Car Dealers Renew Opposition To EV Mandates: Industry Fights Back

Table of Contents
Economic Challenges Posed by EV Mandates
The economic implications of rapid EV adoption are a major source of concern for car dealerships. The upfront investments and potential for reduced profitability represent substantial risks.
High Upfront Costs and Inventory Management
Dealerships face significant capital expenditures to adapt to the EV market. This includes:
- Substantial investment in new infrastructure: Installing charging stations requires significant capital investment, varying based on the number of stalls and charging speeds needed. This is particularly challenging for smaller dealerships with limited resources.
- Specialized EV mechanic training: Maintaining and repairing EVs requires specialized knowledge and tools, necessitating employee training programs that add to operational costs.
- Difficulty in forecasting EV demand: Fluctuating consumer preferences and rapid technological advancements in the EV sector make accurate demand forecasting extremely difficult, leading to potential inventory management challenges.
- Risk of obsolescence: Rapid technological changes mean that unsold EVs can quickly become obsolete, leading to significant financial losses for dealerships.
Specific financial burdens include:
- Charging station installation costs (ranging from thousands to hundreds of thousands of dollars, depending on size and type).
- Employee training expenses (including wages, training materials, and certification fees).
- Potential losses from unsold inventory due to technological obsolescence or slow consumer adoption.
Reduced Profit Margins on Electric Vehicles
Dealerships also face reduced profit margins on EVs compared to gasoline-powered vehicles. Several factors contribute to this:
- Higher manufacturing costs: The manufacturing process for EVs is currently more expensive than for internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles.
- Competitive pricing pressures: Intense competition in the EV market necessitates competitive pricing, squeezing profit margins.
- Difficulty in recouping infrastructure investment: The high initial investment in EV infrastructure may not be easily recouped through increased EV sales, especially during the early stages of market adoption.
Factors affecting profitability include:
- Lower service revenue from EVs (as they generally require less frequent maintenance).
- Government incentives that often reduce the final sale price, impacting dealership profit.
- Higher initial investment costs related to infrastructure and training.
Concerns Regarding Consumer Readiness and Infrastructure Limitations
Beyond the economic challenges, car dealers express serious concerns about consumer readiness and the limitations of existing infrastructure.
Insufficient Charging Infrastructure
A major barrier to widespread EV adoption is the lack of adequate public charging infrastructure.
- Range anxiety: The limited range of many EVs and the fear of running out of charge (range anxiety) remains a significant deterrent for potential buyers.
- Uneven distribution: Charging stations are unevenly distributed geographically, with rural areas often underserved. This makes EV ownership impractical for many people.
- Inconsistent charging standards: The lack of standardized charging connectors and protocols adds further complexity and inconvenience for EV drivers.
Specific infrastructure inadequacies include:
- Insufficient numbers of fast-charging stations, particularly along major highways.
- Uneven geographic distribution of charging stations, leaving many areas without convenient access.
- Inconsistent charging standards and connector types, creating confusion and incompatibility issues.
Consumer Education and Awareness
Many consumers still lack sufficient understanding of EVs, their benefits, and limitations.
- Misconceptions and anxieties: Misconceptions about charging times, range, battery life, and maintenance cost continue to hinder consumer adoption.
- Need for effective education: More effective consumer education programs and targeted marketing initiatives are crucial to dispel misinformation and address consumer concerns.
Key consumer concerns include:
- Battery range and charging time.
- Purchase price and overall cost of ownership.
- Maintenance requirements and associated costs.
- Battery life and replacement costs.
The Impact on Dealership Employment and the Automotive Workforce
The shift to EVs also poses challenges to dealership employment and the broader automotive workforce.
Job Displacement Due to Changes in Service Requirements
EVs require less frequent and less complex maintenance than gasoline-powered vehicles, leading to potential job displacement in service departments.
- Reduced service needs: Fewer moving parts and simpler mechanical systems in EVs result in reduced service requirements.
