Competition Bureau Takes On Google: A Potential Constitutional Showdown
Table of Contents
The Competition Bureau's Case Against Google
Allegations of Anti-Competitive Behavior
The Competition Bureau alleges that Google has engaged in anti-competitive behavior, leveraging its dominant market position to stifle competition and harm consumers. Their accusations center around Google's practices within the digital advertising market.
- Market Dominance: The Bureau argues Google holds an undue amount of control over online advertising, hindering smaller competitors' ability to gain a foothold.
- Abuse of Power: Specific allegations include manipulating search results to favor Google's own products and services, thereby disadvantaging rival businesses.
- Exclusionary Practices: The Bureau claims Google has used its market power to exclude competitors from accessing essential digital advertising tools and resources.
- Relevant Legislation: The Competition Act of Canada is the primary legislation underpinning the Competition Bureau's case. Specific sections focusing on anti-competitive mergers, abuse of dominant position, and misleading advertising practices are likely to be cited.
Evidence Presented by the Competition Bureau
The Competition Bureau's case rests on a multi-pronged evidentiary approach:
- Market Analysis: Detailed economic studies analyzing Google's market share and the impact of its practices on competition.
- Consumer Complaints: A collection of documented complaints from businesses and consumers alleging unfair treatment and harm due to Google's practices.
- Internal Google Documents: Potentially leaked or obtained internal documents that may reveal Google's strategies and intentions regarding its market dominance.
The Bureau's Goals and Objectives
The Competition Bureau aims to achieve several key objectives through this legal action:
- Increased Competition: Fostering a more competitive digital advertising market by leveling the playing field for smaller players.
- Fairer Market Practices: Ensuring that all businesses, regardless of size, have a fair opportunity to compete.
- Consumer Protection: Protecting consumers from potential harm caused by Google's alleged anti-competitive behavior, such as higher prices or reduced choice.
- Potential Outcomes: If successful, the Competition Bureau could secure significant fines, structural remedies (like forced divestitures), or behavioral remedies (like changes to Google's business practices).
Google's Defense Strategy
Google's Arguments Against the Allegations
Google's defense strategy likely hinges on these arguments:
- Innovation and Consumer Benefit: Google will likely argue that its innovations benefit consumers by providing superior products and services at competitive prices.
- Competitive Market: They might contest the notion of a truly "dominant" market position, highlighting the presence of other significant players in the digital advertising landscape.
- Adherence to Regulations: Google will likely argue that its practices comply with existing regulations and that the Competition Bureau's interpretation of the law is overly broad.
Constitutional Challenges
Google might raise constitutional challenges based on:
- Freedom of Expression: Arguments may be made that regulations restricting Google's search algorithm or advertising practices infringe on its freedom of expression.
- Due Process: Google might contest the fairness of the Competition Bureau's investigation and the procedural aspects of the legal process.
- Property Rights: Arguments could be made about the potential impact on Google’s intellectual property and business model.
Potential Economic Impacts of the Ruling
The outcome of this case will have significant economic consequences:
- Job Impacts: A ruling against Google could lead to job losses within Google's Canadian operations or a slowdown in its growth. Conversely, increased competition might create new jobs in the digital advertising sector.
- Technological Innovation: The outcome may influence the pace of technological innovation in the digital advertising space, potentially accelerating or slowing down depending on the final decision.
- Consumer Prices: The impact on consumer prices is uncertain, with potential for both increases (due to reduced competition) or decreases (due to increased competition and innovation) depending on the outcome.
The Constitutional Implications
Freedom of Expression and Innovation
The case raises complex issues concerning the intersection of antitrust law and freedom of expression. Restricting Google's search algorithm or advertising practices could be perceived as censorship, potentially stifling innovation. Similar issues have been raised in other cases involving major tech companies.
Due Process and Fair Treatment
Ensuring due process and fair treatment for Google throughout the investigation and legal proceedings is paramount. Any procedural irregularities or perceived biases could undermine the legitimacy of the Competition Bureau's actions and potentially impact the final outcome.
Conclusion: The Future of the Competition Bureau and Google – A Constitutional Reckoning?
The "Competition Bureau Takes on Google" case presents a fascinating collision between the need for fair competition and the protection of fundamental constitutional rights. Both sides have strong arguments, and the ultimate outcome could reshape the landscape of digital advertising in Canada and set a precedent for future regulatory actions against tech giants globally. The potential constitutional implications are profound, and the case will undoubtedly shape future discussions on the balance between government regulation and the rights of tech companies.
