Bond Market Volatility: Understanding The Tariff Shock Fallout
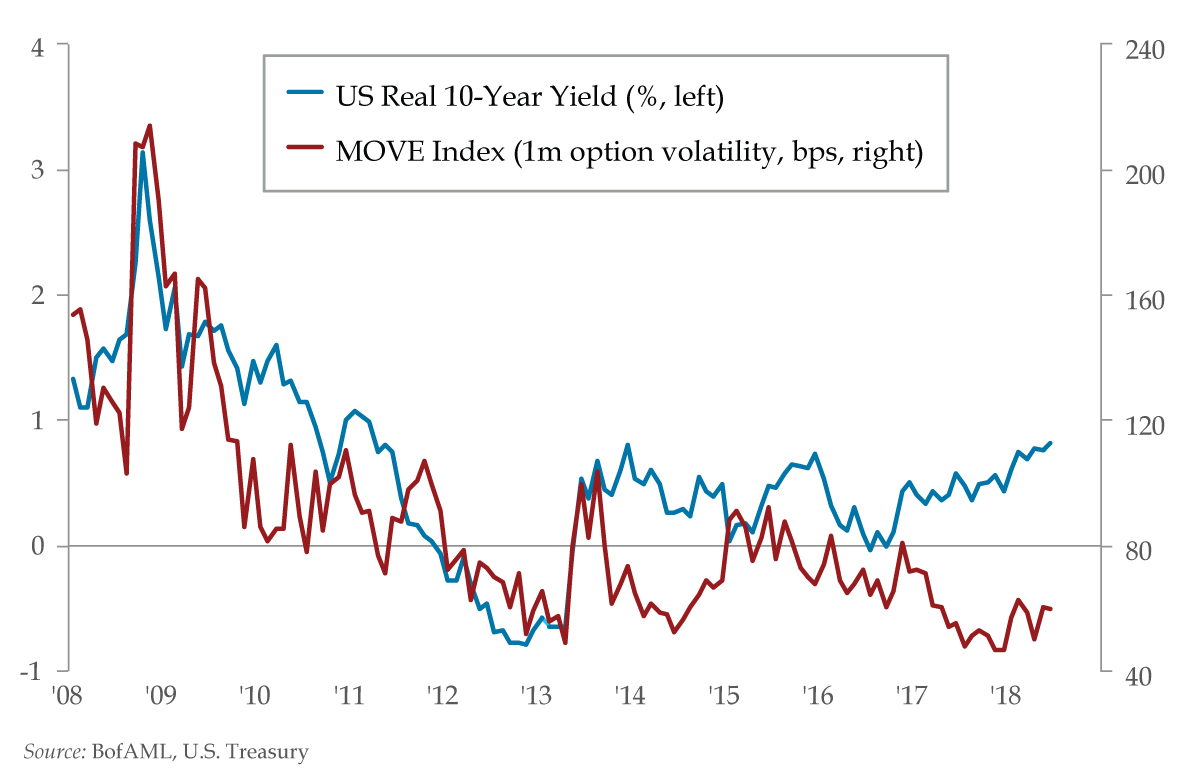
Table of Contents
The Mechanism of Tariff Shock on Bond Yields
Tariffs significantly impact inflation, economic growth, and consequently, bond yields. The imposition of tariffs increases the cost of imported goods, leading to higher inflation. This higher inflation erodes the purchasing power of fixed-income assets like bonds, making them less attractive to investors. Simultaneously, reduced economic growth, a common consequence of tariff disputes, diminishes the overall demand for bonds. This decreased demand, coupled with increased uncertainty surrounding future economic growth, increases risk aversion among investors.
- Increased import costs lead to higher inflation. Tariffs directly increase the price of imported goods, pushing up the consumer price index (CPI) and impacting inflation expectations.
- Higher inflation erodes the purchasing power of fixed-income assets. The return on bonds is fixed, so higher inflation reduces the real return an investor receives.
- Reduced economic growth diminishes demand for bonds. Slower economic growth often leads to lower corporate profits and reduced investment, decreasing the demand for corporate bonds.
- Uncertainty surrounding future economic growth increases risk aversion. The unpredictable nature of tariff wars creates uncertainty, making investors hesitant to invest in riskier assets, including certain types of bonds.
- Central banks' responses (interest rate hikes or cuts) further impact bond yields. Central banks may intervene to counteract inflationary pressures or stimulate economic growth, influencing interest rates and subsequently bond yields.
The complexities of inflation expectations play a crucial role in influencing long-term bond yields. Investors' expectations about future inflation directly affect their demand for bonds, impacting their price and yield. Different types of bonds, such as government bonds, corporate bonds, and municipal bonds, also exhibit varied responses to tariff shocks due to their differing risk profiles and characteristics. For instance, longer-term bonds are generally more sensitive to changes in inflation expectations than shorter-term bonds.
Assessing the Impact on Different Bond Types
Tariff shocks differentially impact various bond types. Understanding these nuances is critical for effective portfolio management.
Government Bonds
Government bonds, often considered safe-haven assets, experience a "flight-to-safety" effect during times of economic uncertainty.
- Increased demand for safe-haven assets like government bonds. Investors seek the relative safety of government bonds during times of heightened risk.
- Potential for lower yields due to increased demand. Increased demand pushes bond prices up, leading to lower yields.
