Is The Rising Federal Debt A Risk To Your Mortgage?
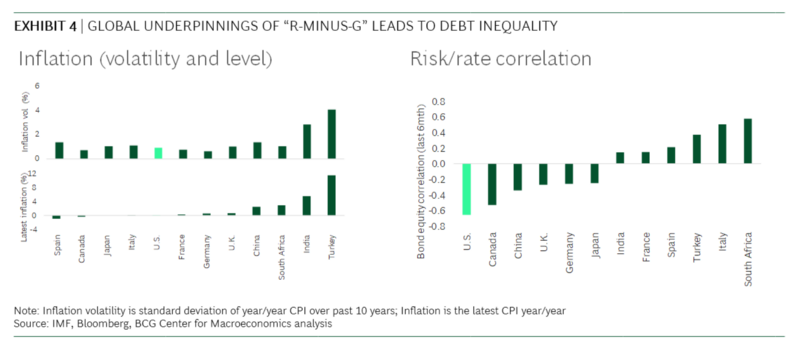
Table of Contents
How Government Debt Influences Interest Rates
The government's borrowing habits significantly influence interest rates. When the federal government borrows heavily to finance its deficits, it increases the demand for loanable funds. This increased demand can drive up interest rates across the board, including mortgage rates. Think of it like this: more borrowers competing for a limited pool of money increases the price of borrowing.
Several factors contribute to this relationship:
- Increased demand for loanable funds: The government's borrowing competes with private sector borrowing for available capital, pushing rates higher.
- Potential inflation due to increased money supply: To finance its debt, the government might increase the money supply, potentially leading to inflation. Higher inflation often prompts the Federal Reserve to raise interest rates to cool down the economy.
- The Federal Reserve's role in managing interest rates: The Federal Reserve (the Fed) uses monetary policy tools, like adjusting the federal funds rate, to influence interest rates. High government debt can complicate the Fed's efforts to maintain price stability and full employment.
- The Fisher effect: This economic theory suggests a direct relationship between inflation and nominal interest rates. Higher expected inflation generally leads to higher nominal interest rates.
The Impact of Inflation on Mortgage Payments
Inflation erodes the purchasing power of money. When prices rise, your money buys less. While your mortgage payment might remain the same in nominal terms, its real value decreases as inflation increases. This indirectly affects your mortgage payments through several channels:
- Rising prices of building materials: If you're planning renovations or are in the construction industry, inflation directly impacts your costs.
- Increased cost of living impacting mortgage affordability: Higher inflation makes everything more expensive, reducing your disposable income and potentially making your mortgage payments a larger burden.
- Potential for higher interest rates to combat inflation: As mentioned, the Fed might raise interest rates to combat inflation, leading to higher mortgage rates for new borrowers and potentially impacting refinancing options for existing homeowners.
Government Policies and Their Effect on the Housing Market
Government policies implemented to manage the rising federal debt can significantly impact the housing market and mortgage availability. Fiscal policy decisions, such as tax increases or spending cuts, can influence economic growth and affect mortgage rates.
Here's how these policies play out:
- Impact of fiscal policy on mortgage rates: Austerity measures (spending cuts) can slow economic growth, potentially lowering inflation and interest rates. Conversely, tax increases can reduce disposable income, impacting consumer spending and potentially depressing the housing market.
- Changes in lending regulations: Government intervention might tighten or loosen lending regulations, influencing the availability and affordability of mortgages.
- Potential effects of economic slowdowns spurred by debt management: Efforts to reduce the national debt might lead to economic slowdowns, resulting in reduced demand for housing and potentially lower home prices. This can create uncertainty in the housing market.
Mitigating the Risks: Strategies for Homeowners
The rising federal debt presents challenges, but homeowners can take proactive steps to mitigate potential risks:
- Locking in fixed-rate mortgages: A fixed-rate mortgage protects you from rising interest rates.
- Building a strong financial foundation: Maintain an emergency fund and manage your debt responsibly to withstand economic shocks.
- Diversifying investments: Don't put all your eggs in one basket. Diversify your investments to reduce risk.
- Regularly monitoring interest rates and market trends: Staying informed allows you to adapt your financial strategy as needed.
- Seeking professional financial advice: Consult a financial advisor for personalized guidance on managing your mortgage and investments in the current economic climate.
Understanding the Rising Federal Debt and Your Mortgage
The rising federal debt presents a complex economic picture with potential implications for interest rates, inflation, and the housing market. Understanding the interplay between government borrowing, monetary policy, and economic conditions is crucial for homeowners. The potential impact on mortgage affordability and long-term financial security should not be underestimated. Managing your financial future in the face of a growing national debt is crucial for securing your mortgage. Stay informed, plan proactively, and seek professional advice to navigate this challenging economic landscape.

Featured Posts
-
 Investing In Ubers Driverless Technology An Etf Analysis
May 19, 2025
Investing In Ubers Driverless Technology An Etf Analysis
May 19, 2025 -
 The Fsu Shooting A Victims Connection To Cold War Espionage
May 19, 2025
The Fsu Shooting A Victims Connection To Cold War Espionage
May 19, 2025 -
 Ufc 313 Alex Pereira Vs Magomed Ankalaev Predictions And Betting Odds
May 19, 2025
Ufc 313 Alex Pereira Vs Magomed Ankalaev Predictions And Betting Odds
May 19, 2025 -
 New Uber Shuttle 5 Rides From United Center For Fans
May 19, 2025
New Uber Shuttle 5 Rides From United Center For Fans
May 19, 2025 -
 Kyriaki Toy Antipasxa Sta Ierosolyma Istoria Ethima Kai Paradoseis
May 19, 2025
Kyriaki Toy Antipasxa Sta Ierosolyma Istoria Ethima Kai Paradoseis
May 19, 2025
