Black Screens, Silent Radios: The Growing Threat Of Air Traffic Control Failures

Table of Contents
The Causes of Air Traffic Control Failures
Air traffic control failures, encompassing both ATC failures and air traffic control system failures, stem from a complex interplay of technological, human, and environmental factors. Understanding these causes is crucial to developing effective preventative measures.
Technological Issues
Outdated technology is a significant contributor to ATC failures. Many air traffic control systems are reliant on aging infrastructure and software, making them vulnerable to malfunctions and cybersecurity threats.
- Software glitches: Bugs and unforeseen software interactions can lead to system crashes or inaccurate data display.
- Hardware malfunctions: The failure of critical hardware components, such as radar systems or communication networks, can severely impact ATC operations.
- Cybersecurity threats: ATC systems are increasingly vulnerable to cyberattacks, which could compromise system integrity and disrupt air traffic flow. A successful cyberattack could have far-reaching and potentially devastating consequences.
- Lack of Interoperability: Inconsistent systems and communication protocols between different ATC facilities can lead to communication breakdowns and increased risk of errors.
The cost of upgrading and maintaining ATC systems is substantial, but the cost of inaction is far greater, measured in potential loss of life and economic damage. Studies indicate that technology-related ATC failures account for a significant percentage of all incidents.
Human Error
Human error remains a considerable factor in ATC failures. Factors such as fatigue, inadequate training, and communication breakdowns can lead to mistakes with potentially dire consequences.
- Fatigue: Long working hours and irregular shifts can impair the judgment and performance of air traffic controllers.
- Training deficiencies: Insufficient or outdated training can leave controllers unprepared for unexpected situations.
- Communication breakdowns: Misunderstandings or unclear communication between controllers and pilots can lead to critical errors.
- Inadequate staffing levels: Understaffing can lead to increased workload and stress, increasing the likelihood of human error.
Implementing comprehensive training programs focusing on stress management, workload management, and effective communication protocols is vital for minimizing human error in ATC operations.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors can significantly impact ATC operations. Severe weather conditions and electromagnetic interference can disrupt communication and navigation systems.
- Extreme weather: Heavy storms, snow, or fog can affect radar performance and visibility, limiting the ability of controllers to effectively manage air traffic.
- Electromagnetic interference: Electromagnetic pulses from solar flares or other sources can disrupt radio communication and navigation systems.
- Natural Disasters: Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, or wildfires can directly damage ATC infrastructure and lead to operational disruptions.
Robust contingency plans, advanced weather forecasting systems, and redundant communication networks are essential for mitigating the effects of environmental factors on ATC operations.
The Consequences of Air Traffic Control Failures
The consequences of ATC failures are far-reaching, impacting safety, economics, and public trust.
Safety Risks
ATC failures pose significant safety risks, increasing the probability of mid-air collisions, ground collisions, and runway incursions.
- Mid-air collisions: A failure to properly separate aircraft can result in catastrophic mid-air collisions with potentially fatal outcomes.
- Ground collisions: Errors in ground guidance can lead to collisions between aircraft and ground vehicles or other obstructions.
- Runway incursions: Improper runway access control can result in dangerous runway incursions, jeopardizing aircraft and ground personnel safety.
The impact on passenger safety is immeasurable, and even near-miss incidents can cause significant psychological trauma to passengers and crew.
Economic Impacts
ATC failures cause significant economic disruption, resulting in substantial financial losses for airlines, airports, and related industries.
- Flight cancellations and delays: ATC failures lead to flight disruptions, resulting in significant costs for airlines and inconvenience for passengers.
- Passenger compensation: Airlines are often obligated to compensate passengers for delays and cancellations caused by ATC failures.
- Damage to airline reputations: ATC-related disruptions can damage the reputation of airlines and erode passenger confidence.
The ripple effect extends beyond the aviation industry, affecting tourism, freight transport, and other sectors reliant on air travel.
