CNN's Guide To Understanding And Combating Misinformation

Table of Contents
Identifying Misinformation: Spotting the Red Flags
Recognizing misinformation often requires a keen eye and a healthy dose of skepticism. Mastering the art of identifying false information is the first step in effectively combating it.
Recognizing Common Tactics
Misinformation often employs subtle – and sometimes not-so-subtle – techniques designed to manipulate and deceive. Be on the lookout for these red flags:
- Clickbait Headlines and Emotionally Charged Language: Sensationalist headlines and emotionally charged language are often used to grab attention and encourage sharing without regard for accuracy. Think headlines like "You Won't BELIEVE What Happened Next!" or overly dramatic phrasing designed to provoke strong emotional responses.
- Lack of Credible Sources and Citations: Legitimate news sources and factual claims always provide sources and citations. The absence of these is a major warning sign.
- Suspicious Websites and Domains: Be wary of websites with unusual URLs, poor design, or an abundance of pop-up ads. Look for secure HTTPS connections (indicated by a padlock icon in the address bar).
- Misleading Images and Videos (Deepfakes, Manipulated Content): Advanced technology allows for the creation of deepfakes and manipulated media, making it harder to distinguish between reality and fabrication. Reverse image searches can help verify the authenticity of images.
- Inconsistencies and Factual Errors: Misinformation often contains contradictory information or easily verifiable factual inaccuracies.
- One-Sided Arguments and Absence of Opposing Views: A balanced and objective perspective presents different viewpoints. If a piece of information only presents one side of an issue, it could be biased or misleading.
Verifying Information Sources
Before accepting information as truth, take the time to verify its source:
- Check the Website's "About Us" Section: This section provides information about the website's ownership, purpose, and editorial policies. A lack of transparency should raise suspicion.
- Cross-Reference Information with Multiple Reputable Sources: Don't rely on a single source. Check the information against multiple reputable sources, such as fact-checking websites (like Snopes or PolitiFact) and established news outlets.
- Look for Evidence of Bias or Agenda-Driven Reporting: Consider the source's potential biases and motivations. Does the information align with a particular political or ideological agenda?
- Evaluate the Author's Expertise and Credentials: Is the author an expert on the subject matter? Are their credentials verifiable?
Understanding the Spread of Misinformation: How it Works
Misinformation doesn't spread randomly; it leverages specific mechanisms and exploits psychological vulnerabilities.
The Role of Social Media
Social media platforms play a significant role in the rapid dissemination of misinformation:
- Algorithms that Prioritize Engagement Over Accuracy: Social media algorithms often prioritize content that generates engagement, regardless of its accuracy. This creates a system where sensational and misleading information can spread quickly.
- The Spread of Misinformation Through Echo Chambers and Filter Bubbles: Algorithms can inadvertently create "echo chambers" where users are primarily exposed to information that confirms their existing beliefs, reinforcing biases and making them more susceptible to misinformation.
- The Ease of Sharing and Forwarding False Information: The ease of sharing content on social media platforms makes it simple to spread misinformation unintentionally.
Psychological Factors
Our own cognitive biases can make us vulnerable to misinformation:
- Confirmation Bias: This is the tendency to favor information that confirms our existing beliefs, even if it's inaccurate.
- Cognitive Biases: Various cognitive biases, such as the availability heuristic (overestimating the likelihood of events that are easily recalled) and the bandwagon effect (believing something because many others do), can make us susceptible to misinformation.
- Emotional Responses that Drive Sharing, Regardless of Accuracy: Information that evokes strong emotional responses (fear, anger, outrage) is more likely to be shared, even if it's untrue.
Combating Misinformation: What You Can Do
Combating misinformation is a collective responsibility. Here's what you can do:
Developing Critical Thinking Skills
Sharpen your critical thinking skills by:
- Questioning Information Sources Critically: Don't passively accept information; actively question its source, motives, and supporting evidence.
- Analyzing Information for Biases and Inaccuracies: Look for signs of bias, inconsistencies, or factual errors.
- Learning to Distinguish Between Facts and Opinions: Understand the difference between verifiable facts and subjective opinions or interpretations.
Responsible Sharing
Practice responsible information sharing:
- Verify Information Before Sharing: Take the time to verify information from multiple reputable sources before sharing it.
- Avoid Sharing Information That Evokes Strong Emotional Responses Without Confirmation: If something makes you angry or scared, verify its accuracy before sharing it.
- Report Misinformation on Social Media Platforms: Most social media platforms have mechanisms for reporting misinformation. Use these tools to help curb the spread of false information.
Supporting Fact-Checking Organizations
Support organizations dedicated to combating misinformation:
- Familiarize Yourself with Reputable Fact-Checking Websites: Learn to identify and utilize credible fact-checking websites.
