Investigation Into Toxic Chemical Persistence In Buildings After Ohio Train Derailment
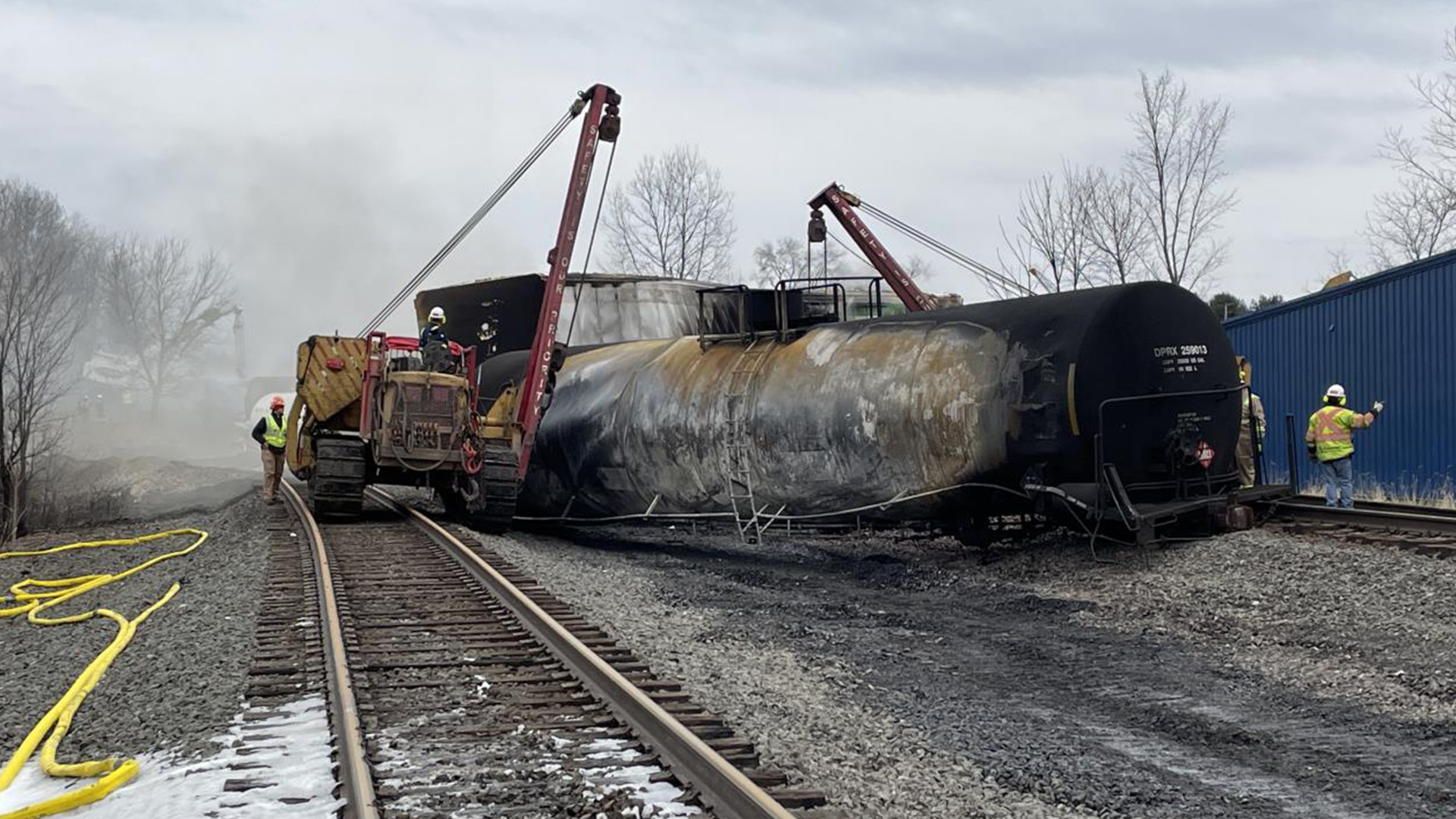

Table of Contents
Types of Toxic Chemicals Released and Their Persistence
The Ohio train derailment involved the release of several hazardous materials, most notably vinyl chloride and butyl acrylate. Understanding the properties of these chemicals is crucial to assessing the extent and duration of their persistence in buildings.
-
Vinyl Chloride: A colorless gas used in the production of PVC, vinyl chloride is highly volatile and can readily evaporate into the air. However, it can also be absorbed into porous materials like drywall and insulation, leading to long-term off-gassing and potential exposure. Its persistence is further complicated by its ability to react with other substances, forming new, potentially harmful compounds.
-
Butyl Acrylate: A colorless liquid used in paints and adhesives, butyl acrylate is less volatile than vinyl chloride but still poses a significant risk due to its potential for adhesion to surfaces and absorption into building materials. Its persistence can be influenced by temperature and humidity.
The following factors contribute to the persistence of these toxic chemicals in buildings:
- Absorption into porous materials: Drywall, wood, insulation, and other porous building materials can act as sponges, absorbing these chemicals and releasing them slowly over time.
- Adhesion to surfaces: Chemicals can adhere to surfaces such as paint, flooring, and furniture, creating a persistent source of contamination.
- Potential for long-term off-gassing: Volatile chemicals like vinyl chloride can continue to off-gas from building materials for months or even years after the initial release.
