ECB Report: Post-Pandemic Fiscal Policies Contribute To Inflation
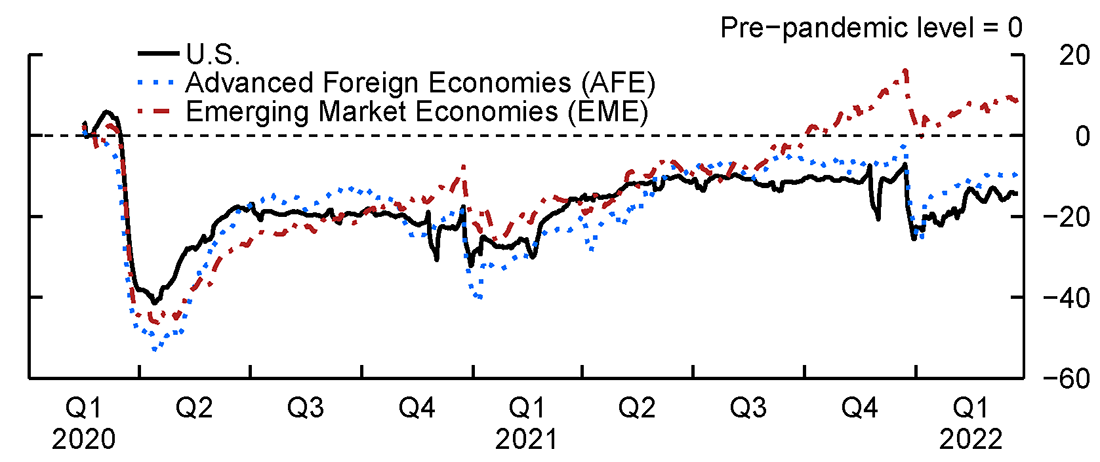
Table of Contents
The ECB Report's Key Findings on Fiscal Stimulus and Inflation
The ECB report directly links the surge in inflation across the Eurozone to the substantial fiscal stimulus packages implemented in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. The report concludes that while these measures were necessary to mitigate the immediate economic fallout, their scale and duration inadvertently contributed to inflationary pressures.
- Increased Aggregate Demand: The massive injection of government funds into the economy significantly boosted aggregate demand, outpacing the capacity of supply to meet this increased demand.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Fiscal policies, while intended to support businesses, may have inadvertently exacerbated pre-existing supply chain vulnerabilities, leading to shortages and higher prices for goods and services. The report highlights the impact of these disruptions on energy prices and the broader inflationary picture.
- Wage Growth: The report also notes a correlation between increased government support and subsequent wage growth, further contributing to inflationary pressures.
The report cites data showing Eurozone inflation reaching X% in [Month, Year], significantly exceeding the ECB's target of 2%. GDP growth figures, while initially strong due to the fiscal stimulus, are now showing signs of slowing due to the impact of inflation on consumer spending and business investment.
Analysis of Specific Fiscal Measures and their Inflationary Effects
The ECB's analysis delves into the specific mechanisms through which various fiscal measures contributed to inflation.
Increased Government Spending
Increased government spending on programs like unemployment benefits and business support schemes injected vast sums of money into the economy. This boosted aggregate demand, pushing prices upward, especially in sectors with limited production capacity. For example, the increased demand for certain goods and services led to shortages and subsequently, price hikes.
Supply Chain Bottlenecks and Fiscal Policy
The report suggests that while fiscal policies aimed to alleviate the economic hardships caused by the pandemic, they might have unintentionally worsened existing supply chain issues. The increased demand fueled by government spending further strained already fragile supply chains, leading to increased transportation costs and higher prices for consumers. Examples include delays in shipping and increased costs for raw materials.
The Role of Monetary Policy in Responding to Inflation
The ECB's response to rising inflation has involved raising interest rates and gradually unwinding its quantitative easing program. These monetary policy adjustments aim to cool down the economy and curb inflation, but they also risk slowing economic growth and potentially increasing unemployment. The interplay between fiscal and monetary policy is complex and crucial in managing the current inflationary environment.
Alternative Perspectives and Counterarguments
It's important to acknowledge that not all economists agree on the extent to which post-pandemic fiscal policies contributed to inflation. Some argue that other factors, such as global supply chain disruptions, the war in Ukraine, and rising energy prices, played a more significant role.
These alternative explanations highlight the complexity of inflation and the difficulty in isolating the impact of any single factor. Furthermore, the ECB report's methodology and data limitations should also be considered, as any economic analysis involves inherent uncertainties and potential biases. However, the report's findings present a compelling case for the significant role of fiscal policy in driving inflation.
Future Outlook and Policy Recommendations
The ECB forecasts that inflation will remain elevated in the near term, though the rate of increase is expected to slow gradually. The report suggests that a careful unwinding of fiscal stimulus, combined with continued adjustments to monetary policy, is crucial to navigate the current economic situation.
The ECB recommends a gradual reduction in government spending and a continued focus on structural reforms to enhance the productive capacity of the Eurozone economy. The long-term consequences of current fiscal and monetary policies are uncertain, but careful management is essential to avoid prolonged inflationary pressures or a severe economic downturn.
Conclusion
The ECB report clearly indicates that post-pandemic fiscal policies have significantly contributed to the current inflationary environment in the Eurozone. The analysis of specific measures, coupled with the acknowledgement of alternative perspectives, underscores the complexity of the situation. The future outlook depends on the careful management of both fiscal and monetary policies. Understanding the impact of post-pandemic fiscal policies on inflation is crucial. Read the full ECB report and stay informed about the evolving economic landscape to better understand the implications for your investments and financial planning. The ongoing debate surrounding the appropriate response to this complex challenge necessitates continued attention to the interplay between post-pandemic fiscal policies and inflation in the Eurozone.

Featured Posts
-
 Minnesota Faces Federal Pressure Over Trumps Transgender Athlete Ban
Apr 29, 2025
Minnesota Faces Federal Pressure Over Trumps Transgender Athlete Ban
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Blue Origins Launch Scrubbed Investigation Into Subsystem Issue Underway
Apr 29, 2025
Blue Origins Launch Scrubbed Investigation Into Subsystem Issue Underway
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Nyt Strands March 3 2025 Complete Hints And Answers Guide
Apr 29, 2025
Nyt Strands March 3 2025 Complete Hints And Answers Guide
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Ramiro Helmeyer And The Pursuit Of Fc Barcelonas Triumph
Apr 29, 2025
Ramiro Helmeyer And The Pursuit Of Fc Barcelonas Triumph
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Kentucky Flood Warning State Of Emergency In Effect
Apr 29, 2025
Kentucky Flood Warning State Of Emergency In Effect
Apr 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Inaccurate Social Media Posts Following Deadly D C Plane Crash
Apr 29, 2025
Inaccurate Social Media Posts Following Deadly D C Plane Crash
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Severe Weather Emergency In Louisville Tornado And Major Flooding Expected
Apr 29, 2025
Severe Weather Emergency In Louisville Tornado And Major Flooding Expected
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Social Media Errors In Reporting D C Midair Collision Pilot Death
Apr 29, 2025
Social Media Errors In Reporting D C Midair Collision Pilot Death
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Louisville State Of Emergency Tornado Damage And Severe Flooding Warnings
Apr 29, 2025
Louisville State Of Emergency Tornado Damage And Severe Flooding Warnings
Apr 29, 2025 -
 False Reports Circulate Online Following D C Plane Crash
Apr 29, 2025
False Reports Circulate Online Following D C Plane Crash
Apr 29, 2025