- Support Organizations Dedicated to Combating Misinformation: Consider supporting organizations that are actively working to combat the spread of misinformation.
Conclusion: Taking Action Against Misinformation
Understanding and combating misinformation requires a multifaceted approach. By developing critical thinking skills, verifying information sources diligently, and practicing responsible information sharing, we can significantly reduce the impact of fake news and manipulated content. Remember, combating misinformation isn't just about protecting yourself; it's about protecting our collective understanding of reality and fostering a more informed society. Learn to identify and combat misinformation using CNN's guide and become a responsible digital citizen.

Featured Posts
-
 Is Xrp Ripple A Good Investment Below 3
May 02, 2025
Is Xrp Ripple A Good Investment Below 3
May 02, 2025 -
 The End Of Ryujinx Nintendos Influence On Emulator Development
May 02, 2025
The End Of Ryujinx Nintendos Influence On Emulator Development
May 02, 2025 -
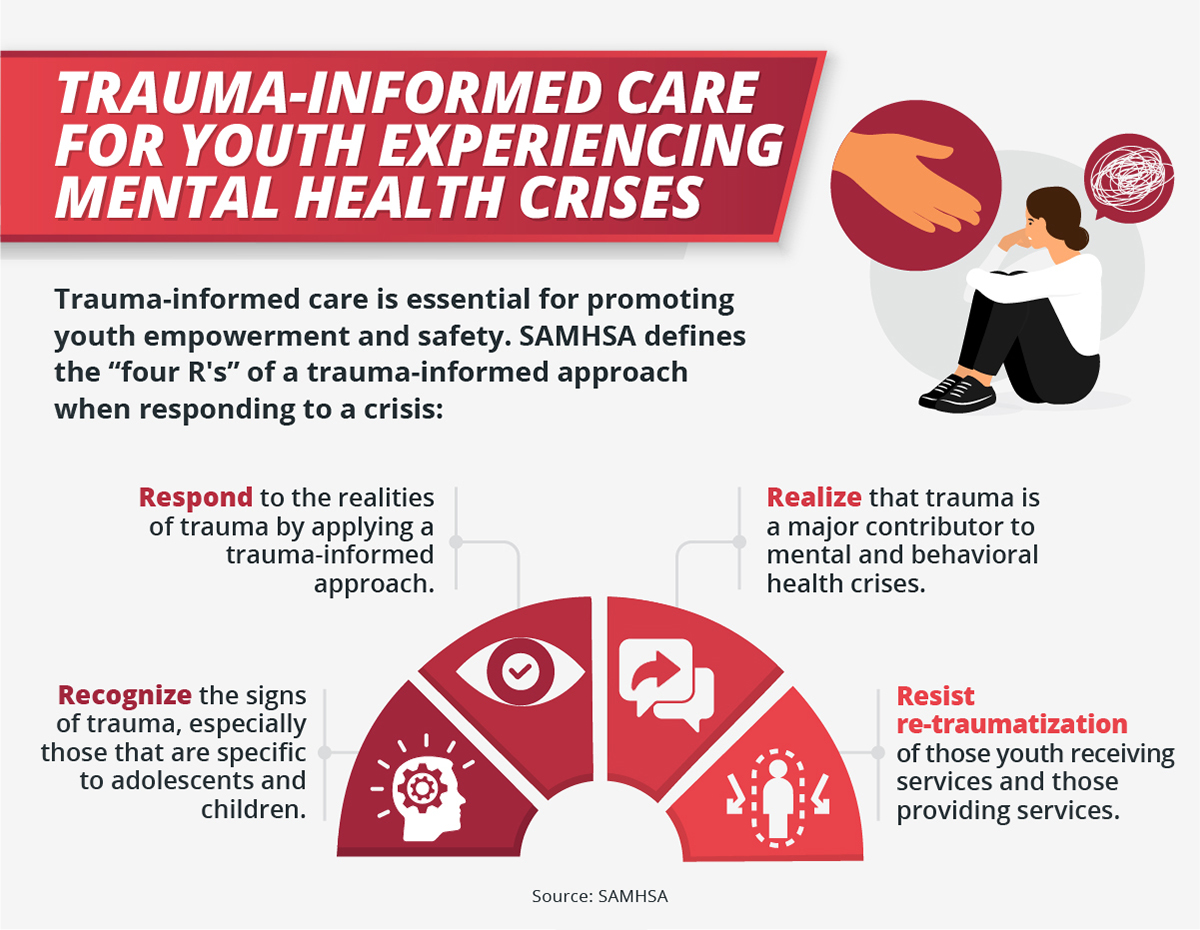 Invest In Childhood Preventing A Generations Mental Health Crisis
May 02, 2025
Invest In Childhood Preventing A Generations Mental Health Crisis
May 02, 2025 -