Public Trust and Confidence
ATC failures can erode public trust and confidence in the aviation industry.
- Passenger anxiety: News of ATC failures can cause anxiety among air travelers, making them hesitant to fly.
- Need for transparent communication: Open and honest communication about ATC failures and the measures taken to address them is crucial to rebuilding public trust.
Building and maintaining public trust requires a proactive approach, including transparent incident reporting, effective communication, and visible commitment to safety improvements.
Mitigating the Risks of Air Traffic Control Failures
Addressing the growing threat of ATC failures requires a multi-pronged approach focusing on technological upgrades, enhanced training, and improved communication.
Technological Upgrades
Modernizing ATC systems is paramount. This includes implementing redundant systems, improving cybersecurity measures, and leveraging new technologies.
- Next Generation Air Transportation System (NextGen): Implementing NextGen technologies improves situational awareness and efficiency.
- Data analytics and AI: Utilizing data analytics and artificial intelligence can improve predictive capabilities and enhance system reliability.
- Improved cybersecurity measures: Robust cybersecurity protocols are essential to protect ATC systems from cyberattacks.
Investing in modern technology is a crucial step towards enhancing ATC safety and efficiency.
Enhanced Training and Procedures
Rigorous training programs, standardized procedures, and effective communication protocols are vital for preventing human error.
- Advanced simulation training: Utilizing advanced simulation training allows controllers to practice handling various scenarios in a safe environment.
- Regular audits and inspections: Regular audits and inspections ensure that ATC systems and procedures meet the highest safety standards.
- Crew Resource Management (CRM): Implementing CRM principles enhances teamwork, communication, and decision-making among air traffic controllers.
Continual investment in training and development programs is essential to build a highly skilled and proficient workforce.
Improved Communication and Coordination
Seamless communication and coordination between all stakeholders, including ATC facilities, airlines, and other agencies, is essential.
- Enhanced data sharing: Sharing real-time data between different ATC facilities improves situational awareness and coordination.
- Improved inter-agency collaboration: Closer collaboration between ATC authorities and other agencies, such as weather services and law enforcement, enhances preparedness for unexpected events.
- Standardized communication protocols: Implementing universally understood communication protocols minimizes the risk of misunderstandings and errors.
Stronger inter-agency collaboration and streamlined communication processes are vital for preventing and mitigating the effects of ATC failures.
Conclusion
Air traffic control failures pose a significant and growing threat to aviation safety and efficiency. The causes are complex, ranging from outdated technology and human error to environmental disruptions. The consequences are equally far-reaching, impacting safety, economics, and public trust. Understanding the challenges of air traffic control failures is the first step towards developing effective mitigation strategies. By investing in modern technology, enhancing training programs, and improving communication and coordination, we can significantly reduce the risk of future air traffic control system failures and ensure the safe and efficient operation of the global air transportation system. Let's work together to improve air traffic control safety and prevent future tragedies. Join the conversation and advocate for improved infrastructure and training to ensure a safer future for air travel.

