Canadian Wildfire Smoke Impacts Minnesota's Air Quality
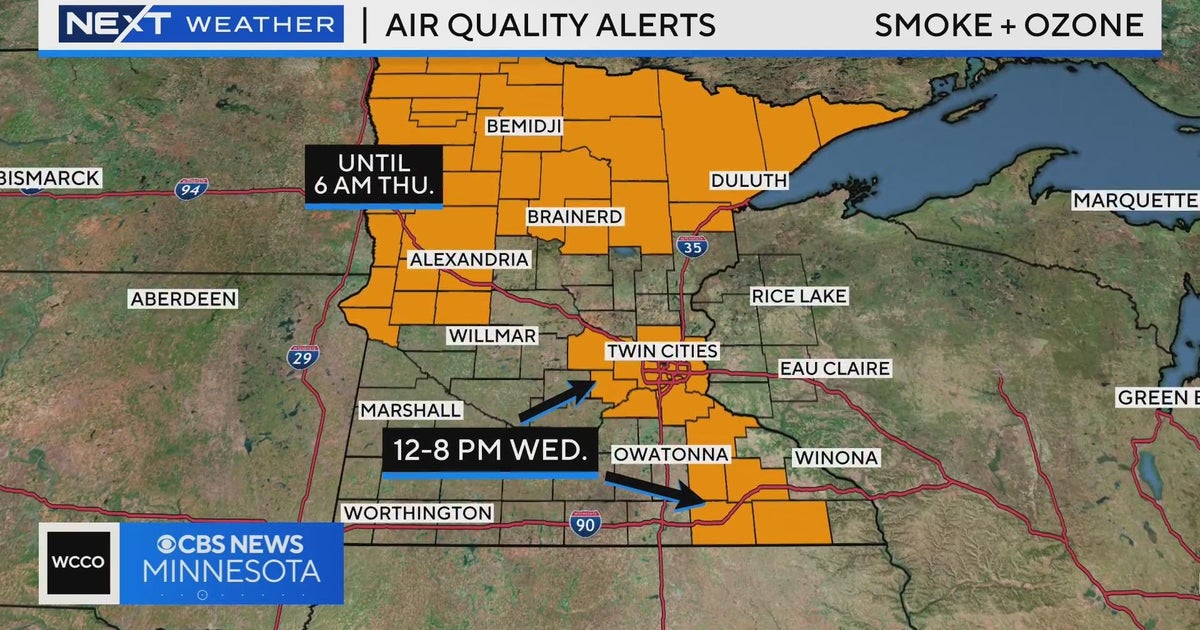
Table of Contents
The Science Behind the Smoke's Journey
Atmospheric Transportation of Pollutants
Wildfire smoke doesn't stay localized; it can travel vast distances, carried by prevailing winds and atmospheric pressure systems. The transport of Canadian wildfire smoke to Minnesota is a complex meteorological phenomenon. High-pressure systems, often associated with clear skies and calm conditions in Minnesota, can act as a "lid," trapping pollutants near the surface. Conversely, low-pressure systems and strong winds can efficiently transport smoke plumes hundreds, even thousands, of miles.
- Recent Weather Patterns: The unusually persistent and strong westerly wind patterns in spring and summer 2024 (adjust year as needed) facilitated the long-range transport of smoke from significant wildfires in Ontario, Quebec, and Saskatchewan.
- Specific Canadian Fire Locations: Major fire complexes in areas like Northwestern Ontario and the boreal forests of Quebec were particularly significant contributors to the smoke plumes reaching Minnesota.
Composition of Wildfire Smoke and its Health Impacts
Wildfire smoke is a complex mixture of harmful pollutants, significantly impacting human health. Key components include:
-
PM2.5 (Particulate Matter 2.5): These tiny particles penetrate deep into the lungs, causing respiratory irritation and exacerbating conditions like asthma and bronchitis.
-
Ozone: A ground-level pollutant formed by chemical reactions involving smoke components, ozone can irritate the lungs and worsen respiratory illnesses.
-
Carbon Monoxide: A colorless, odorless gas that reduces the blood's ability to carry oxygen, leading to cardiovascular issues.
