Late-Diagnosed Autism In Adults: A Guide To Support And Transformation
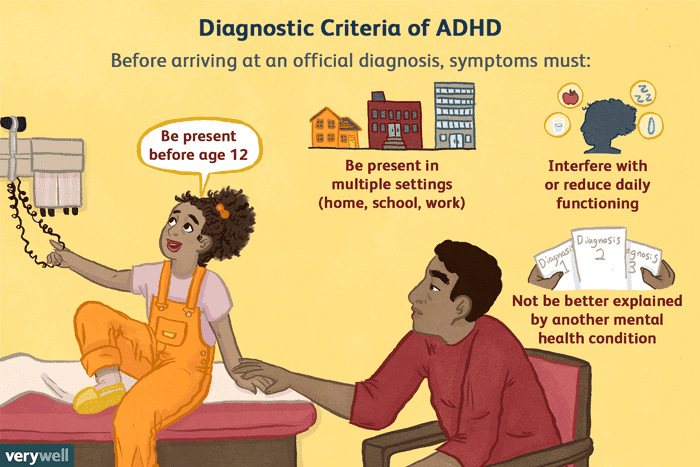
Table of Contents
Understanding Late Diagnosis of Autism in Adults
Challenges of Late Diagnosis
Receiving a diagnosis of autism as an adult presents unique challenges. Many individuals have spent years grappling with misunderstandings, social difficulties, and a lack of support, often without understanding why. The delayed access to support and resources that characterize late-diagnosed autism in adults significantly impacts their lives.
- Social isolation: Adults may have struggled with building and maintaining relationships, leading to feelings of loneliness and isolation.
- Difficulty adjusting to the diagnosis: The emotional impact of a retrospective diagnosis can be significant, leading to a period of adjustment and processing.
- Financial challenges related to therapy: The cost of therapy and related services can be prohibitive for some.
- Career implications: Understanding how autism may have impacted career paths and opportunities can be a complex process.
Common Signs of Autism in Adults
Autistic traits in adults can manifest differently than in children. Recognizing these signs is crucial for seeking appropriate support. While every individual is unique, some common signs include:
- Sensory sensitivities: Over- or under-sensitivity to light, sound, touch, taste, or smell.
- Social communication challenges: Difficulties with interpreting nonverbal cues, engaging in small talk, or understanding social nuances.
- Repetitive behaviors or routines: A strong need for predictability and routine, and distress when routines are disrupted.
- Executive functioning difficulties: Challenges with planning, organization, time management, and task initiation.
Seeking Professional Help for Late-Diagnosed Autism
It's essential to seek a professional diagnosis from a qualified specialist. This involves a thorough assessment that considers various aspects of an individual's life.
- Find a qualified professional: Look for psychologists, psychiatrists, or neuropsychologists specializing in autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in adults.
- Diagnostic process: Expect a comprehensive evaluation involving interviews, questionnaires, and potentially neuropsychological testing.
- Multidisciplinary approach: Consider a multidisciplinary approach involving therapists specializing in different areas like speech, occupational, and social skills therapy.
Support and Resources for Adults with Late-Diagnosed Autism
Therapy and Treatment Options
Several therapeutic approaches can help adults manage autistic traits and improve their quality of life.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Helps manage anxiety and depression associated with autism.
- Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA): Focuses on developing positive behaviors and reducing challenging behaviors.
- Speech therapy: Addresses communication and social interaction challenges.
- Occupational therapy: Helps develop adaptive skills for daily living.
- Social skills training: Provides strategies for improving social interactions and communication.
Support Groups and Online Communities
Connecting with others who share similar experiences offers invaluable support and understanding.
- Online communities: Numerous online forums and support groups provide a safe space for sharing experiences and seeking advice.
- Peer support: The importance of peer support and shared experiences cannot be overstated.
Advocacy and Self-Advocacy
Understanding your rights and accessing available support services is vital. Learning to self-advocate is an empowering skill.