Stay informed about the developments in this crucial case by following reputable news sources and legal experts specializing in competition law. The implications of the "Competition Bureau Takes on Google" case are far-reaching, and understanding its progress is crucial for anyone interested in the future of digital markets and constitutional law.

Featured Posts
-
 Nvidia Forecasts Growth Despite Economic Headwinds In China
May 30, 2025
Nvidia Forecasts Growth Despite Economic Headwinds In China
May 30, 2025 -
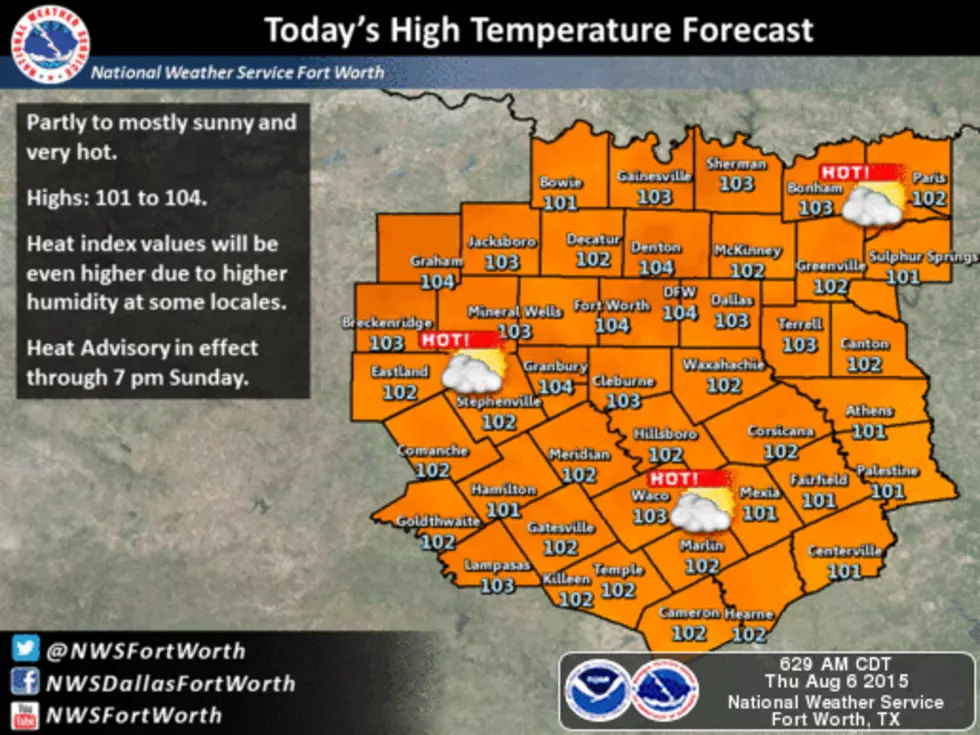 Texas Heat Advisory Prepare For 111 Degree Temperatures
May 30, 2025
Texas Heat Advisory Prepare For 111 Degree Temperatures
May 30, 2025 -
 Taylor Swift Fans Rejoice Ticketmaster Shows Your Place In Line
May 30, 2025
Taylor Swift Fans Rejoice Ticketmaster Shows Your Place In Line
May 30, 2025 -
 Southern California Bioluminescent Waves Peak Seasons And Best Beaches
May 30, 2025
Southern California Bioluminescent Waves Peak Seasons And Best Beaches
May 30, 2025 -
 Mercado Da Bola Al Hilal Busca Contratacao De Bruno Fernandes
May 30, 2025
Mercado Da Bola Al Hilal Busca Contratacao De Bruno Fernandes
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 The Texas Panhandle Wildfire A Year Of Recovery And Rebirth
May 31, 2025
The Texas Panhandle Wildfire A Year Of Recovery And Rebirth
May 31, 2025 -
 Eastern Newfoundland Wildfires A Growing Crisis
May 31, 2025
Eastern Newfoundland Wildfires A Growing Crisis
May 31, 2025 -
 Update Fierce Wildfires In Eastern Manitoba
May 31, 2025
Update Fierce Wildfires In Eastern Manitoba
May 31, 2025 -
 Homes Reduced To Ashes Eastern Newfoundland Battles Devastating Wildfires
May 31, 2025
Homes Reduced To Ashes Eastern Newfoundland Battles Devastating Wildfires
May 31, 2025 -
 Deadly Wildfires Continue To Threaten Eastern Manitoba
May 31, 2025
Deadly Wildfires Continue To Threaten Eastern Manitoba
May 31, 2025
