delays and costs can make them less competitive, impacting employment levels.
- The uncertainty created by tariffs makes businesses hesitant to invest in expansion or new projects, leading to a slowdown in job creation.
- "Supply chain disruption" can cause cascading effects throughout the economy, impacting businesses and consumers alike.
The Bank of Canada's Response: Interest Rate Cuts
The Bank of Canada plays a crucial role in managing the Canadian economy through monetary policy, including adjusting interest rates. The "Bank of Canada monetary policy" aims to maintain price stability and promote sustainable economic growth.
Monetary Policy Tools
Interest rates are a key tool used by the Bank of Canada to influence economic activity. Lowering the "interest rate target" makes borrowing cheaper, encouraging businesses and consumers to invest and spend more, thereby stimulating economic growth.
- Lower interest rates reduce borrowing costs for businesses, making it more affordable to invest in expansion, hire new employees, and increase production.
- Lower rates also reduce mortgage rates, potentially encouraging housing investment and related job creation.
- However, interest rate cuts alone may not be sufficient to fully counteract the negative effects of tariffs, especially if the primary issue is reduced export demand or significant supply chain disruptions.
Interest Rate Cuts and Employment
The anticipated impact of "interest rate cuts impact" on employment is a key consideration for the Bank of Canada. Lower interest rates are intended to stimulate the economy and boost job creation.
- By making borrowing cheaper, businesses are incentivized to invest and expand, leading to increased hiring.
- Consumer spending may also increase as lower interest rates reduce the cost of borrowing for purchases like homes and vehicles.
- However, the effectiveness of interest rate cuts in boosting employment can be delayed, and their impact might be limited if businesses face other significant challenges, such as tariffs that reduce export demand.
Interest Rate Cuts and Inflation
The Bank of Canada faces a delicate balancing act. While interest rate cuts can stimulate the economy, they can also contribute to inflation. The "interest rate cuts inflation" dynamic is a central consideration. Tariffs already exert inflationary pressure, complicating the situation.
- Lower interest rates can increase demand, potentially pushing up prices further.
- The Bank of Canada needs to carefully assess the trade-off between stimulating the economy and controlling inflation to maintain "price stability."
- A potential conflict arises between the goal of boosting employment through rate cuts and preventing inflation from spiralling out of control due to existing inflationary pressures.
Economic Outlook: Forecasting the Future
Predicting the future is inherently uncertain, but analyzing different economic scenarios helps to understand potential outcomes. The "economic outlook Canada" depends on several factors.
Scenarios and Predictions
Several scenarios are possible, depending on future tariff policies and the effectiveness of interest rate cuts.
- Scenario 1 (Optimistic): A resolution of trade disputes, combined with effective interest rate cuts, could lead to a strong economic recovery, with increased employment and moderate inflation. "Canadian GDP" growth could be robust.
- Scenario 2 (Pessimistic): Continued trade tensions and limited effectiveness of interest rate cuts could lead to prolonged economic weakness, high unemployment, and persistent inflationary pressures. "Economic growth projections" would be subdued.
- Scenario 3 (Moderate): A partial resolution of trade issues and a measured response from the Bank of Canada could result in moderate economic growth, gradual job creation, and relatively stable inflation.
[Include charts and graphs illustrating these scenarios if data is available]. Economic forecasting is always subject to uncertainty; these are just potential outcomes.
The Role of Government Policy
Government policies beyond monetary policy play a crucial role in mitigating the negative impacts of tariffs. "Fiscal policy," such as targeted support for affected industries or worker retraining programs, can help cushion the blow. Furthermore, "government intervention" through trade negotiations is vital.
- Targeted financial assistance and support programs can help businesses and workers affected by tariffs to weather the storm.
- Investing in worker retraining programs can help displaced workers transition to new industries and acquire new skills.
- Negotiating new trade agreements or resolving existing trade disputes can reduce the impact of tariffs and promote economic recovery.
Conclusion: Navigating the Impact of Bank of Canada Interest Rate Cuts
The interplay between tariffs, Bank of Canada interest rate cuts, employment, and the overall economic outlook is complex. Understanding this interplay is crucial for navigating the current economic climate. Tariffs present significant challenges to the Canadian economy, affecting employment across various sectors and adding to inflationary pressures. While interest rate cuts can stimulate economic activity, their effectiveness in mitigating the negative effects of tariffs is uncertain, and a delicate balance must be struck with inflation control. Government policies play a vital role in supporting the economy during this challenging period. Stay updated on the latest developments regarding Bank of Canada interest rate cuts and their implications for your financial well-being, and continue monitoring the impact of tariffs and Bank of Canada interest rate decisions on the Canadian employment landscape.

Featured Posts
-
 Muchova Defeats Raducanu At Dubai Tennis Championships British Stars Tournament Ends
May 14, 2025
Muchova Defeats Raducanu At Dubai Tennis Championships British Stars Tournament Ends
May 14, 2025 -
 Tottenham And Crystal Palace Vie For Top English Talent
May 14, 2025
Tottenham And Crystal Palace Vie For Top English Talent
May 14, 2025 -
 Stream Captain America Brave New World On Pvod Your Guide
May 14, 2025
Stream Captain America Brave New World On Pvod Your Guide
May 14, 2025 -
 Budget Friendly Kendra Scott Jewelry New Disney Snow White Collection
May 14, 2025
Budget Friendly Kendra Scott Jewelry New Disney Snow White Collection
May 14, 2025 -
 Intentionally Walking Aaron Judge Weighing The Risks And Rewards
May 14, 2025
Intentionally Walking Aaron Judge Weighing The Risks And Rewards
May 14, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Sabalenkas Hard Fought Victory Over Mertens At Madrid Open
May 14, 2025
Sabalenkas Hard Fought Victory Over Mertens At Madrid Open
May 14, 2025 -
 Kasatkinas Australian Tennis Adventure Begins Wta Rankings Reflect Change
May 14, 2025
Kasatkinas Australian Tennis Adventure Begins Wta Rankings Reflect Change
May 14, 2025 -
 Daria Kasatkinas New Beginning First Day As Australian Wta Player
May 14, 2025
Daria Kasatkinas New Beginning First Day As Australian Wta Player
May 14, 2025 -
 Swiateks Ranking Plunge After Rome Loss To Collins
May 14, 2025
Swiateks Ranking Plunge After Rome Loss To Collins
May 14, 2025 -
 Zheng Qinwen Out Of Madrid Open After Potapova Upset
May 14, 2025
Zheng Qinwen Out Of Madrid Open After Potapova Upset
May 14, 2025
