India's Solar Industry: Navigating The Fallout From Trump's Southeast Asia Tariffs
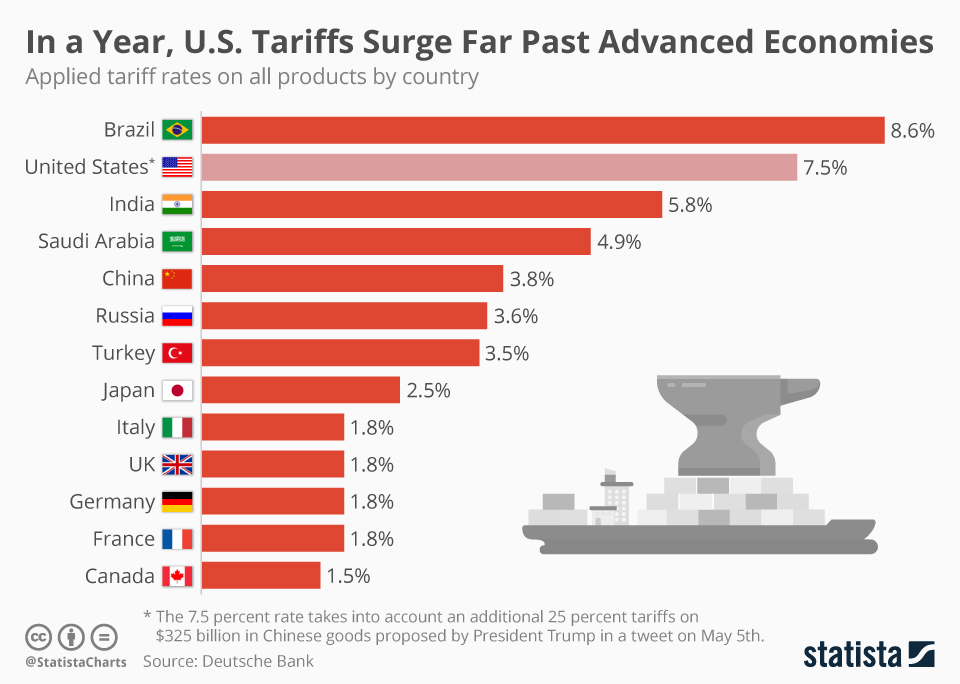
Table of Contents
The Impact of Southeast Asia Tariffs on Solar Panel Prices in India
The imposition of tariffs on solar panels from Southeast Asia, a major source of supply for India, has directly increased the cost of solar energy projects. This surge in solar panel prices India has had several knock-on effects:
-
Increased import costs: Higher import duties on solar modules from Southeast Asia translate to significantly higher project costs for developers, making solar power less competitive compared to traditional energy sources.
-
Supply chain disruptions: The tariffs have caused delays in project implementation due to reduced availability and increased lead times for solar panels. This uncertainty impacts project timelines and overall project feasibility.
-
Price volatility and market uncertainty: The fluctuating prices of solar panels have created a volatile market, making it challenging for investors to accurately assess risks and plan long-term investments in solar energy. This uncertainty discourages investment and slows down the growth of the sector.
-
Differential impact on panel types: The tariff rates have varied across different types of solar panels, disproportionately affecting certain segments of the market and impacting the competitiveness of various project designs.
-
Case studies of affected projects: Several large-scale solar projects across India have reported significant cost overruns and delays due to the increased prices and supply chain disruptions stemming from these tariffs. This underscores the real-world impact of these trade policies on the growth of the Indian solar sector. Specific examples of such projects highlight the severity of this issue.
Strategies for Mitigating the Impact of Tariffs
To counter the negative effects of the Southeast Asia tariffs, India needs to implement a multi-pronged approach focusing on both short-term mitigation and long-term strategic planning. These strategies include:
-
Boosting domestic solar manufacturing: Government initiatives promoting domestic solar manufacturing are crucial. Policies like production-linked incentives (PLIs), streamlined approvals, and access to capital are vital to reduce dependence on imports and create a robust domestic solar industry.
-
Diversifying import sources: India should explore alternative suppliers from countries not affected by the tariffs. This diversification reduces reliance on any single region and creates a more resilient supply chain for the Indian solar power sector.