- Variation in response based on credit rating and maturity. The impact of tariff shocks varies depending on the creditworthiness of the issuing government and the maturity of the bond. Bonds issued by countries with higher credit ratings tend to be less affected.
Corporate Bonds
Corporate bonds are more sensitive to economic downturns and tariff-related risks than government bonds.
- Increased default risk for companies heavily reliant on imports or exports. Companies heavily involved in international trade face higher risks during tariff wars.
- Wider credit spreads as investors demand higher yields for riskier corporate bonds. Investors demand higher yields to compensate for the increased risk of default.
- Impact on different sectors (e.g., manufacturing vs. technology). Certain sectors, such as manufacturing, are more directly impacted by tariffs than others, like technology.
Emerging Market Bonds
Emerging market bonds are particularly vulnerable to global trade tensions.
- Increased capital flight from emerging markets. Investors pull their money out of emerging markets seeking safer havens.
- Currency depreciation impacting returns for foreign investors. Currency fluctuations can significantly reduce the returns for foreign investors holding emerging market bonds.
- Higher risk premiums demanded by investors. Investors require higher returns to compensate for the increased risk associated with emerging markets during times of global uncertainty.
Strategies for Navigating Bond Market Volatility
Effectively navigating bond market volatility requires a proactive approach incorporating various strategies.
Diversification
Diversification is paramount in mitigating risk.
- Reduce exposure to specific risks. Spreading investments across various bond types, maturities, and issuers reduces the impact of any single event.
- Improve overall portfolio resilience. A diversified portfolio is better equipped to withstand market shocks.
- Consider different geographical regions. Diversification across different countries can help reduce exposure to region-specific risks.
Hedging
Hedging strategies can help mitigate risks associated with bond market volatility.
- Interest rate swaps. These can help protect against changes in interest rates.
- Inflation-indexed bonds. These offer protection against inflation.
- Options contracts. These can provide downside protection or the opportunity to profit from volatility.
Active Management
Active bond management can be beneficial during periods of heightened uncertainty.
- Ability to adjust portfolio positioning based on market conditions. Active managers can swiftly react to changing market dynamics.
- Expertise in identifying undervalued bonds. Active managers can potentially identify opportunities in the market.
- Potential for higher returns compared to passive strategies. While not guaranteed, active management offers the potential for superior returns.
Conclusion
The impact of tariff shocks on bond market volatility is complex and requires a thorough understanding of economic mechanisms. By analyzing the influence of tariffs on inflation, economic growth, and investor sentiment, investors can better anticipate the response of different bond types. Implementing diversification, hedging, and potentially active management strategies are crucial for navigating this uncertainty. Staying informed about global trade developments and adapting your investment strategy accordingly is essential for mitigating risks related to bond market volatility and achieving long-term investment success. Regularly assess your portfolio’s exposure to tariff-related risks and consider consulting a financial advisor to develop a robust investment plan that accounts for the complexities of the bond market.

Featured Posts
-
 Mainz Vs Holstein Kiel Relegation Battle And Champions League Aspirations Collide
May 12, 2025
Mainz Vs Holstein Kiel Relegation Battle And Champions League Aspirations Collide
May 12, 2025 -
 Discovering The Countrys Top New Business Locations
May 12, 2025
Discovering The Countrys Top New Business Locations
May 12, 2025 -
 Regalo Presidencial Tres Toros Uruguayos Parten Hacia China Para Xi Jinping
May 12, 2025
Regalo Presidencial Tres Toros Uruguayos Parten Hacia China Para Xi Jinping
May 12, 2025 -
 How Payton Pritchard Achieved A Breakout Season Dedication And Development
May 12, 2025
How Payton Pritchard Achieved A Breakout Season Dedication And Development
May 12, 2025 -
 Fabers U Turn Full Support For Royal Distinctions For Asylum Volunteer Program
May 12, 2025
Fabers U Turn Full Support For Royal Distinctions For Asylum Volunteer Program
May 12, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Kemenangan Telak Persipura Jayapura Atas Rans Fc 8 0 Di Playoff Liga 2
May 13, 2025
Kemenangan Telak Persipura Jayapura Atas Rans Fc 8 0 Di Playoff Liga 2
May 13, 2025 -
 Persipura Jayapura Dominasi Rans Fc 8 0 Di Playoff Liga 2 Kokoh Di Puncak Grup K
May 13, 2025
Persipura Jayapura Dominasi Rans Fc 8 0 Di Playoff Liga 2 Kokoh Di Puncak Grup K
May 13, 2025 -
 Persipura Jayapura Hancurkan Rans Fc 8 0 Di Playoff Liga 2 Puncaki Klasemen Grup K
May 13, 2025
Persipura Jayapura Hancurkan Rans Fc 8 0 Di Playoff Liga 2 Puncaki Klasemen Grup K
May 13, 2025 -
 Victorie Cruciala As Roma Se Califica In Optimile Europa League Dupa Succesul Contra Fc Porto
May 13, 2025
Victorie Cruciala As Roma Se Califica In Optimile Europa League Dupa Succesul Contra Fc Porto
May 13, 2025 -
 Your Guide To Bar Roma Blog Tos Take On This Toronto Bar
May 13, 2025
Your Guide To Bar Roma Blog Tos Take On This Toronto Bar
May 13, 2025
