Big Rig ROCK Report 3.12: Your Comprehensive Rock 101 Resource
Table of Contents
A Brief History of Rock Music
Rock music, a genre synonymous with rebellion, energy, and innovation, didn't emerge from a vacuum. Understanding its history is crucial to appreciating its impact.
The Roots of Rock and Roll:
Rock and roll didn't spring forth fully formed; it's a vibrant tapestry woven from diverse musical threads. Its foundations lie in several genres:
- Blues: The blues, with its soulful vocals, blues scales, and often melancholic lyrics, provided the emotional core of rock and roll. Artists like Robert Johnson, with his legendary guitar skills and haunting songs, are considered foundational figures.
- Rhythm and Blues (R&B): R&B, with its emphasis on rhythm and upbeat tempos, added a crucial element of danceability and energy.
- Country: Country music contributed its storytelling tradition and strong, often simple melodies.
- Gospel Music: The fervent energy and powerful vocals of gospel music significantly impacted the vocal styles of early rock and roll artists. The call-and-response style, in particular, found its way into many rock anthems.
The emergence of electric instruments like the electric guitar further revolutionized the sound, amplifying the raw power and energy that would become hallmarks of the genre.
The Rise of Rock and Roll in the 1950s:
The 1950s witnessed the explosive arrival of rock and roll as a cultural phenomenon. This wasn't just about music; it was a reflection of societal shifts and youthful rebellion.
- Elvis Presley: "The King" transcended music, becoming a cultural icon whose charisma and raw talent captivated audiences worldwide.
- Little Richard: His flamboyant style and powerful vocals brought a unique energy and showmanship to rock and roll.
- Buddy Holly: His clean-cut image and catchy melodies contrasted with the raw energy of other early rock stars, broadening the genre's appeal.
Radio and television played a pivotal role in spreading rock and roll's popularity, broadcasting its infectious rhythms across the nation, and further solidifying its place in popular culture.
Rock's Evolution Through the Decades:
Rock music didn't stand still; it continuously evolved, branching into diverse subgenres and reflecting the changing times.
- 1960s: The British Invasion brought bands like The Beatles and The Rolling Stones to prominence, influencing countless artists. Psychedelic rock emerged, exploring experimental sounds and mind-expanding themes.
- 1970s: Hard rock and heavy metal emerged, characterized by powerful riffs and amplified volume. Progressive rock explored complex song structures and extended instrumental passages. Glam rock embraced flamboyant aesthetics and theatrical performances.
- 1980s: Hair metal bands with their polished sound and anthemic choruses dominated the airwaves. Punk rock emerged as a rebellious reaction, embracing simplicity and raw energy.
- 1990s: Grunge, with its raw emotionality and angst, redefined rock, bringing bands like Nirvana and Pearl Jam to the forefront. Alternative rock offered a diverse range of styles and influences.
- 2000s and Beyond: Rock music continues to evolve, incorporating elements of other genres and reflecting contemporary social and cultural trends.
Key Characteristics of Rock Music
While incredibly diverse, rock music shares certain core characteristics that define its identity.
Instrumentation:
The typical instrumentation of rock music forms the bedrock of its sound:
- Electric Guitar: The driving force, often featuring distortion, feedback, and soaring solos.
- Bass Guitar: Provides the rhythmic foundation and low-end frequencies.
- Drums: The percussive backbone, setting the tempo and driving the energy.
- Vocals: The emotional core, ranging from raw shouts to soaring melodies.
Keyboards and other instruments often augment the core instrumentation, enriching the sonic palette in various subgenres.
Song Structure:
Rock music typically adheres to a basic song structure:
- Verse-Chorus Structure: The most common form, with verses presenting the story and the chorus providing a memorable hook.
- Bridge: A contrasting section that adds variety and emotional depth.
- Instrumental Breaks/Solos: Often showcasing instrumental virtuosity.
However, many subgenres experiment with and deviate from these basic structures, pushing boundaries and fostering innovation.
Performance and Stage Presence:
Live performance is integral to the rock experience. The energy and showmanship of live concerts are a defining characteristic of the genre.
- Iconic Performances: From Woodstock to Live Aid, legendary performances have cemented rock's place in music history.
- Stage Presence: Rock stars often cultivate powerful stage personas, further enhancing the visceral experience of a live show.
Exploring Rock Subgenres:
Rock music encompasses a vast landscape of subgenres, each with its unique characteristics and influential artists:
- Hard Rock: Powerful, guitar-driven rock with a strong emphasis on riffs and energy (e.g., Led Zeppelin, AC/DC).
- Heavy Metal: Characterized by distorted guitars, aggressive vocals, and often complex song structures (e.g., Black Sabbath, Metallica).
- Punk Rock: A raw, rebellious style emphasizing simplicity and energy (e.g., The Ramones, Sex Pistols).
