Economists Predict Rate Cuts Following Weak Retail Sales Figures
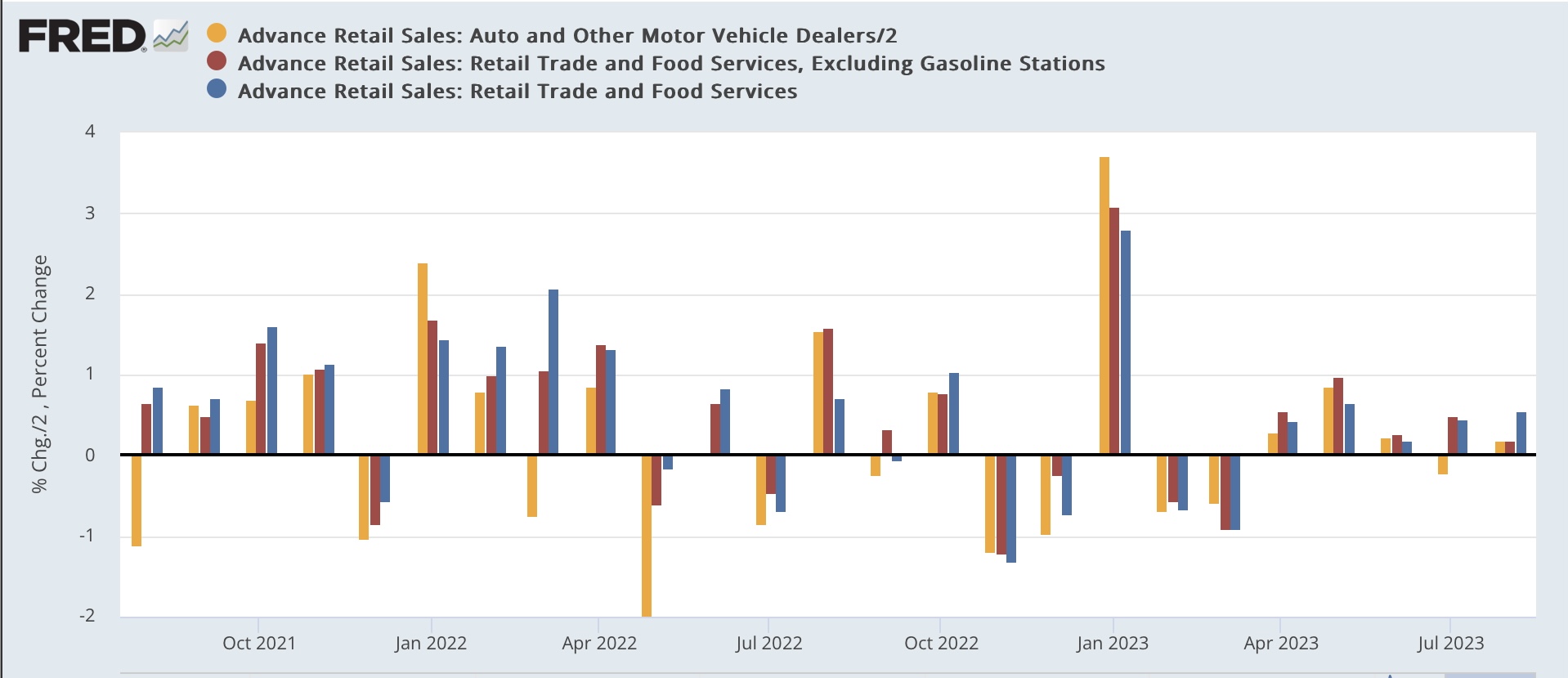
Table of Contents
Analysis of Weak Retail Sales Data
Specifics of the Retail Sales Decline
Official government statistics reveal a concerning drop in retail sales. For example, preliminary data from [insert source, e.g., the Bureau of Economic Analysis] shows a [insert percentage]% decrease in retail sales during [insert timeframe, e.g., July 2024], marking the sharpest decline in [insert timeframe, e.g., the last six months]. This downturn was particularly pronounced in the [insert specific sectors, e.g., automotive and furniture] sectors, indicating a broader trend beyond isolated incidents. Geographical variations are also apparent, with [insert regions, e.g., the Midwest] experiencing a more significant contraction in consumer spending than other regions. This data underscores a significant retail sector slowdown, a worrying sign for the overall health of the economy and a key economic indicator of weakening consumer spending.
Underlying Causes of the Decline
Several factors contribute to this worrying trend of weakened retail sales. These include:
- High Inflation: Persistent inflationary pressures have significantly eroded consumer purchasing power, leaving less disposable income for non-essential spending.
- Increased Interest Rates: Recent interest rate hikes aimed at curbing inflation have increased borrowing costs, making it more expensive for consumers to finance purchases. This directly impacts consumer confidence and willingness to spend.
- High Consumer Debt: Many households already grapple with substantial debt levels, limiting their ability to further increase spending.
- Shifting Consumer Behavior: Changing consumer preferences and priorities, including increased savings and a focus on value, also play a role in the slowdown.
These factors combine to create a challenging environment for retailers and signal a need for policy adjustments. The term "inflationary pressures" is constantly being debated, and its impact on consumer behavior is a key area of research.
