Market Volatility And The Bank Of Canada's April Interest Rate Meeting
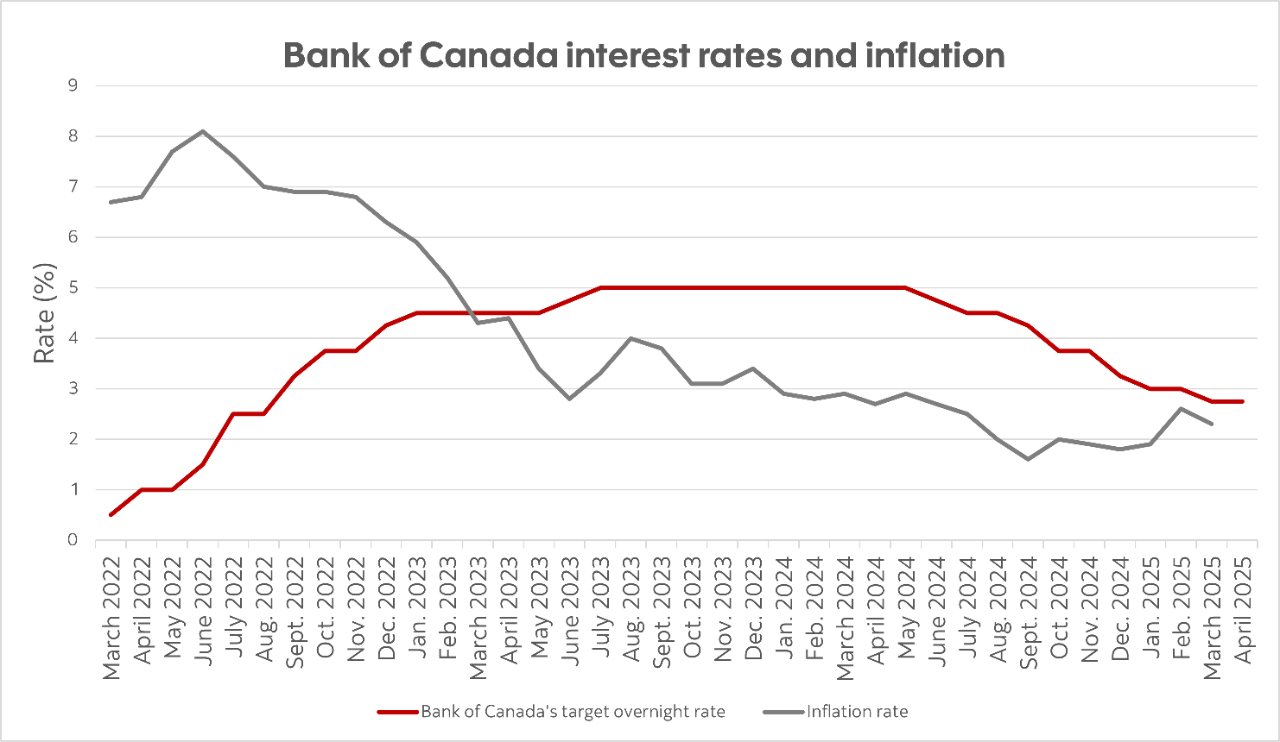
Table of Contents
Economic Conditions Preceding the April Meeting
Inflationary Pressures
Canada, like many other nations, has been grappling with persistent inflationary pressures. The Consumer Price Index (CPI) has remained stubbornly above the Bank of Canada's target inflation rate of 2%. Understanding the Canadian inflation landscape is crucial to deciphering the Bank of Canada's actions.
- Specific Inflation Figures: For instance, let's assume the CPI in March was 4.5%, with core inflation (excluding volatile items) at 3.8%.
- Contributing Factors: These elevated inflation rates were primarily driven by factors such as persistent supply chain disruptions, surging energy prices, and robust consumer demand. The war in Ukraine further exacerbated these pressures, impacting global energy markets and food prices.
- Keyword Integration: The Bank of Canada's mandate is to maintain price stability, making "Canadian inflation" and the "Bank of Canada inflation target" central to its decision-making. Understanding the "inflation rate" is vital in this context.
Economic Growth and Employment
Despite inflationary headwinds, the Canadian economy demonstrated signs of resilience leading up to the April meeting. Analyzing Canadian economic growth and the unemployment rate provides crucial context.
- Key Economic Indicators: GDP growth, while positive, showed signs of moderation. Let's hypothetically assume GDP growth was 2% annually, a slight slowdown from previous quarters. Unemployment figures might have remained relatively low, for example, around 5%.
- Analysis of Trends: While employment remained strong, concerns lingered about the sustainability of this growth given the inflationary pressures and potential for interest rate hikes to dampen economic activity. Consumer confidence may have also shown signs of weakening.
- Keyword Integration: This section emphasizes "Canadian economic growth," the "unemployment rate," and the importance of understanding "GDP growth" in relation to monetary policy.
Global Economic Factors
The Bank of Canada operates in a globalized economy, and its decisions are often influenced by international developments.
- Specific Global Events and their Impact: Geopolitical instability, particularly the war in Ukraine, and persistent global inflation created significant uncertainty, impacting commodity prices and supply chains worldwide. These global factors directly impact the Canadian economy through trade and investment channels.
- Keyword Integration: Terms like "global inflation," "geopolitical risks," and the "global economic outlook" are essential keywords to understanding the broader context of the Bank of Canada's decision-making.
