Global Forest Destruction: Wildfires Contribute To Unprecedented Losses
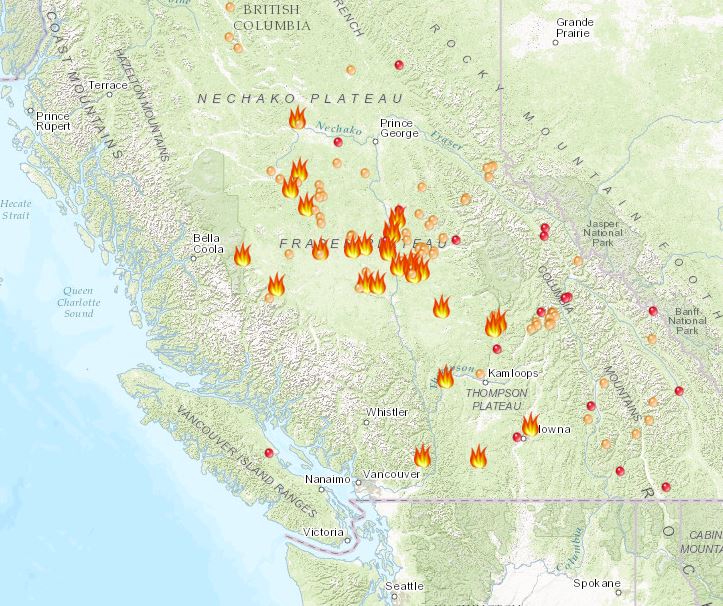
Table of Contents
The Growing Threat of Wildfires
The frequency and intensity of wildfires are escalating at an alarming rate, posing a significant threat to global forests. This increase is largely driven by climate change and unsustainable human activities.
H3: Climate Change's Role in Increased Wildfire Frequency and Intensity
Rising global temperatures, prolonged droughts, and shifts in weather patterns are creating ideal conditions for wildfires to ignite and spread rapidly. Longer and hotter summers, combined with reduced rainfall, dry out vegetation, transforming forests into tinderboxes.
- Increased wildfire season length: Many regions are experiencing significantly longer wildfire seasons, extending the period of risk.
- Higher temperatures: Higher ambient temperatures increase the flammability of vegetation.
- Extreme weather events: More frequent and intense heatwaves, droughts, and lightning strikes contribute to wildfire ignition and spread.
- Examples: The Amazon rainforest, Australia's bushfires, and the western United States have all experienced record-breaking wildfires in recent years, directly linked to climate change. For instance, the 2019-2020 Australian bushfires burned an estimated 18.6 million hectares, releasing an immense amount of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
H3: Human Activities Contributing to Wildfire Risk
Human activities significantly exacerbate wildfire risk. Deforestation, unsustainable land management practices, and accidental ignitions create a dangerous combination that fuels these devastating events.
- Deforestation: Clearing forests for agriculture, logging, and urban development removes natural firebreaks and creates continuous fuel loads.
- Poor forest management: Lack of controlled burns and inadequate forest thinning can lead to the accumulation of dry underbrush, increasing wildfire intensity.
- Accidental ignitions: Power lines, discarded cigarettes, and unattended campfires are common causes of wildfires.
- Data: Studies consistently show a strong correlation between human population density near forested areas and the incidence of wildfires.
The Devastating Impact of Wildfires on Forest Ecosystems
The consequences of wildfires extend far beyond the immediate destruction of trees. These events have profound and long-lasting impacts on forest ecosystems, biodiversity, and the global climate.
H3: Loss of Biodiversity and Habitat Destruction
Wildfires decimate habitats, pushing numerous plant and animal species towards extinction. The sudden loss of food sources and shelter disrupts ecological balance, creating cascading effects throughout the ecosystem.
- Endangered species: Many endangered species, such as the koala in Australia and various bird species in the Amazon, are particularly vulnerable to wildfires.
- Habitat fragmentation: Wildfires create fragmented habitats, isolating populations and reducing genetic diversity.
- Loss of forest cover: The destruction of forest cover leads to a decrease in biodiversity and ecosystem services.
H3: Soil Degradation and Erosion
Wildfires severely damage soil structure, making it vulnerable to erosion. The loss of vegetation cover exposes the soil to wind and rain, leading to nutrient depletion and reduced soil fertility.
- Loss of topsoil: Wildfires can remove the topsoil layer, which is rich in organic matter and essential nutrients.
- Increased runoff: Loss of vegetation increases water runoff, leading to soil erosion and flooding.
- Reduced water infiltration: Damaged soil structure reduces its ability to absorb water, leading to droughts.
H3: Impact on Carbon Sequestration and Climate Change
Wildfires release massive amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere, significantly contributing to climate change. This further exacerbates the risk of future wildfires, creating a dangerous feedback loop.