-
Health Risks: Exposure to these pollutants increases the risk of:
- Asthma attacks and exacerbations
- Respiratory infections (bronchitis, pneumonia)
- Cardiovascular problems (heart attacks, strokes)
- Eye irritation
- Worsening of pre-existing lung and heart conditions.
Vulnerable populations, including children, the elderly, and individuals with pre-existing respiratory or cardiovascular diseases, are particularly susceptible to the negative health effects of wildfire smoke.
The Impact on Minnesota's Air Quality Index (AQI)
AQI Readings and Public Health Alerts
Minnesota experienced alarmingly high AQI readings during periods of heavy Canadian wildfire smoke. Many cities, including Minneapolis and Duluth, saw AQI levels reaching "unhealthy" and even "hazardous" categories.
- Data Points and Resources: [Insert links to Minnesota Pollution Control Agency (MPCA) AQI data and maps]. The MPCA provides real-time AQI updates for various locations across the state. An AQI above 100 indicates unhealthy air quality for sensitive groups, while levels above 200 are unhealthy for everyone.
- Understanding AQI Levels: Different AQI levels correspond to different health risks. Higher AQI values necessitate more stringent precautions.
Governmental Response and Public Health Recommendations
The MPCA and other state agencies issued numerous public health advisories urging residents to take precautions during periods of high AQI.
- Public Health Advisories: Advisories recommended limiting outdoor activities, staying indoors with windows and doors closed, using air purifiers with HEPA filters, and checking on vulnerable family members and neighbors.
- Governmental Actions: Beyond advisories, the state might have implemented temporary restrictions on certain outdoor activities or construction projects to mitigate the impact of the poor air quality (depending on actual events).
Long-Term Environmental and Economic Consequences
Environmental Impacts Beyond Air Quality
The environmental consequences of Canadian wildfire smoke extend beyond poor air quality:
- Reduced Visibility: Smoke significantly impairs visibility, affecting transportation and potentially impacting wildlife navigation.
- Damage to Vegetation: Deposition of pollutants can damage sensitive vegetation, potentially altering ecosystems.
- Water Resource Impacts: Ash and pollutants carried by rain can contaminate water sources.
- Long-Term Research: Ongoing research is needed to fully assess the long-term ecological consequences of repeated wildfire smoke events.
Economic Impacts on Minnesota
Poor air quality has substantial economic implications for Minnesota:
- Healthcare Costs: Increased hospitalizations and emergency room visits due to respiratory and cardiovascular problems strain the healthcare system.
- Lost Productivity: Reduced work productivity due to illness and decreased outdoor activity leads to economic losses.
- Tourism Impacts: Poor air quality can deter tourism, leading to revenue losses for businesses in the hospitality sector. Examples could include canceled outdoor events or reduced attendance at state parks.
Conclusion
The impact of Canadian wildfire smoke on Minnesota's air quality is undeniable, posing significant health risks and creating substantial environmental and economic challenges. The frequency and intensity of these events underscore the need for proactive measures to improve air quality monitoring, public health communication, and ultimately, address the root causes of wildfires. Stay safe during periods of high air pollution caused by Canadian wildfire smoke. Protect your health by understanding the impact of Canadian wildfire smoke on Minnesota air quality and by monitoring AQI updates from the Minnesota Pollution Control Agency. Share this article to raise awareness and encourage others to take necessary precautions.

Featured Posts
-
 Northeast Ohio Braces For Strong Thunderstorms Latest Forecast
May 31, 2025
Northeast Ohio Braces For Strong Thunderstorms Latest Forecast
May 31, 2025 -
 Analysis Of The Trump Administrations List Of Targeted Sanctuary Jurisdictions
May 31, 2025
Analysis Of The Trump Administrations List Of Targeted Sanctuary Jurisdictions
May 31, 2025 -
 Cleveland And Akron Special Weather Statement Increased Fire Danger
May 31, 2025
Cleveland And Akron Special Weather Statement Increased Fire Danger
May 31, 2025 -
 Exploring The Nintendo Switchs Impact On The Indie Game Landscape
May 31, 2025
Exploring The Nintendo Switchs Impact On The Indie Game Landscape
May 31, 2025 -
 Watch The Giro D Italia Mens Race Live
May 31, 2025
Watch The Giro D Italia Mens Race Live
May 31, 2025
