Creatine 101: Your Guide To Understanding And Using Creatine
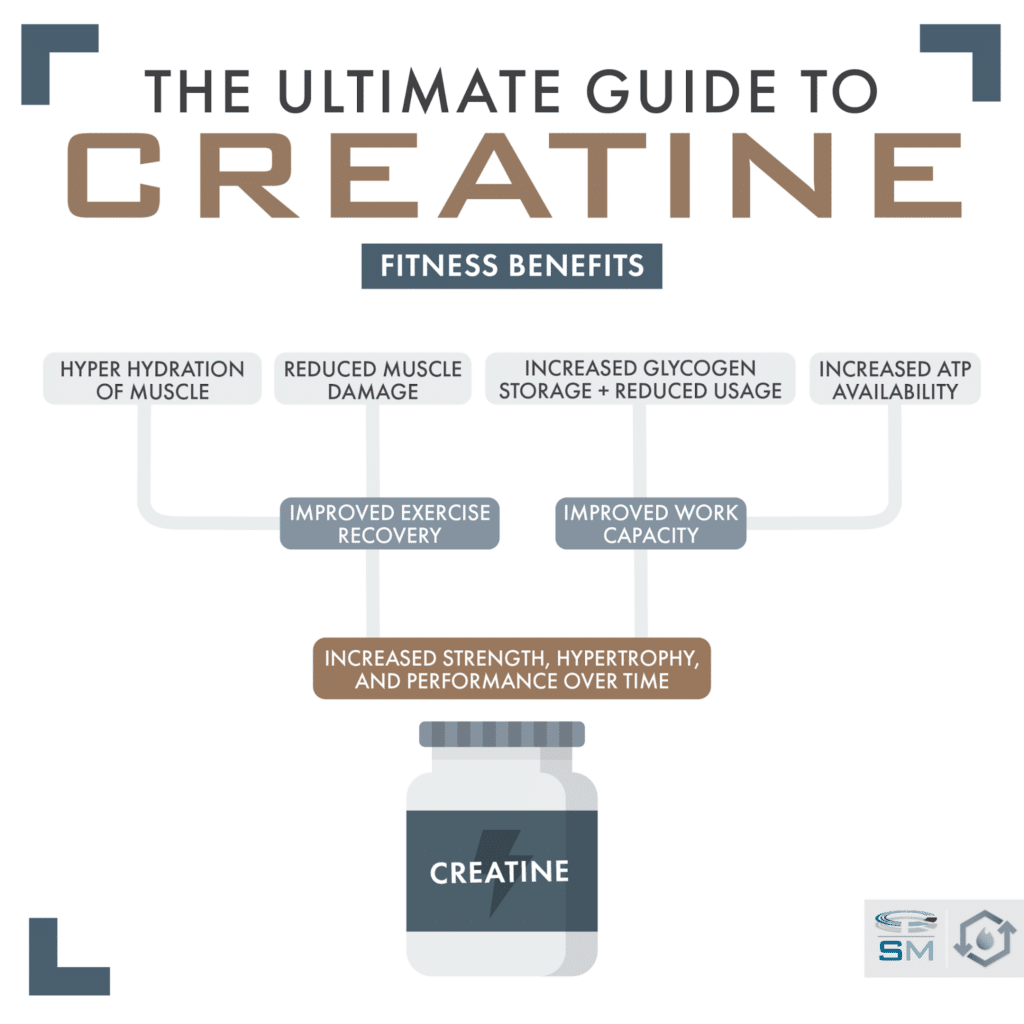
Table of Contents
What is Creatine and How Does it Work?
Creatine is a naturally occurring compound primarily found in skeletal muscle. It plays a crucial role in energy production within your muscles, specifically in the resynthesis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP is the primary energy source for muscle contractions, allowing you to perform high-intensity exercises like weightlifting or sprinting. When your ATP levels deplete, your performance suffers. Creatine helps replenish ATP stores quickly, leading to improved performance and increased strength.
While several types of creatine exist, including creatine HCL and creatine ethyl ester, creatine monohydrate remains the most researched and widely recommended form. Its effectiveness, safety, and affordability make it the gold standard among creatine supplements.