Impact on Consumer Sentiment and Spending
The weak retail sales figures have had a demonstrably negative impact on consumer sentiment. The decline in sales creates a vicious cycle: lower sales lead to reduced business activity, potentially resulting in job losses and further dampening spending habits. This economic uncertainty is likely to exacerbate the problem, creating a negative feedback loop that can prolong the economic slowdown. Indices tracking consumer sentiment, such as the [insert relevant index, e.g., Consumer Confidence Index], are closely watched for indicators of future spending patterns.
Economists' Predictions and Rationale for Rate Cuts
Expert Opinions and Forecasts
Several leading economists have voiced their expectations of imminent interest rate cuts. [Insert name and affiliation of economist 1], for example, predicts a [insert percentage]% rate cut by [insert date], citing the weakening retail sales data as a key reason. Similarly, [Insert name and affiliation of economist 2] from [insert institution] believes that monetary policy needs to shift towards easing to stimulate the economy. These expert opinions suggest a broad consensus favoring interest rate cuts as a necessary response to the deteriorating economic outlook. The possibility of quantitative easing or other economic stimulus measures is also being debated.
The Central Bank's Likely Response
The central bank, likely the [insert name of central bank, e.g., Federal Reserve], is expected to respond to these weak figures. Facing the challenge of addressing both inflation and fostering economic growth, a rate cut is seen as a strategic move to inject liquidity into the market and stimulate demand. The rationale hinges on the belief that addressing the slowing economy is paramount, even if it carries a risk of temporarily higher inflation. This approach prioritizes achieving a balance between inflation targeting and supporting healthy economic growth through monetary easing.
Potential Timing and Magnitude of Rate Cuts
Predictions regarding the timing and magnitude of the rate cuts vary. While some economists anticipate a swift and significant cut of [insert percentage]% in the next [insert timeframe, e.g., two months], others project a more gradual approach with smaller cuts over a longer period. The interest rate trajectory will heavily depend on future economic data and the central bank's assessment of the situation. Determining the future interest rates accurately remains a challenge, given the complexity of interconnected economic factors. The overall economic outlook continues to be a central point of discussion among experts.
Alternative Economic Scenarios and Risks
Potential for Further Economic Slowdown
The current situation presents a risk of a more significant economic slowdown. A sustained period of weak retail sales could trigger a broader economic downturn, potentially leading to a recession. The interconnectedness of the global economy means that this slowdown could have significant international repercussions, leading to increased market volatility.
Risks Associated with Rate Cuts
While rate cuts are viewed by many as necessary, they carry potential risks. Easing monetary policy could reignite inflationary pressures, particularly if demand recovers quickly. There is also the risk of creating asset bubbles, as lower interest rates often lead to increased investment in assets such as real estate and stocks. Alternative policy responses, including fiscal policy measures, are also under consideration, but rate cuts appear to be the most likely initial response.
Conclusion: Rate Cuts on the Horizon Following Weak Retail Sales Figures
In summary, weak retail sales figures have triggered widespread predictions of imminent interest rate cuts by economists. This response aims to address the slowing economy and counter the risk of a deeper recession. However, this approach carries inherent risks, including the potential for increased inflation or asset bubbles. Understanding the implications of these predicted rate cuts and their impact on consumers and businesses is crucial. To stay informed about further developments regarding interest rates and their impact on the economy, we encourage you to continue following our updates and analyzing retail sales data to better understand the interest rate implications. By carefully analyzing these factors, one can better position themselves in the evolving financial landscape.

Featured Posts
-
 Live Stream Blue Jays Vs Yankees Mlb Spring Training Free Online Viewing Guide March 7 2025
Apr 28, 2025
Live Stream Blue Jays Vs Yankees Mlb Spring Training Free Online Viewing Guide March 7 2025
Apr 28, 2025 -
 The Countrys New Business Hot Spots Investment Opportunities And Growth Potential
Apr 28, 2025
The Countrys New Business Hot Spots Investment Opportunities And Growth Potential
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Yukon Politicians Cite Contempt Over Mine Managers Evasive Answers
Apr 28, 2025
Yukon Politicians Cite Contempt Over Mine Managers Evasive Answers
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Chinas Tariff Exemptions Some Us Goods Get A Break
Apr 28, 2025
Chinas Tariff Exemptions Some Us Goods Get A Break
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Virginia Giuffres Passing Impact On Prince Andrew Case And Epstein Legacy
Apr 28, 2025
Virginia Giuffres Passing Impact On Prince Andrew Case And Epstein Legacy
Apr 28, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Updated Red Sox Lineup Casas Moved Down Outfielder Returns From Injury
Apr 28, 2025
Updated Red Sox Lineup Casas Moved Down Outfielder Returns From Injury
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Red Sox Starting Lineup Casas Position Shift Outfielders Comeback
Apr 28, 2025
Red Sox Starting Lineup Casas Position Shift Outfielders Comeback
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Red Sox Lineup Shakeup Casas Demoted Struggling Outfielder Returns
Apr 28, 2025
Red Sox Lineup Shakeup Casas Demoted Struggling Outfielder Returns
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Jarren Duran 2 0 This Red Sox Outfielders Potential For A Breakout Season
Apr 28, 2025
Jarren Duran 2 0 This Red Sox Outfielders Potential For A Breakout Season
Apr 28, 2025 -
 The Curse Is Broken Orioles Announcer And The 160 Game Hit Streak
Apr 28, 2025
The Curse Is Broken Orioles Announcer And The 160 Game Hit Streak
Apr 28, 2025
