Canada's Economic Future: Urgent Issues For The Next Prime Minister
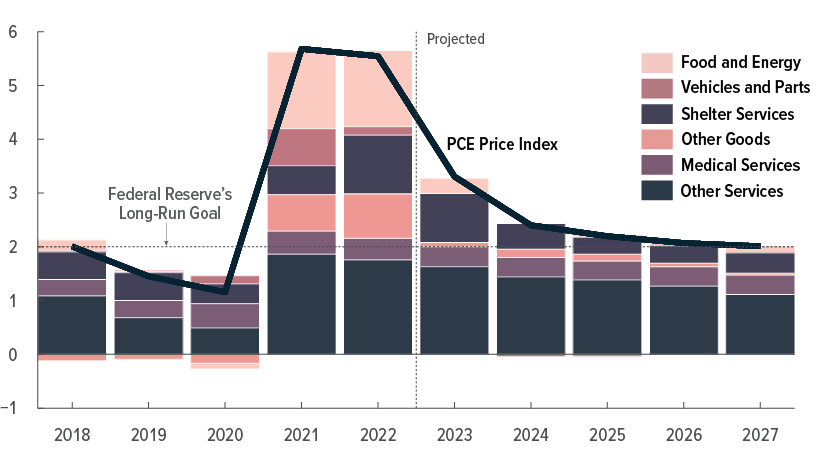
Table of Contents
Inflation and the Cost of Living Crisis
Soaring Inflation Rates and Their Impact
Canada's inflation rate has surged in recent years, significantly impacting household budgets. The rising cost of living is squeezing Canadians, particularly low-income families, and eroding consumer confidence. This has led to a decrease in discretionary spending and an overall slowdown in economic growth.
- Rising food prices: Grocery bills have increased dramatically, forcing many families to make difficult choices about what they can afford.
- Housing costs: Soaring rent and home prices are making it increasingly difficult for Canadians to find affordable housing, impacting their financial stability and mental well-being.
- Energy prices: Fluctuations in energy prices, particularly gasoline, add to the burden on households and businesses.
- Impact on consumer confidence and spending: High inflation erodes consumer purchasing power and leads to reduced spending, potentially triggering a recessionary spiral.
Potential Solutions and Policy Recommendations
Addressing this crisis requires a multi-pronged approach. The government needs to implement policies that both control inflation and mitigate its impact on vulnerable populations.
- Targeted subsidies: Providing direct financial assistance to low-income families to help offset the rising cost of essential goods and services.
- Tax breaks: Implementing temporary tax cuts to boost disposable income and stimulate consumer spending.
- Supply chain efficiency: Investing in infrastructure and supply chain improvements to reduce bottlenecks and increase the availability of goods.
- Examples of successful inflation-control policies from other countries: Learning from international best practices in managing inflationary pressures.
- Collaboration between the government and the Bank of Canada: Close cooperation is crucial to coordinate monetary and fiscal policies effectively.
Housing Affordability and the Housing Crisis
The Severity of Canada's Housing Shortage
Canada is grappling with a severe housing shortage, marked by skyrocketing house prices, escalating rental costs, and a lack of affordable housing options. This crisis is impacting both homeownership and rental markets across the country.
- Statistics on homeownership rates: Homeownership rates are declining, particularly among younger generations, hindering wealth accumulation.
- Rental vacancy rates: Low rental vacancy rates are driving up rents, making it challenging for many Canadians to find affordable places to live.
- The growing number of homeless individuals: The housing crisis is exacerbating homelessness, a significant social and economic issue.
- Impact on intergenerational wealth transfer: The rising cost of housing is making it difficult for parents to assist their children in purchasing homes, impacting intergenerational wealth transfer.
Addressing the Housing Crisis Through Policy
Addressing the housing crisis requires a comprehensive strategy that increases supply, regulates the market, and supports affordable housing initiatives.
- Increased investment in social housing: Significant public investment is needed to expand the availability of affordable housing options for low-income individuals and families.
- Zoning reforms: Modernizing zoning regulations to permit higher density development and the construction of more diverse housing types.
- Incentives for developers to build affordable units: Offering tax breaks and other incentives to encourage the construction of affordable housing.
- The role of immigration in addressing the housing shortage: Managing immigration strategically to ensure sufficient housing supply is available.
Diversification of the Canadian Economy and Global Competitiveness
Over-Reliance on Natural Resources
Canada's economy has traditionally been heavily reliant on natural resources. While this has provided economic benefits, it also creates vulnerabilities to commodity price fluctuations and global market instability. Diversification is crucial to mitigate these risks.
- The importance of investing in technology, innovation, and the green economy: Developing a robust and diversified technological sector can create high-paying jobs and improve Canada's economic resilience.
- Attracting foreign investment in diverse sectors: Creating an attractive investment climate to attract foreign capital into sectors beyond natural resources.
Strengthening Canada's Global Competitiveness
To thrive in a globalized economy, Canada must enhance its international competitiveness.
- Trade agreements and their impact on economic growth: Negotiating and maintaining beneficial trade agreements to expand market access for Canadian goods and services.
- The importance of attracting and retaining skilled workers: Implementing policies to attract and retain highly skilled workers from around the world.
- Improving Canada's ranking in global competitiveness indices: Focusing on policy improvements to increase Canada's ranking in international competitiveness assessments.
Climate Change and the Transition to a Green Economy
The Economic Opportunities of a Green Transition
Transitioning to a sustainable economy presents significant economic opportunities.
- Investing in renewable energy, green infrastructure, and sustainable transportation: Creating jobs in emerging green industries and technologies.
- The potential for Canada to become a global leader in green technology: Positioning Canada as a pioneer and exporter of green technologies.
Managing the Economic Challenges of Climate Change
Climate change poses significant economic risks.