- Grunge: Characterized by a raw, distorted sound and introspective lyrics (e.g., Nirvana, Pearl Jam).
- Alternative Rock: A broad category encompassing various styles that deviate from mainstream rock (e.g., Radiohead, The Smashing Pumpkins).
Many other subgenres exist, showcasing the genre's incredible breadth and diversity. Further exploration of these subgenres will reveal even more about the rich history and continuing evolution of rock music.
Conclusion:
This Big Rig ROCK Report 3.12 has provided a foundational understanding of rock music, from its origins to its diverse subgenres and key characteristics. Whether you're a budding musician, a dedicated listener, or simply curious about this influential genre, we hope this comprehensive overview has sparked your interest and fueled your appreciation for the power and impact of rock and roll. Keep exploring the vast landscape of rock music; delve deeper into the subgenres that resonate with you, discover new artists, and continue to rock on! For more in-depth information on specific aspects of rock music, be sure to check out our other resources on [link to related resources]. Keep rocking with Big Rig ROCK Reports!

Featured Posts
-
 Zimbabwe Triumphs Historic Test Win Against Bangladesh
May 23, 2025
Zimbabwe Triumphs Historic Test Win Against Bangladesh
May 23, 2025 -
 England Announces Xi To Face Zimbabwe In Test Cricket
May 23, 2025
England Announces Xi To Face Zimbabwe In Test Cricket
May 23, 2025 -
 Kalendar Ta Rezultati Ligi Natsiy 20 03 2025
May 23, 2025
Kalendar Ta Rezultati Ligi Natsiy 20 03 2025
May 23, 2025 -
 F1 Season Preview Russell Sets The Pace On Final Day
May 23, 2025
F1 Season Preview Russell Sets The Pace On Final Day
May 23, 2025 -
 Liga Natsiy 2023 2024 Rezultati Ta Rozklad Matchiv Na 20 03 2025
May 23, 2025
Liga Natsiy 2023 2024 Rezultati Ta Rozklad Matchiv Na 20 03 2025
May 23, 2025
Latest Posts
-
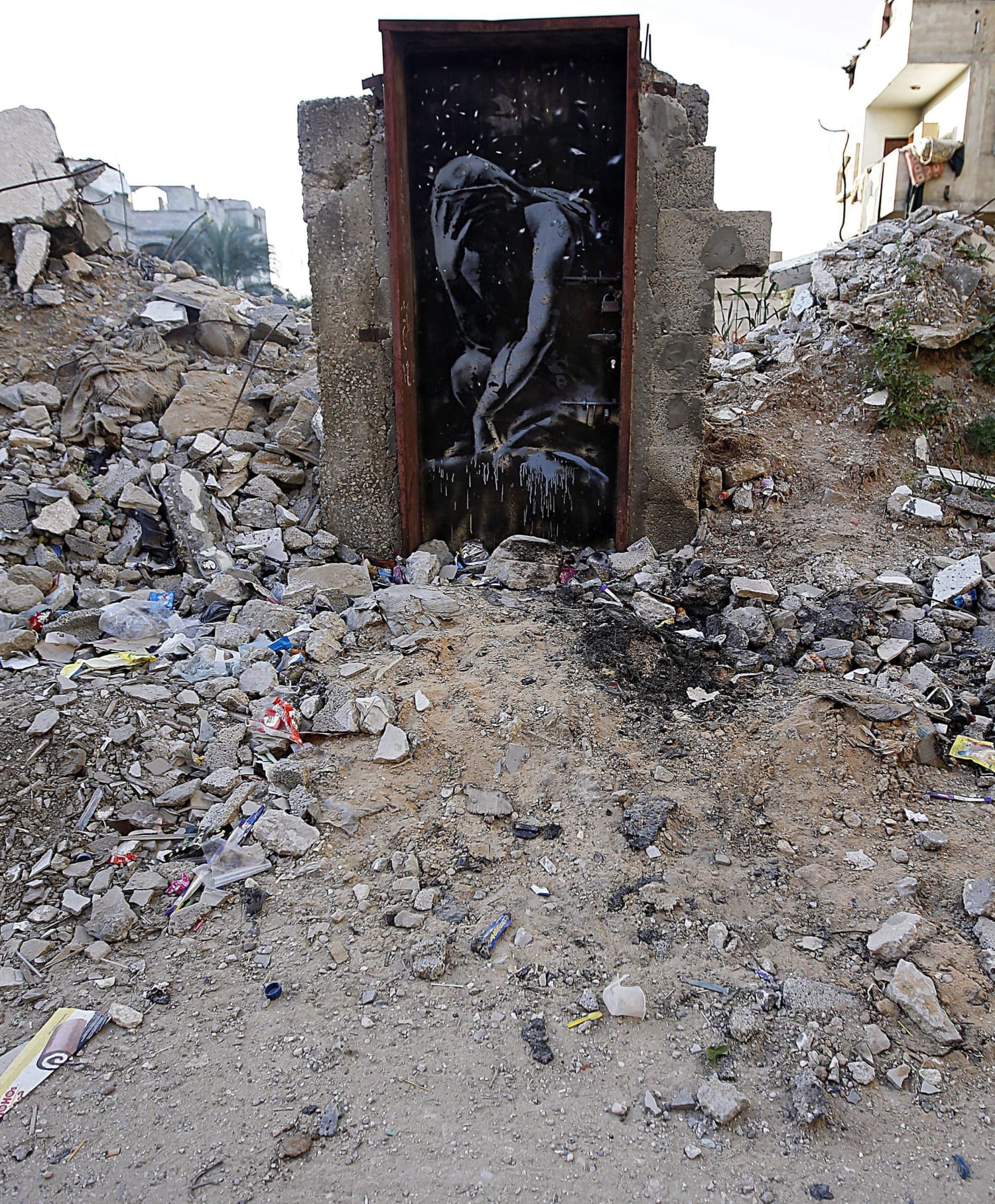 Emissarys Account Was Witkoff Duped By Hamas
May 23, 2025
Emissarys Account Was Witkoff Duped By Hamas
May 23, 2025 -
 Hamas Deception Witkoffs Account Of Being Duped
May 23, 2025
Hamas Deception Witkoffs Account Of Being Duped
May 23, 2025 -
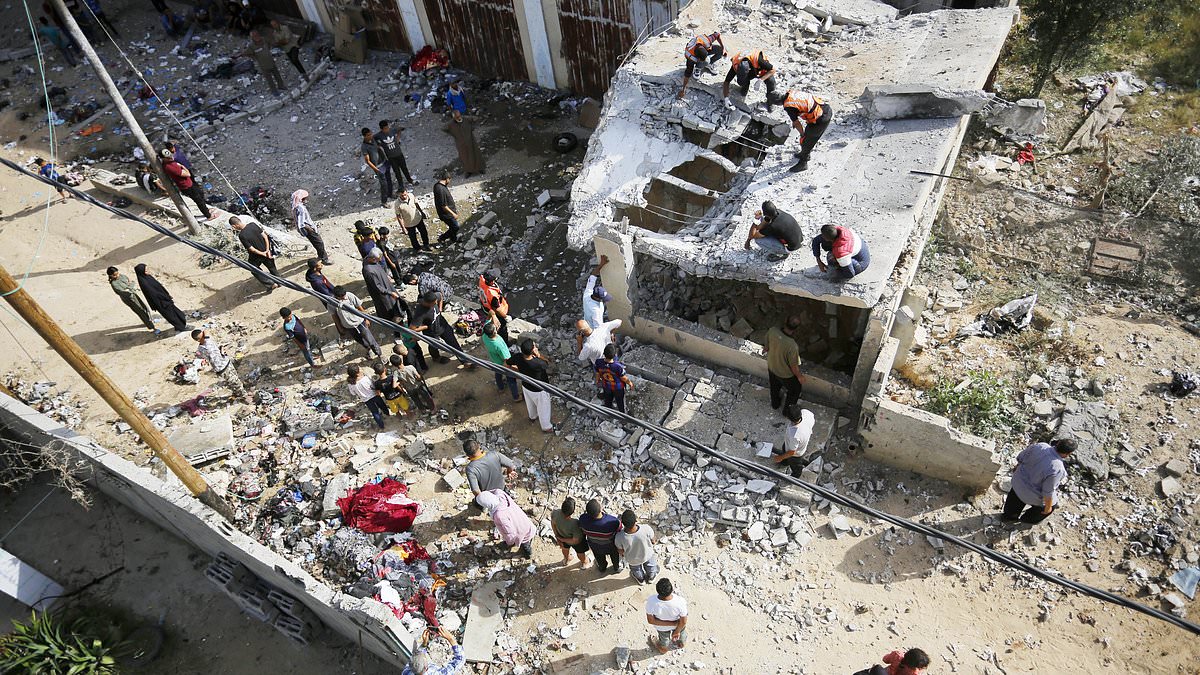 Witkoffs Claim Duped By Hamas Emissary Reveals Allegations
May 23, 2025
Witkoffs Claim Duped By Hamas Emissary Reveals Allegations
May 23, 2025 -
 Ooredoo Qatar And Qtspbf Renewed Commitment To Collaboration
May 23, 2025
Ooredoo Qatar And Qtspbf Renewed Commitment To Collaboration
May 23, 2025 -
 Extended Partnership Ooredoo Qatar And Qtspbf On Continued Success
May 23, 2025
Extended Partnership Ooredoo Qatar And Qtspbf On Continued Success
May 23, 2025