- Carbon emissions: Large wildfires release millions of tons of CO2, methane, and other greenhouse gases.
- Reduced carbon sequestration: The destruction of forests reduces the planet's capacity to absorb atmospheric CO2.
- Climate change impact: The increased CO2 emissions contribute to global warming, creating a vicious cycle of escalating wildfire risks.
Combating Global Forest Destruction: Mitigation and Prevention Strategies
Addressing global forest destruction requires a multi-pronged approach that integrates improved forest management, climate change mitigation, and international cooperation.
H3: Improved Forest Management Practices
Sustainable forestry practices are crucial in mitigating wildfire risk. This involves careful planning, controlled burns (prescribed fires), and the implementation of early detection and suppression systems.
- Sustainable logging: Responsible logging practices minimize forest fragmentation and maintain healthy forest ecosystems.
- Prescribed burns: Controlled burns reduce the accumulation of dry underbrush, minimizing the risk of large, intense wildfires.
- Early detection systems: Advanced technologies, such as satellite monitoring and remote sensing, enable early detection of wildfires, allowing for faster response times.
H3: Addressing Climate Change
Reducing greenhouse gas emissions is paramount to mitigating climate change and reducing wildfire risk. This requires global efforts to transition to renewable energy sources and implement sustainable practices.
- Renewable energy: Transitioning to renewable energy sources like solar and wind power reduces carbon emissions.
- Sustainable transportation: Promoting public transportation, cycling, and walking reduces reliance on fossil fuels.
- Energy efficiency: Improving energy efficiency in buildings and industries minimizes energy consumption and carbon emissions.
H3: International Cooperation and Policy
International collaboration and strong environmental policies are essential for effective forest conservation and wildfire prevention. This involves sharing best practices, coordinating efforts, and enforcing regulations.
- International agreements: International treaties and agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, play a crucial role in coordinating global efforts to address climate change and protect forests.
- National policies: Strong national policies are needed to regulate deforestation, promote sustainable forestry, and enforce fire prevention measures.
- Community engagement: Involving local communities in forest management and fire prevention efforts is essential for success.
Conclusion
Global forest destruction caused by wildfires is a grave threat to our planet's ecosystems and climate. Climate change and unsustainable human activities are the primary drivers of this devastating trend. The consequences include significant biodiversity loss, soil degradation, increased carbon emissions, and exacerbated climate change. Combating this requires a concerted global effort that focuses on improving forest management practices, addressing climate change through emissions reduction, and strengthening international cooperation. Learn more about the impact of wildfires on global forest destruction and take action today! Support organizations working to protect forests and advocate for policies that prioritize sustainable forestry and climate change mitigation. Together, we can help prevent further global forest destruction and preserve these vital ecosystems for future generations.

Featured Posts
-
 Reporte Del Coe Niveles De Alerta En Provincias De La Republica Dominicana
May 23, 2025
Reporte Del Coe Niveles De Alerta En Provincias De La Republica Dominicana
May 23, 2025 -
 Metallica Dublin Aviva Stadium Weekend 2026
May 23, 2025
Metallica Dublin Aviva Stadium Weekend 2026
May 23, 2025 -
 Concern Grows Sheinelle Jones Absence From The Today Show Prompts Colleague Statements
May 23, 2025
Concern Grows Sheinelle Jones Absence From The Today Show Prompts Colleague Statements
May 23, 2025 -
 Jasprit Bumrah Top Ranked Test Bowler In Icc Rankings
May 23, 2025
Jasprit Bumrah Top Ranked Test Bowler In Icc Rankings
May 23, 2025 -
 Analysis Of Egan Bernals Recovery Following A Severe Bicycle Crash
May 23, 2025
Analysis Of Egan Bernals Recovery Following A Severe Bicycle Crash
May 23, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Neal Mc Donough Would Damien Darhk Beat Superman Exclusive Interview
May 23, 2025
Neal Mc Donough Would Damien Darhk Beat Superman Exclusive Interview
May 23, 2025 -
 The Last Rodeo Neal Mc Donough Faces The Danger Of Pro Bull Riding
May 23, 2025
The Last Rodeo Neal Mc Donough Faces The Danger Of Pro Bull Riding
May 23, 2025 -
 Celebrity Sighting Neal Mc Donough At Acero Boards And Bottles Boise
May 23, 2025
Celebrity Sighting Neal Mc Donough At Acero Boards And Bottles Boise
May 23, 2025 -
 Neal Mc Donough Visits Boises Acero Boards And Bottles
May 23, 2025
Neal Mc Donough Visits Boises Acero Boards And Bottles
May 23, 2025 -
 Dallas Chef Tiffany Derrys Master Chef Judging Return
May 23, 2025
Dallas Chef Tiffany Derrys Master Chef Judging Return
May 23, 2025