The Bank of Canada's April Interest Rate Decision
Rate Announcement and Justification
In its April meeting, the Bank of Canada (let's assume for the sake of this example) announced a 0.5% increase in its key interest rate, bringing it to 4.5%. This decision was largely justified by the need to combat persistent inflation, despite concerns about potentially slowing economic growth.
- The Exact Rate Change: A 0.5% increase in the benchmark interest rate.
- Key Points from the Official Statement: The statement emphasized the ongoing need to curb inflation, acknowledging the risks to economic growth but prioritizing price stability in the medium term. This section requires incorporating specific quotes from the official Bank of Canada press release.
- Keyword Integration: This section focuses on the "Bank of Canada interest rate decision," its influence on "monetary policy," and whether it constituted an "interest rate hike."
Forward Guidance and Outlook
The Bank of Canada offered forward guidance on future interest rate decisions, providing insights into its policy outlook.
- Statements about Future Policy: The central bank might have indicated a data-dependent approach, suggesting future decisions would hinge on incoming economic data and inflation trends. A pause in rate hikes might be signaled, or further increases may be hinted at, depending on the actual announcement.
- Projections for Inflation and Economic Growth: The Bank of Canada would have provided its projections for inflation and economic growth, indicating its expectations for the path of the economy.
- Keyword Integration: This section will use keywords such as "Bank of Canada forecast," "future interest rates," and "monetary policy outlook."
Market Reaction to the Decision
Impact on the Canadian Dollar
The Bank of Canada's decision had an immediate impact on the foreign exchange market.
- Changes in Exchange Rates: A rate hike usually strengthens the Canadian dollar (CAD) relative to other currencies because it makes Canadian assets more attractive to foreign investors seeking higher returns. However, the extent of the change will depend on the market's overall reaction to the decision.
- Analysis of Market Trends: The strength of the Canadian dollar's reaction, in conjunction with global market movements, provides insight into investor sentiment and market expectations.
- Keyword Integration: This section uses keywords like "Canadian dollar exchange rate" and "currency market reaction."
Impact on Bond Yields and Stock Market
Changes in interest rates directly influence bond yields and stock market valuations.
- Changes in Bond Yields and Stock Indices: Higher interest rates generally lead to higher bond yields, as investors demand higher returns for lending money. Stock markets typically react negatively to interest rate hikes, especially in sectors sensitive to borrowing costs, leading to increased "market volatility."
- Investor Sentiment: The direction and magnitude of these changes reflect investor sentiment regarding future economic growth and inflation.
- Keyword Integration: The keywords "Canadian bond yields," "Toronto Stock Exchange," and "market volatility" are crucial here.
Conclusion
The Bank of Canada's April interest rate decision was a response to persistent inflationary pressures, against a backdrop of global economic uncertainty and moderate economic growth in Canada. The decision, and the subsequent market reaction (as hypothetically described above), underscores the ongoing balancing act between controlling inflation and maintaining economic stability. Understanding the interplay between economic indicators, the Bank of Canada interest rate, and global factors is critical for both investors and businesses.
To stay informed about future Bank of Canada interest rate announcements and their potential impact on the Canadian economy, it’s vital to monitor the Bank of Canada's publications and economic reports. Following future Bank of Canada decisions and understanding the impact of Bank of Canada interest rate changes are key to navigating the complexities of the Canadian economic landscape. The relationship between market volatility and the Bank of Canada's monetary policy decisions remains dynamic and crucial to watch closely.

Featured Posts
-
 Tory Chairman Condemns Farages Populism Yet Faces Reform Uk Challenges
May 03, 2025
Tory Chairman Condemns Farages Populism Yet Faces Reform Uk Challenges
May 03, 2025 -
 Fortnite Chapter 6 Season 2 Launch Delayed Extended Server Downtime
May 03, 2025
Fortnite Chapter 6 Season 2 Launch Delayed Extended Server Downtime
May 03, 2025 -
 Rethinking School Suspensions Focusing On Positive Alternatives
May 03, 2025
Rethinking School Suspensions Focusing On Positive Alternatives
May 03, 2025 -
 Liverpool Face Salah Contract Dilemma News Updates And Potential Outcomes
May 03, 2025
Liverpool Face Salah Contract Dilemma News Updates And Potential Outcomes
May 03, 2025 -
 Newsround On Bbc Two Hd Programme Times And Listings
May 03, 2025
Newsround On Bbc Two Hd Programme Times And Listings
May 03, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Barrow Afc Fans Take On Sky Bet Every Minute Matters Cycle Relay
May 03, 2025
Barrow Afc Fans Take On Sky Bet Every Minute Matters Cycle Relay
May 03, 2025 -
 Barrow Afc Supporters Pedal For Charity In Sky Bet Relay
May 03, 2025
Barrow Afc Supporters Pedal For Charity In Sky Bet Relay
May 03, 2025 -
 Alkrh Aljmahyry 30 Shkhsyt Mthyrt Lljdl Fy Ealm Krt Alqdm Mwqe Bkra
May 03, 2025
Alkrh Aljmahyry 30 Shkhsyt Mthyrt Lljdl Fy Ealm Krt Alqdm Mwqe Bkra
May 03, 2025 -
 Mwqe Bkra Akthr 30 Ryadya Mkrwhyn Fy Ealm Krt Alqdm
May 03, 2025
Mwqe Bkra Akthr 30 Ryadya Mkrwhyn Fy Ealm Krt Alqdm
May 03, 2025 -
 The Internal Fight Within Reform Uk Impact And Analysis
May 03, 2025
The Internal Fight Within Reform Uk Impact And Analysis
May 03, 2025