- Creatine enhances high-intensity exercise performance: By boosting ATP levels, creatine enables you to perform more repetitions and sets with heavier weights.
- Creatine increases muscle mass and strength: The improved energy production contributes to greater muscle growth and overall strength gains.
- Creatine improves overall athletic performance: This translates to better results in various sports and fitness activities requiring bursts of power and strength.
The Benefits of Creatine Supplementation
Numerous studies support the numerous benefits of creatine supplementation. Beyond the increased strength and power output, creatine offers several advantages for athletes and fitness enthusiasts alike.
- Increased strength and power output: Studies consistently demonstrate significant improvements in strength and power following creatine supplementation, allowing for heavier lifts and more explosive movements.
- Enhanced muscle growth and hypertrophy: Creatine promotes muscle protein synthesis, leading to increased muscle size and hypertrophy. This is partly due to its ability to increase cell volumization, leading to greater muscle protein synthesis.
- Improved recovery time between workouts: By speeding up ATP replenishment, creatine helps reduce muscle fatigue and shorten the recovery time between training sessions. This allows for more frequent and intense workouts.
- Potential cognitive benefits: Although more research is needed, some studies suggest creatine may improve cognitive functions, such as memory and reasoning, particularly in individuals with cognitive impairments.
How to Use Creatine Effectively: Dosage and Cycling
To maximize the benefits of creatine, a structured approach to dosing and cycling is recommended. This typically involves a loading phase followed by a maintenance phase.
- Loading Phase: During the loading phase, you consume a higher dose of creatine monohydrate (typically 20 grams per day) for 5-7 days. This rapidly saturates your muscles with creatine, leading to quicker results.
- Maintenance Phase: After the loading phase, you switch to a lower, maintenance dose (3-5 grams per day). This ensures your muscles maintain optimal creatine levels. You can continue the maintenance phase indefinitely.
- Consistent use is key for optimal results: Skipping doses can negate the effects of the creatine loading phase, reducing the benefits. Consistency is crucial for maintaining elevated creatine stores in your muscles.
- Drink plenty of water: Creatine draws water into your muscle cells. Ensure adequate hydration (at least 2-3 liters of water per day) to prevent dehydration and potential side effects like muscle cramps.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
While generally safe, creatine supplementation can cause some side effects, mostly mild and temporary.
- Water retention (weight gain): Creatine draws water into your muscle cells, leading to a temporary increase in body weight. This is not actual fat gain but water retention.
- Stomach cramps or bloating: These are relatively uncommon but can occur, especially with higher dosages or poor hydration.
- Muscle cramps (rare): While rare, muscle cramps can occur, often due to inadequate hydration.
- Consult your doctor before use, especially if you have kidney problems: While creatine is generally considered safe for healthy individuals, those with pre-existing kidney conditions should consult their doctor before using creatine supplements.
Conclusion
Creatine monohydrate is a safe and effective supplement that can significantly enhance strength, muscle growth, and athletic performance. By following a proper loading and maintenance phase, along with consistent intake and adequate hydration, you can maximize the benefits of creatine supplementation. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
Ready to experience the power of creatine? Learn more about finding the best creatine supplement for your needs and start your journey to enhanced strength and muscle growth today! Remember to always prioritize safe and effective creatine usage.

Featured Posts
-
 Parental Attitudes Toward College Costs A Survey Report
May 17, 2025
Parental Attitudes Toward College Costs A Survey Report
May 17, 2025 -
 Ubers Acquisition Of Foodpanda In Taiwan Blocked By Regulators
May 17, 2025
Ubers Acquisition Of Foodpanda In Taiwan Blocked By Regulators
May 17, 2025 -
 Plei Of Nba 2024 Imerominies Agonon Kai Analysi Zeygarion
May 17, 2025
Plei Of Nba 2024 Imerominies Agonon Kai Analysi Zeygarion
May 17, 2025 -
 Trump Tariffs And Rising Phone Battery Prices A Costly Upgrade
May 17, 2025
Trump Tariffs And Rising Phone Battery Prices A Costly Upgrade
May 17, 2025 -
 Sigue El Partido Venezia Napoles Online
May 17, 2025
Sigue El Partido Venezia Napoles Online
May 17, 2025