Featured Posts
-
 Jurgen Klopp To Real Madrid Agent Comments Fuel Speculation
May 22, 2025
Jurgen Klopp To Real Madrid Agent Comments Fuel Speculation
May 22, 2025 -
 Saskatchewan Political Panel The Future Of Western Canada And Separation
May 22, 2025
Saskatchewan Political Panel The Future Of Western Canada And Separation
May 22, 2025 -
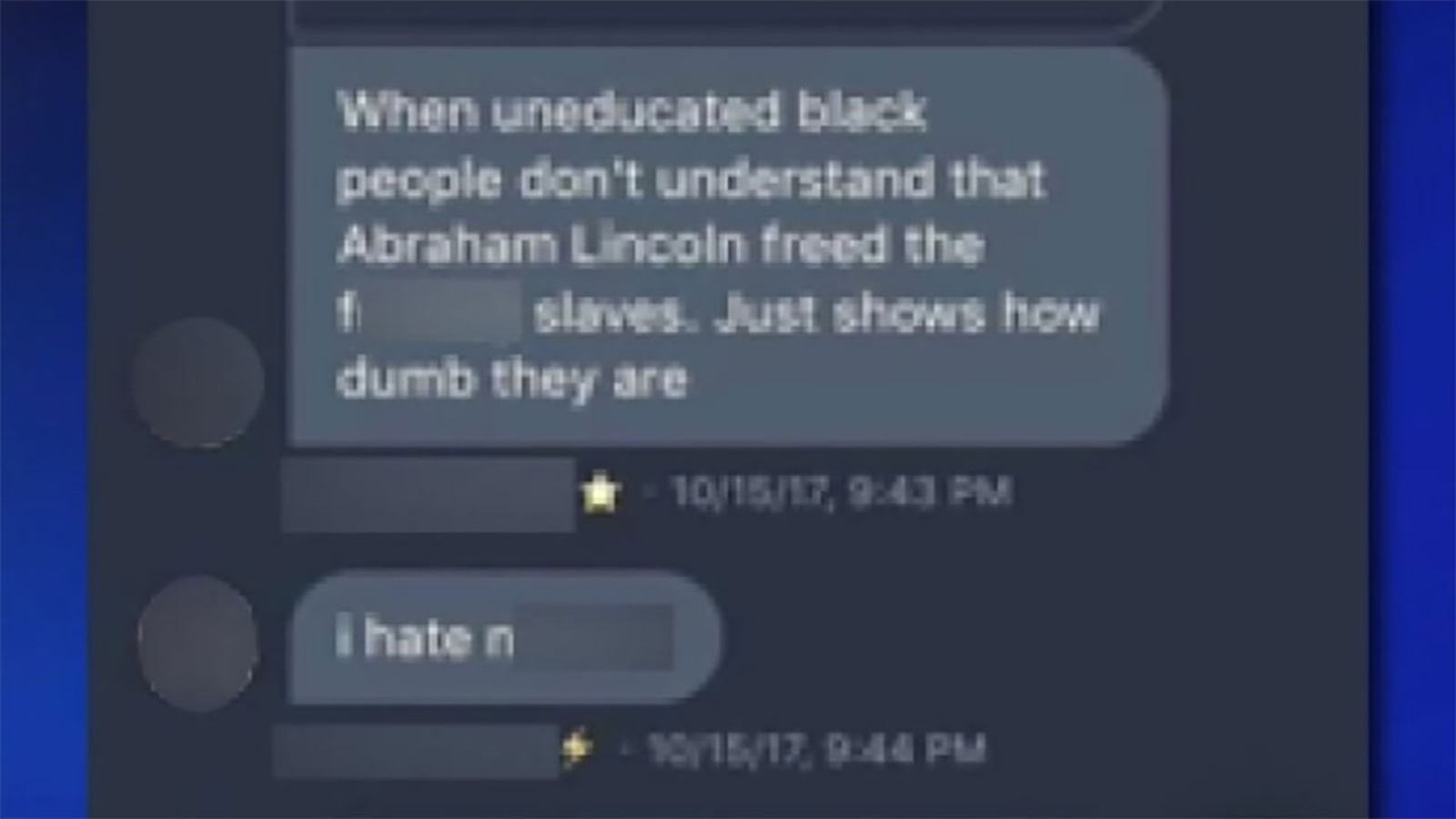 Appeal Launched Against Racial Hatred Tweet Sentence
May 22, 2025
Appeal Launched Against Racial Hatred Tweet Sentence
May 22, 2025 -
 Lindsey Graham Sanctions Inevitable If Russia Rejects Peace Talks
May 22, 2025
Lindsey Graham Sanctions Inevitable If Russia Rejects Peace Talks
May 22, 2025 -
 The Goldbergs A Nostalgic Journey Through 1980s Pop Culture
May 22, 2025
The Goldbergs A Nostalgic Journey Through 1980s Pop Culture
May 22, 2025