- Investing in climate resilience infrastructure: Protecting infrastructure from the impacts of climate change, such as extreme weather events.
- Implementing carbon pricing mechanisms effectively: Designing effective carbon pricing policies that balance environmental goals with economic considerations.
- Supporting industries impacted by climate change policies: Providing support to industries transitioning to a low-carbon economy.
Conclusion
Canada's economic future is at a crossroads. The next Prime Minister must confront these urgent issues head-on with bold and decisive action. Addressing inflation, the housing crisis, economic diversification, and the transition to a green economy are not just political priorities; they are essential for ensuring a prosperous and sustainable future for all Canadians. A comprehensive economic strategy that tackles these challenges effectively will be crucial for Canada's continued growth and stability. Ignoring these critical aspects of Canada's economic future risks jeopardizing the nation's long-term prosperity. The time for decisive leadership on Canada's economic future is now. Let's work together to build a stronger, more resilient Canada for generations to come. The future of Canada's economy depends on it.

Featured Posts
-
 Cp News Alert Ovechkin Ties Gretzkys Nhl Goal Record
Apr 30, 2025
Cp News Alert Ovechkin Ties Gretzkys Nhl Goal Record
Apr 30, 2025 -
 The Yates Story Dr Jessica Johnson Showcases Black Historys Strength
Apr 30, 2025
The Yates Story Dr Jessica Johnson Showcases Black Historys Strength
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Tien Linh Dai Su Tinh Nguyen Binh Duong Cau Thu Trai Tim Nhan Ai
Apr 30, 2025
Tien Linh Dai Su Tinh Nguyen Binh Duong Cau Thu Trai Tim Nhan Ai
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Ryys Shbab Bn Jryr Mthm B Tfasyl Alqdyt
Apr 30, 2025
Ryys Shbab Bn Jryr Mthm B Tfasyl Alqdyt
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Zoe Kravitz And Noah Centineo Unconfirmed Relationship Sparks Speculation
Apr 30, 2025
Zoe Kravitz And Noah Centineo Unconfirmed Relationship Sparks Speculation
Apr 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Il Venerdi Santo Un Commento Di Feltri
Apr 30, 2025
Il Venerdi Santo Un Commento Di Feltri
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Severe Flooding Cancels Thunder Over Louisville Fireworks Show
Apr 30, 2025
Severe Flooding Cancels Thunder Over Louisville Fireworks Show
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Feltri Sul Venerdi Santo Un Opinione Controversa
Apr 30, 2025
Feltri Sul Venerdi Santo Un Opinione Controversa
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Kentuckys Louisville Under State Of Emergency Due To Tornado And Imminent Flooding
Apr 30, 2025
Kentuckys Louisville Under State Of Emergency Due To Tornado And Imminent Flooding
Apr 30, 2025 -
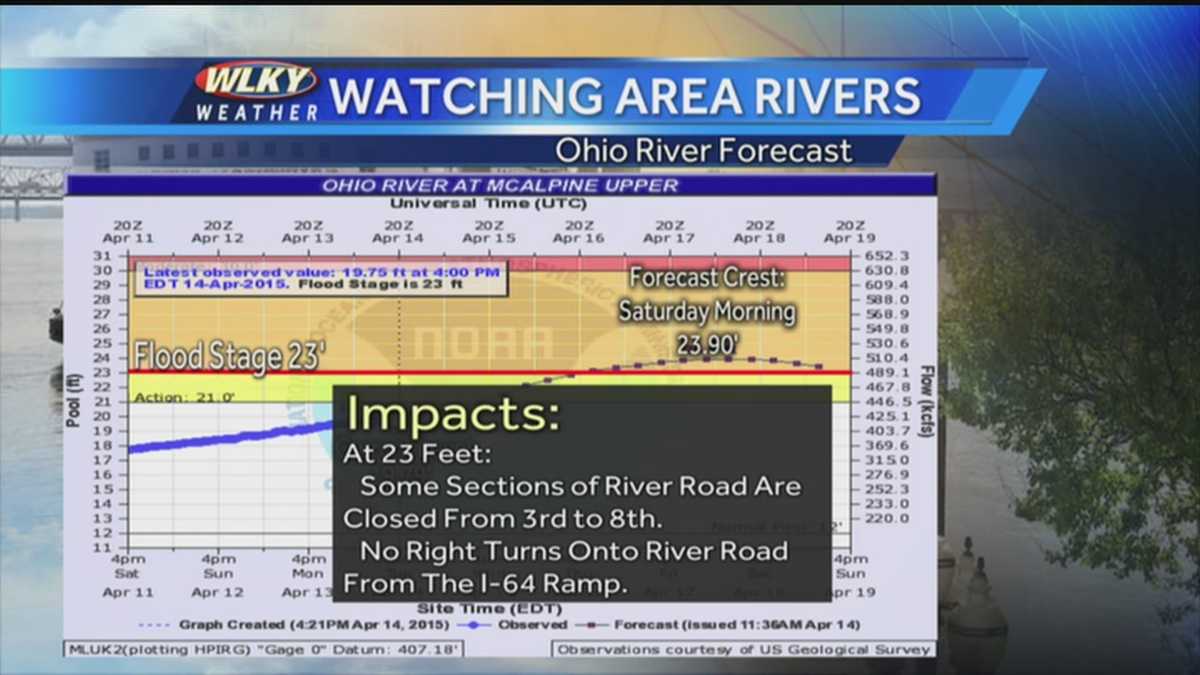 Ohio River Flooding Forces Cancellation Of Thunder Over Louisville Fireworks
Apr 30, 2025
Ohio River Flooding Forces Cancellation Of Thunder Over Louisville Fireworks
Apr 30, 2025