- Need for upskilling: Dealership mechanics need to be retrained to service and repair EVs, requiring significant investment in training programs.
- Potential for job losses: The shift to EVs may lead to job losses in service departments without adequate retraining and workforce transition plans.
Employment implications include:
- Job losses in traditional service departments, potentially impacting dealership profitability and community economies.
- The need for comprehensive retraining programs to equip mechanics with the skills to work on EVs.
- Potential negative economic impact on communities reliant on automotive sector jobs.
The Need for Government Support for Workforce Transition
Government intervention is critical to mitigate job displacement and support the transition to an EV-centric workforce.
- Retraining programs: Government funding for retraining programs is crucial to upskill automotive workers for EV-related jobs.
- Job creation initiatives: Investment in infrastructure projects related to EV charging and manufacturing can create new jobs.
- Industry-education partnerships: Collaborations between government, industry, and educational institutions are vital to develop relevant training programs and curricula.
Government intervention is needed to:
- Fund comprehensive retraining programs for automotive workers.
- Establish partnerships between educational institutions and the automotive industry to develop EV-specific training programs.
- Implement job creation initiatives to offset job losses in traditional automotive sectors.
Conclusion
Car dealers' renewed opposition to EV mandates underscores the substantial challenges in transitioning to electric mobility. Addressing the economic anxieties, infrastructure limitations, and workforce transition issues is vital for a successful and equitable transformation. A collaborative effort between the government, the automotive industry, and consumers is essential to overcome these obstacles and ensure the sustainable growth of the EV market. Ignoring the concerns of car dealers will only hinder the effective implementation of EV mandates and potentially harm the overall adoption of electric vehicles. A balanced approach, incorporating feedback from all stakeholders, is crucial for a smooth and efficient transition to electric mobility, fostering productive dialogue around EV mandates and their broader impact.

Featured Posts
-
 Analysis Justice Departments Termination Of School Desegregation Order
May 03, 2025
Analysis Justice Departments Termination Of School Desegregation Order
May 03, 2025 -
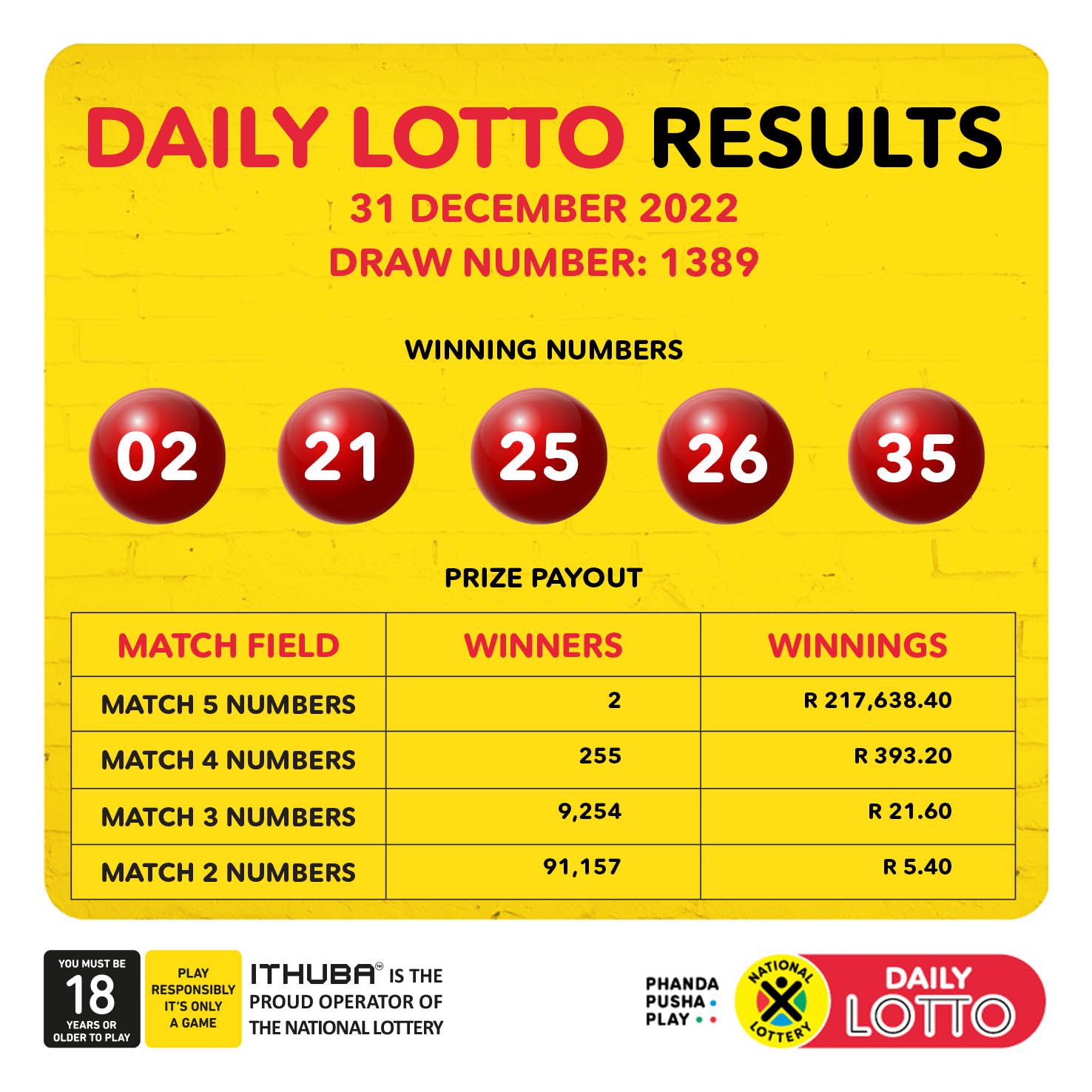 Latest Lotto Results Lotto Plus 1 And Lotto Plus 2 Draws
May 03, 2025
