Conclave Explained: The Process Of Selecting The Next Pope

Table of Contents
The Pre-Conclave Preparations
The period between a Pope's death or resignation and the conclave itself is a time of meticulous preparation and solemn reflection. This interregnum, known as the sede vacante (vacant see), is a crucial period where the Catholic Church is without a visible head. The smooth transition to the next papacy relies heavily on the careful orchestration of various activities by the College of Cardinals.
- The Announcement: The death or resignation of the Pope is officially announced, often accompanied by a period of mourning and prayer within the Vatican and across the globe. This announcement triggers the commencement of the processes leading up to the Papal Conclave.
- Sede Vacante: During the sede vacante, the College of Cardinals assumes the responsibility of governing the Church. Their role is to maintain order, continuity, and ensure the smooth functioning of the Vatican City State until a new Pope is elected. This period is marked by a sense of solemnity and reflection.
- Role of the College of Cardinals: The College of Cardinals, comprised of the highest-ranking clergy in the Catholic Church, plays a central role in preparing for the conclave. They are responsible for organizing logistics, establishing rules for the election process, and ensuring the secrecy and integrity of the conclave.
- Securing the Vatican: The Vatican undergoes rigorous security measures to ensure the safety and privacy of the cardinals participating in the conclave. Access to the Vatican City is restricted, and communication lines are monitored to maintain the confidentiality of the proceedings.
- Consistory (if applicable): Sometimes, a consistory, a formal meeting of the Pope and the cardinals, might be held before the conclave. This can be used to elevate new cardinals to the College, thus influencing the composition of the body that will elect the next Pope.
The Conclave: Entering the Seclusion
The conclave itself is a period of intense deliberation and secrecy. The cardinals participating in the election are confined to a specific location, traditionally the Sistine Chapel in the Vatican Palace, effectively cutting off contact with the outside world.
- Location: The Sistine Chapel is renowned for its historical significance and its suitability as the venue for the conclave. Its grandeur and rich history symbolize the weight of the decision being made within its walls. However, other locations may be used, as long as they ensure the required level of seclusion and security.
- Living Arrangements: During the conclave, cardinals live in simple accommodations within the chosen location. Their comfort is secondary to the solemnity and focus required for the selection process. They are given basic necessities and live in relative austerity.
- Communication Restrictions: Contact with the outside world is strictly prohibited during the conclave. This isolation is intended to ensure that the cardinals are free from external influence and pressure during their deliberations. Cell phones and other communication devices are prohibited.
- Security Measures: Robust security measures are implemented to guarantee the confidentiality of the conclave. Strict protocols control access to the site, while all communication is monitored to prevent leaks of information to the media or outside parties.
- The Papal Master of Ceremonies: The Papal Master of Ceremonies plays a vital role in managing the logistics and ceremonial aspects of the conclave, ensuring the smooth flow of proceedings according to established tradition.
The Scrutiny (Voting Process)
The heart of the conclave lies in the scrutiny, the voting process to elect the next Pope. This is a highly secretive process, meticulously designed to ensure the integrity and fairness of the election.
- Secret Ballot: The cardinals cast their votes using secret ballots. This ensures that each cardinal can vote according to their conscience, free from pressure or influence from others.
- Two-Thirds Majority: A two-thirds majority is required for the election of a new Pope. This high threshold ensures that the chosen candidate receives broad support within the College of Cardinals.
- Vote Counting: The ballots are meticulously counted by appointed officials. The process is carefully monitored to prevent any irregularities or disputes.
- No Two-Thirds Majority: If no candidate receives a two-thirds majority, multiple rounds of voting occur until a clear winner emerges. The process continues until a Pope is elected.
- Fumata Bianca and Fumata Negra: The iconic signals of the conclave—fumata bianca (white smoke) signaling the election of a new Pope, and fumata negra (black smoke) indicating that no consensus has yet been reached—announces the results to the world, creating a moment of intense global anticipation.
After the Election: Announcing the New Pope
Once a candidate achieves the necessary two-thirds majority, the election is officially confirmed, setting in motion a series of events to officially welcome the new Pope.
- Confirmation: The election is confirmed by the College of Cardinals, marking the official end of the conclave.
- Habemus Papam!: The iconic phrase "Habemus Papam!" ("We have a Pope!") is announced to the world, often accompanied by the ringing of bells, signifying the start of a new papacy.
- First Appearance: The newly elected Pope then makes his first public appearance, often from the balcony of St. Peter's Basilica, to greet the faithful and address the world.