-
Negotiating better terms with suppliers: Active engagement with existing suppliers to negotiate better prices and payment terms can help to alleviate some of the pressure caused by the tariffs. This requires a proactive and strategic approach by the Indian government and the industry.
-
Government policy interventions: Targeted government support for solar, such as subsidies, tax breaks, and streamlined regulatory processes, can lessen the financial burden on solar developers and boost the competitiveness of solar power in the Indian market.
-
Investment in R&D: Investing in research and development to improve the efficiency of solar panels and reduce the reliance on imports is a long-term strategy to achieve greater energy independence and lower costs. This will help India become a leader in renewable energy technologies.
The Long-Term Outlook for India's Solar Energy Ambitions
Despite the challenges presented by the tariffs, India's commitment to achieving its ambitious renewable energy targets remains strong. The long-term outlook for India's solar energy sector remains positive, but requires strategic adjustments.
-
Renewable energy targets in light of tariffs: India's renewable energy targets will need to be reassessed and potentially adjusted to account for the current economic and geopolitical challenges. A careful balance needs to be struck between ambition and achievable goals.
-
Energy independence and climate goals: Solar power plays a critical role in achieving India's energy independence and reducing its carbon footprint. Continued focus on solar energy is crucial for meeting its climate commitments.
-
Growth in other renewable energy sectors: Diversification into other renewable energy sources, such as wind and hydro, can reduce over-reliance on solar and enhance overall energy security.
-
Geopolitical implications of reliance: The tariffs highlight the risks associated with relying heavily on a single region for critical technologies. Strategic partnerships and diversified sourcing are vital to reduce geopolitical vulnerabilities.
-
Long-term projections for solar panel costs: Although current costs are elevated, long-term projections suggest that solar panel prices will continue to decline, eventually making solar power even more competitive.
The Role of Government Policy
The Indian government has a critical role to play in shaping the future of the India solar industry. Effective policy interventions are essential:
-
Analysis of current policies: A thorough review of current Indian solar policies is necessary to assess their effectiveness in addressing the challenges posed by the tariffs.
-
Evaluation of policy effectiveness: Careful evaluation of the impact of existing policies – such as subsidies, tax incentives, and streamlined approval processes – will inform future policy decisions.
-
Recommendations for future policies: Recommendations for new policies and adjustments to existing ones should focus on supporting domestic manufacturing, diversifying supply chains, and creating a stable and attractive investment climate for the solar sector. This will require a collaborative effort between the government and private sector stakeholders.
Conclusion
The fallout from Trump's Southeast Asia tariffs has presented significant headwinds for India's ambitious solar energy plans. However, by strategically focusing on domestic manufacturing, diversifying import sources, and enacting supportive government policies, India can navigate these challenges and maintain its momentum towards a sustainable energy future. The long-term outlook for the India solar industry remains optimistic, but proactive measures are crucial to mitigate the current disruptions and maintain the trajectory of achieving India's ambitious renewable energy goals. Further research into mitigating the effects of global trade policies on the Indian solar industry is vital for its continued growth and the country's energy security. Stay informed about the latest developments and adapt your strategies accordingly.

Featured Posts
-
 Augsburgs Trainer Rauswurf Kommentar Zur Aktuellen Situation
May 30, 2025
Augsburgs Trainer Rauswurf Kommentar Zur Aktuellen Situation
May 30, 2025 -
 Jones Vs Aspinall Six Months Preparation Requested By Jones
May 30, 2025
Jones Vs Aspinall Six Months Preparation Requested By Jones
May 30, 2025 -
 Illegal Vehicle Registrations Maryland Residents Costing Virginia Millions
May 30, 2025
Illegal Vehicle Registrations Maryland Residents Costing Virginia Millions
May 30, 2025 -
 Gorillaz Full Album Shows In London The Ultimate Ticket Buying Guide
May 30, 2025
Gorillaz Full Album Shows In London The Ultimate Ticket Buying Guide
May 30, 2025 -
 Pasxalines Tileoptikes Metadoseis 2024 Odigos Programmatos E Thessalia Gr
May 30, 2025
Pasxalines Tileoptikes Metadoseis 2024 Odigos Programmatos E Thessalia Gr
May 30, 2025