Latest Lotto Results Lotto Plus 1 And Lotto Plus 2 Draws
May 03, 2025 -
 Rolls Royce Addresses Tariff Concerns Reaffirms 2025 Goals
May 03, 2025
Rolls Royce Addresses Tariff Concerns Reaffirms 2025 Goals
May 03, 2025 -
 Fortnites Future Concerns After Game Mode Removal
May 03, 2025
Fortnites Future Concerns After Game Mode Removal
May 03, 2025 -
 Souness Slams Manchester Uniteds Transfer Policy
May 03, 2025
Souness Slams Manchester Uniteds Transfer Policy
May 03, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Farmings Future Can The Reform Uk Party Be Trusted
May 03, 2025
Farmings Future Can The Reform Uk Party Be Trusted
May 03, 2025 -
 Asterad Wrqt Syasat Alastthmar Aljdydt Alsadrt En Amant Aljbht Alwtnyt
May 03, 2025
Asterad Wrqt Syasat Alastthmar Aljdydt Alsadrt En Amant Aljbht Alwtnyt
May 03, 2025 -
 Khtt Astthmaryt Jdydt Mn Aljbht Alwtnyt Ahdaf W Bnwd Alwrqt
May 03, 2025
Khtt Astthmaryt Jdydt Mn Aljbht Alwtnyt Ahdaf W Bnwd Alwrqt
May 03, 2025 -
 Aljbht Alwtnyt Tfasyl Wrqt Syasat Alastthmar Aljdydt
May 03, 2025
Aljbht Alwtnyt Tfasyl Wrqt Syasat Alastthmar Aljdydt
May 03, 2025 -
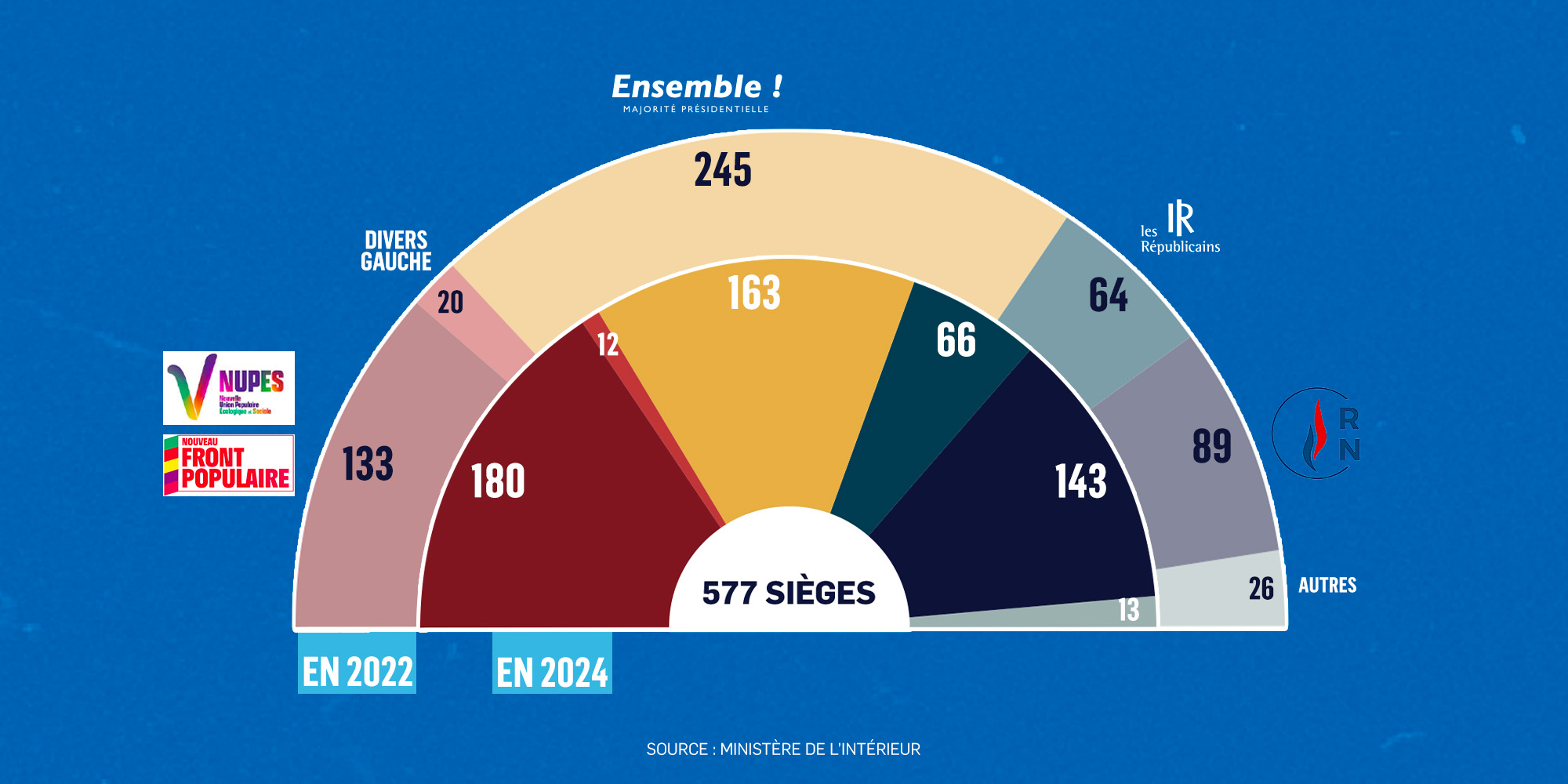 Algerie Reactions Politiques A La Reforme De La Loi Sur Les Partis Pt Ffs Rcd Jil Jadid
May 03, 2025
Algerie Reactions Politiques A La Reforme De La Loi Sur Les Partis Pt Ffs Rcd Jil Jadid
May 03, 2025