- Bioaccumulation in building dust: Chemicals can become trapped in building dust, leading to prolonged exposure through inhalation.
Methods for Detecting and Measuring Toxic Chemical Persistence
Accurately detecting and measuring the persistence of toxic chemicals in buildings requires a multifaceted approach utilizing several testing methods. The challenge lies in the variability of contamination levels and the limitations of available technologies.
- Air quality monitoring: Specialized equipment is used to measure the concentration of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in the air, providing an indication of ongoing off-gassing.
- Surface wipe sampling: Surface swabs are analyzed to determine the presence and concentration of chemical residues on various surfaces.
- Material testing: Samples of building materials (drywall, insulation, etc.) are analyzed to determine the extent of chemical penetration and absorption.
- Blood and urine testing: Testing of residents' blood and urine can detect the presence of specific chemicals and assess the level of exposure.
The limitations of these methods include cost, accessibility, and the potential for false negatives or positives, necessitating a combination of approaches for a comprehensive assessment. Both short-term and long-term monitoring are crucial for tracking the persistence and dissipation of these toxic chemicals.
Health Impacts of Long-Term Exposure to Persistent Toxic Chemicals
Exposure to the persistent toxic chemicals released in the Ohio derailment can have a range of serious health consequences, both short-term and long-term.
- Vinyl chloride: Exposure can lead to liver damage, including liver cancer, as well as various circulatory and neurological problems.
- Butyl acrylate: Can cause respiratory irritation, skin irritation, and eye irritation. Long-term exposure might lead to more serious respiratory problems.
Potential health impacts from exposure include:
- Respiratory problems (e.g., asthma, bronchitis)
- Neurological disorders (e.g., headaches, dizziness, cognitive impairment)
- Cancer (e.g., liver cancer, leukemia)
- Reproductive issues (e.g., birth defects)
- Skin irritation and other dermatological problems
Ongoing health monitoring for residents in the affected area is critical to identify and address potential health problems resulting from long-term exposure.
Remediation Strategies for Buildings Contaminated with Persistent Toxic Chemicals
Remediation of buildings contaminated with persistent toxic chemicals is a complex undertaking requiring a tailored approach based on the specific contamination levels and building characteristics.
- Air purification systems: These systems can remove volatile organic compounds from the air.
- Specialized cleaning solutions and techniques: Specialized cleaning products and techniques are needed to remove chemical residues from surfaces.
- Material replacement: In cases of significant contamination, replacement of affected building materials (drywall, carpet, insulation) may be necessary.
- Building demolition: In severe cases, demolition may be the only feasible option to eliminate the risk of ongoing exposure.
The effectiveness and feasibility of each approach are influenced by factors such as the type and concentration of contaminants, the building's age and construction, and the available resources. A comprehensive remediation plan, developed by qualified professionals, is essential for ensuring the safety of occupants.
Regulatory and Legal Aspects of Toxic Chemical Persistence Following Industrial Accidents
The aftermath of industrial accidents like the Ohio train derailment highlights the need for robust regulatory frameworks and legal recourse for affected individuals.
- EPA guidelines and regulations: The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in establishing guidelines and regulations for handling chemical releases and environmental remediation.
- State and local regulations: State and local agencies also have a role in enforcing regulations and providing oversight for remediation efforts.
- Liability and compensation: Legal avenues may exist for affected residents to seek compensation for damages resulting from exposure to toxic chemicals.
- Long-term monitoring requirements: Regulations may require long-term monitoring of affected areas to assess the effectiveness of remediation efforts and ensure ongoing public safety.
Conclusion:
The persistence of toxic chemicals in buildings following the Ohio train derailment presents a significant and ongoing challenge. Thorough investigation into toxic chemical persistence, employing robust detection methods, and implementing effective remediation strategies are crucial to protecting public health and safety. Continued monitoring and research are essential to fully understand the long-term consequences of this disaster. We urge readers to stay informed about the latest developments concerning toxic chemical persistence and to advocate for comprehensive policies to prevent future incidents and mitigate their devastating effects. Learn more about the ongoing efforts to address toxic chemical persistence and its impact on the community.

Featured Posts
-
 Seagrass Restoration Bids Revitalizing Scotlands Coastal Ecosystems
May 04, 2025
Seagrass Restoration Bids Revitalizing Scotlands Coastal Ecosystems
May 04, 2025 -
 Ufc On Espn 67 A Detailed Look At The Sandhagen Vs Figueiredo Fight Results
May 04, 2025
Ufc On Espn 67 A Detailed Look At The Sandhagen Vs Figueiredo Fight Results
May 04, 2025 -
 The Enduring Appeal Of Fleetwood Macs Most Popular Songs
May 04, 2025
The Enduring Appeal Of Fleetwood Macs Most Popular Songs
May 04, 2025 -
 Images Inedites L Emotion D Emmanuel Macron Apres Une Rencontre Avec Des Victimes En Israel
May 04, 2025
Images Inedites L Emotion D Emmanuel Macron Apres Une Rencontre Avec Des Victimes En Israel
May 04, 2025 -
 Predicting The Stanley Cup Winner Analyzing The 2024 Nhl Playoff Bracket
May 04, 2025
Predicting The Stanley Cup Winner Analyzing The 2024 Nhl Playoff Bracket
May 04, 2025