- Inauguration Ceremonies: Subsequent inauguration ceremonies mark the beginning of the new Pope's official ministry and his formal acceptance of the papacy.
- New Papal Reign: The start of the new papal reign brings with it significant implications for the Catholic Church and the world, setting the course for the future direction and teachings of the faith.
Conclusion
The Papal Conclave is a complex and fascinating process with deep historical roots and significant implications for the Catholic Church globally. Understanding its stages—from the pre-conclave preparations and the rigorous voting process to the announcement of the new Pope—provides valuable insight into the inner workings of the Vatican. By learning more about the Papal Conclave and its significance, you gain a deeper appreciation for this pivotal event in Catholic history. To further your understanding of this intricate selection process, continue exploring various resources on the Papal Conclave and its rich history.

Featured Posts
-
 Section 230 And Banned Chemicals A Judges Ruling On E Bay Listings
May 07, 2025
Section 230 And Banned Chemicals A Judges Ruling On E Bay Listings
May 07, 2025 -
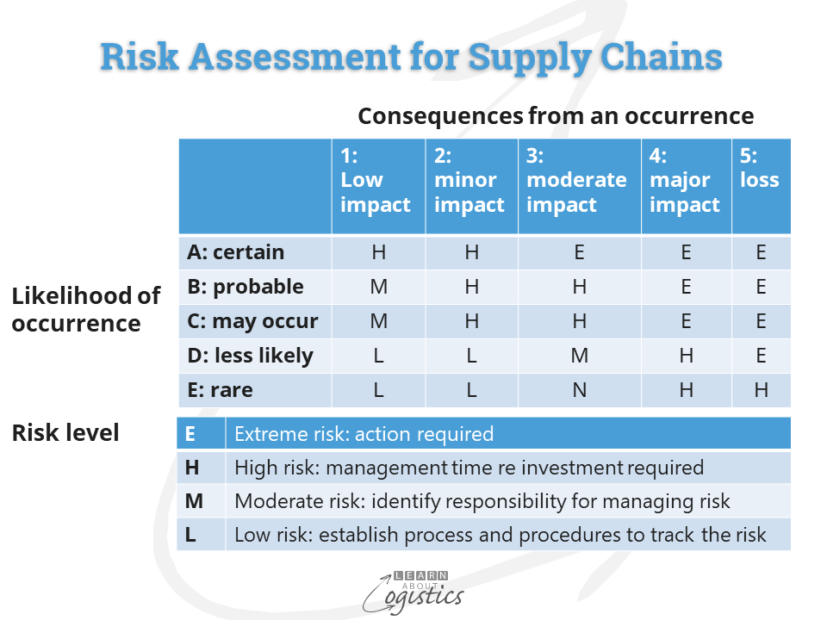 Chinese Plastics Suppliers And The Iran Supply Chain A Risk Assessment
May 07, 2025
Chinese Plastics Suppliers And The Iran Supply Chain A Risk Assessment
May 07, 2025 -
 John Wick 5 Update What Keanu Reeves Said And What It Means
May 07, 2025
John Wick 5 Update What Keanu Reeves Said And What It Means
May 07, 2025 -
 20 Ai
May 07, 2025
20 Ai
May 07, 2025 -
 Nikki Fargas On The Aces Community Impact 2025 Season Outlook And More
May 07, 2025
Nikki Fargas On The Aces Community Impact 2025 Season Outlook And More
May 07, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Saturday Night Live A Pivotal Point In Counting Crows History
May 08, 2025
Saturday Night Live A Pivotal Point In Counting Crows History
May 08, 2025 -
 Performance Geometrique Superieure Des Corneilles Par Rapport Aux Babouins Une Analyse Comportementale
May 08, 2025
Performance Geometrique Superieure Des Corneilles Par Rapport Aux Babouins Une Analyse Comportementale
May 08, 2025 -
 Did Saturday Night Live Make Counting Crows Famous A Look Back
May 08, 2025
Did Saturday Night Live Make Counting Crows Famous A Look Back
May 08, 2025 -
 Capacites Geometriques Inattendues Chez Les Corneilles Depassement Des Performances Des Babouins
May 08, 2025
Capacites Geometriques Inattendues Chez Les Corneilles Depassement Des Performances Des Babouins
May 08, 2025 -
 The Night Counting Crows Changed Their Snl Performance And Its Legacy
May 08, 2025
The Night Counting Crows Changed Their Snl Performance And Its Legacy
May 08, 2025