 Tulsa Day Center Prepares For Winter Clothing Donation Drive
May 02, 2025
Tulsa Day Center Prepares For Winter Clothing Donation Drive
May 02, 2025 -
 Kshmyr Tnaze Bhart Ke Lye Ntyjh Khyz Mdhakrat Ky Rahyn Awr Chylnjz
May 02, 2025
Kshmyr Tnaze Bhart Ke Lye Ntyjh Khyz Mdhakrat Ky Rahyn Awr Chylnjz
May 02, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Gop Candidates North Carolina Supreme Court Appeal What It Means
May 02, 2025
Gop Candidates North Carolina Supreme Court Appeal What It Means
May 02, 2025 -
 Analyzing The 2024 Election Key Insights From Florida And Wisconsin Voter Turnout
May 02, 2025
Analyzing The 2024 Election Key Insights From Florida And Wisconsin Voter Turnout
May 02, 2025 -
 Newsround Viewing Guide Bbc Two Hd Channel
May 02, 2025
Newsround Viewing Guide Bbc Two Hd Channel
May 02, 2025 -
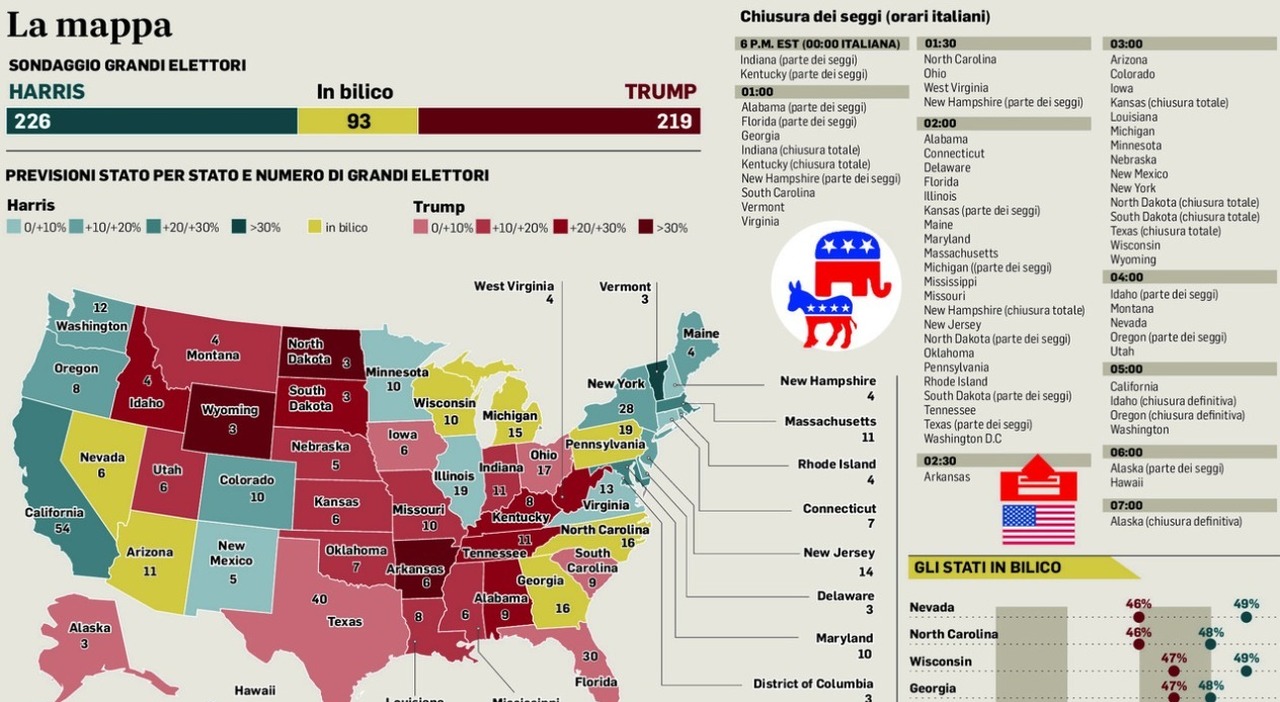 Interpreting The 2024 Election Turnout In Florida And Wisconsin Key Political Insights
May 02, 2025
Interpreting The 2024 Election Turnout In Florida And Wisconsin Key Political Insights
May 02, 2025 -
 What Florida And Wisconsins Voter Turnout Reveals About The Shifting Political Climate
May 02, 2025
What Florida And Wisconsins Voter Turnout Reveals About The Shifting Political Climate
May 02, 2025