- Disability rights legislation: Familiarize yourself with relevant legislation protecting the rights of individuals with disabilities.
- Navigating bureaucratic systems: Learn how to effectively navigate bureaucratic processes to access support services.
- Asserting personal needs: Develop strategies for confidently communicating your needs and preferences.
Transforming Your Life After a Late Autism Diagnosis
Embracing Your Autism
Self-acceptance and embracing your autistic identity are crucial steps in your journey.
- Neurodiversity affirmation: Recognize that autism is a natural variation in the human brain, not a deficit.
- Recognizing strengths and talents: Identify your unique strengths and talents that often accompany autism.
- Building self-esteem: Develop a positive self-image and embrace your autistic identity.
Developing Coping Mechanisms
Developing strategies for managing challenges is essential for improving quality of life.
- Sensory regulation techniques: Learn strategies to manage sensory sensitivities (e.g., noise-canceling headphones, weighted blankets).
- Social scripts: Develop scripts for common social situations to reduce anxiety and improve communication.
- Organizational tools and strategies: Use organizational tools and strategies to manage executive functioning challenges (e.g., planners, to-do lists).
Building a Supportive Network
A strong support system is crucial for navigating the challenges of a late autism diagnosis.
- Open communication with loved ones: Communicate openly with family and friends about your diagnosis and needs.
- Finding mentors: Seek out mentors who understand autism and can provide guidance and support.
- Building positive relationships: Foster relationships with people who accept and support you.
Conclusion
Late-diagnosed autism in adults presents unique challenges but also offers opportunities for self-discovery and positive transformation. By understanding the common signs, seeking professional help, accessing available resources, and embracing your autistic identity, you can build a fulfilling and meaningful life. Remember, receiving a diagnosis is not an ending, but a beginning. Take the first step towards understanding and embracing your late-diagnosed autism—your journey to transformation begins now. For further information and support, please explore resources such as [link to relevant resource 1] and [link to relevant resource 2].

Featured Posts
-
 Deutsche Banks Saudi Arabia Investment Push Wooing Global Investors
May 30, 2025
Deutsche Banks Saudi Arabia Investment Push Wooing Global Investors
May 30, 2025 -
 The Trump Effect How America First Is Reshaping Harvard
May 30, 2025
The Trump Effect How America First Is Reshaping Harvard
May 30, 2025 -
 Addressing The Speculation Toprak Razgatlioglu And Moto Gp
May 30, 2025
Addressing The Speculation Toprak Razgatlioglu And Moto Gp
May 30, 2025 -
 Jins We Ll Return Soon Message At Coldplay Seoul Concert What It Means For Army
May 30, 2025
Jins We Ll Return Soon Message At Coldplay Seoul Concert What It Means For Army
May 30, 2025 -
 Province Expands Advanced Care Paramedic Services In Rural And Northern Manitoba
May 30, 2025
Province Expands Advanced Care Paramedic Services In Rural And Northern Manitoba
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Saskatchewan Wildfires Early Start And Predictions For A Severe Season
May 31, 2025
Saskatchewan Wildfires Early Start And Predictions For A Severe Season
May 31, 2025 -
 Officials Warn Of Intensified Wildfire Season In Saskatchewan Due To Heat
May 31, 2025
Officials Warn Of Intensified Wildfire Season In Saskatchewan Due To Heat
May 31, 2025 -
 Live Streaming Mens Giro D Italia Cycling
May 31, 2025
Live Streaming Mens Giro D Italia Cycling
May 31, 2025 -
 Deadly Wildfires Rage In Eastern Manitoba Emergency Crews Respond
May 31, 2025
Deadly Wildfires Rage In Eastern Manitoba Emergency Crews Respond
May 31, 2025 -
 Watch The Giro D Italia Mens Race Live
May 31, 2025
Watch The Giro D Italia Mens Race Live
May 31, 2025
