Japan's Bond Market: Steep Yield Curve Poses Economic Challenges
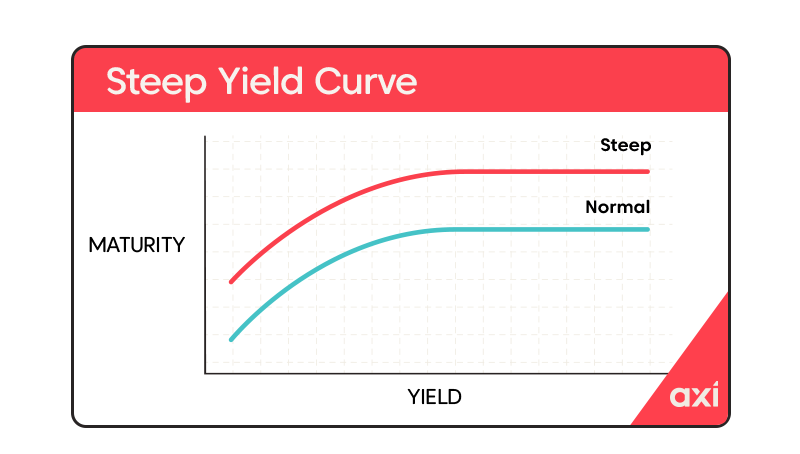
Table of Contents
Understanding Japan's Steep Yield Curve
Yield curves illustrate the relationship between the interest rates (yields) offered on bonds with different maturities. A normal yield curve slopes upward, reflecting the expectation that longer-term investments carry higher risk and thus warrant higher returns. A steep yield curve, however, signifies a substantial difference between short-term and long-term yields, often indicating market expectations of future interest rate increases or economic uncertainty.
In Japan's case, the steepening yield curve is a consequence of several interconnected factors:
-
Rising Inflation Expectations: While still relatively low by global standards, inflation in Japan is creeping upwards, prompting investors to demand higher yields on longer-term bonds to compensate for potential erosion of purchasing power.
-
Bank of Japan (BOJ) Policies: The BOJ's prolonged period of ultra-loose monetary policy, including its Yield Curve Control (YCC) policy, has kept short-term interest rates exceptionally low. The recent shift towards allowing more flexibility in long-term yields, however, has contributed to the steepening curve.
-
Global Interest Rate Hikes: The global trend of rising interest rates, led by central banks like the Federal Reserve, has put upward pressure on Japanese long-term bond yields, widening the gap with short-term rates.
Historically, Japanese bond yields have been exceptionally low. The current spread between short-term and long-term yields represents a significant departure from this historical trend, signaling a shift in market sentiment and expectations. This divergence needs careful monitoring to understand its broader economic implications.
Economic Implications of a Steepening Yield Curve
A steepening yield curve in Japan carries significant economic implications, impacting both government finances and private sector activity:
-
Increased Government Borrowing Costs: Japan's substantial public debt makes it highly sensitive to changes in interest rates. A steep yield curve translates to higher borrowing costs for the government, potentially leading to increased budget deficits and straining public finances.
-
Dampened Private Sector Investment: Higher borrowing costs also impact corporate investment. Businesses may postpone expansion plans or reduce capital expenditures, slowing down economic growth. This reduced investment can have a ripple effect, impacting job creation and overall economic activity.
-
Slower GDP Growth: The combined effects of higher government borrowing costs and reduced private sector investment can lead to slower GDP growth. This poses a considerable challenge for Japan, which has struggled with economic stagnation for an extended period.
-
Inflationary Pressures (Indirect): While seemingly counterintuitive given the BOJ's focus on inflation control, higher borrowing costs can indirectly fuel inflation. Increased production costs for businesses due to higher financing costs might be passed on to consumers in the form of higher prices.
The Bank of Japan's Response and Policy Challenges
The Bank of Japan's monetary policy is at the heart of addressing the steepening yield curve. The BOJ's YCC policy aimed to keep long-term interest rates around zero. However, the recent adjustments to this policy reflect the challenges in balancing inflation control with economic growth.
-
Limitations of YCC: The YCC policy, while initially successful in keeping yields low, has faced increasing strains as market forces push for higher yields. The BOJ's attempts to manage the yield curve have become increasingly difficult and costly.
-
Inflation Control vs. Economic Growth: The BOJ faces a classic policy dilemma: controlling inflation without triggering a sharp economic slowdown. Higher interest rates curb inflation but can also stifle economic activity.
-
Potential Policy Adjustments: The BOJ may need to consider further adjustments to its YCC policy or explore alternative monetary policy tools. This could involve gradually allowing long-term yields to rise more freely or employing other unconventional measures.
-
Ongoing Debate: The future direction of monetary policy in Japan is a subject of intense debate amongst economists and policymakers. Finding the optimal balance between inflation control and economic growth remains a significant challenge.
International Implications and Global Market Reactions
The developments in Japan's bond market have significant global implications:
-
Spillover Effects: Changes in Japanese bond yields can affect other Asian economies through trade and financial linkages. Increased borrowing costs in Japan can ripple through the region.
-
Japanese Yen Value: The steepening yield curve and the BOJ's policy response can influence the value of the Japanese Yen against other currencies. Changes in interest rate differentials can impact currency exchange rates.
-
Global Investor Sentiment: The situation in Japan's bond market influences global investor sentiment toward Japanese assets. Uncertainty about the future direction of the Japanese economy and monetary policy can affect capital flows.
Conclusion
The steepening yield curve in Japan's bond market presents a complex set of economic challenges. Increased borrowing costs, potential for slower economic growth, and the Bank of Japan's policy dilemmas all contribute to a challenging economic outlook. Understanding the intricacies of Japan's bond market, including its international ramifications, is critical for investors and policymakers alike. Continuous monitoring of the evolving situation and further analysis of the policy response are essential. Staying abreast of developments in Japan's bond market is vital for navigating the complexities of this dynamic and crucial aspect of the global financial landscape.

Featured Posts
-
 Rekor Gelir Novak Djokovic 186 Milyon Dolar Kazandi
May 17, 2025
Rekor Gelir Novak Djokovic 186 Milyon Dolar Kazandi
May 17, 2025 -
 Resultado Paysandu 0 1 Bahia Cronica Goles Y Analisis Del Partido
May 17, 2025
Resultado Paysandu 0 1 Bahia Cronica Goles Y Analisis Del Partido
May 17, 2025 -
 Cost Of Emirates Id For Newborns In The Uae March 2025
May 17, 2025
Cost Of Emirates Id For Newborns In The Uae March 2025
May 17, 2025 -
 Could Driverless Uber Pay Off Exploring Etfs For The Autonomous Vehicle Revolution
May 17, 2025
Could Driverless Uber Pay Off Exploring Etfs For The Autonomous Vehicle Revolution
May 17, 2025 -
 Gold Xauusd Recovers Analysis Of Recent Price Action And Market Sentiment
May 17, 2025
Gold Xauusd Recovers Analysis Of Recent Price Action And Market Sentiment
May 17, 2025
