Measles Cases In The U.S.: A State-by-State Update
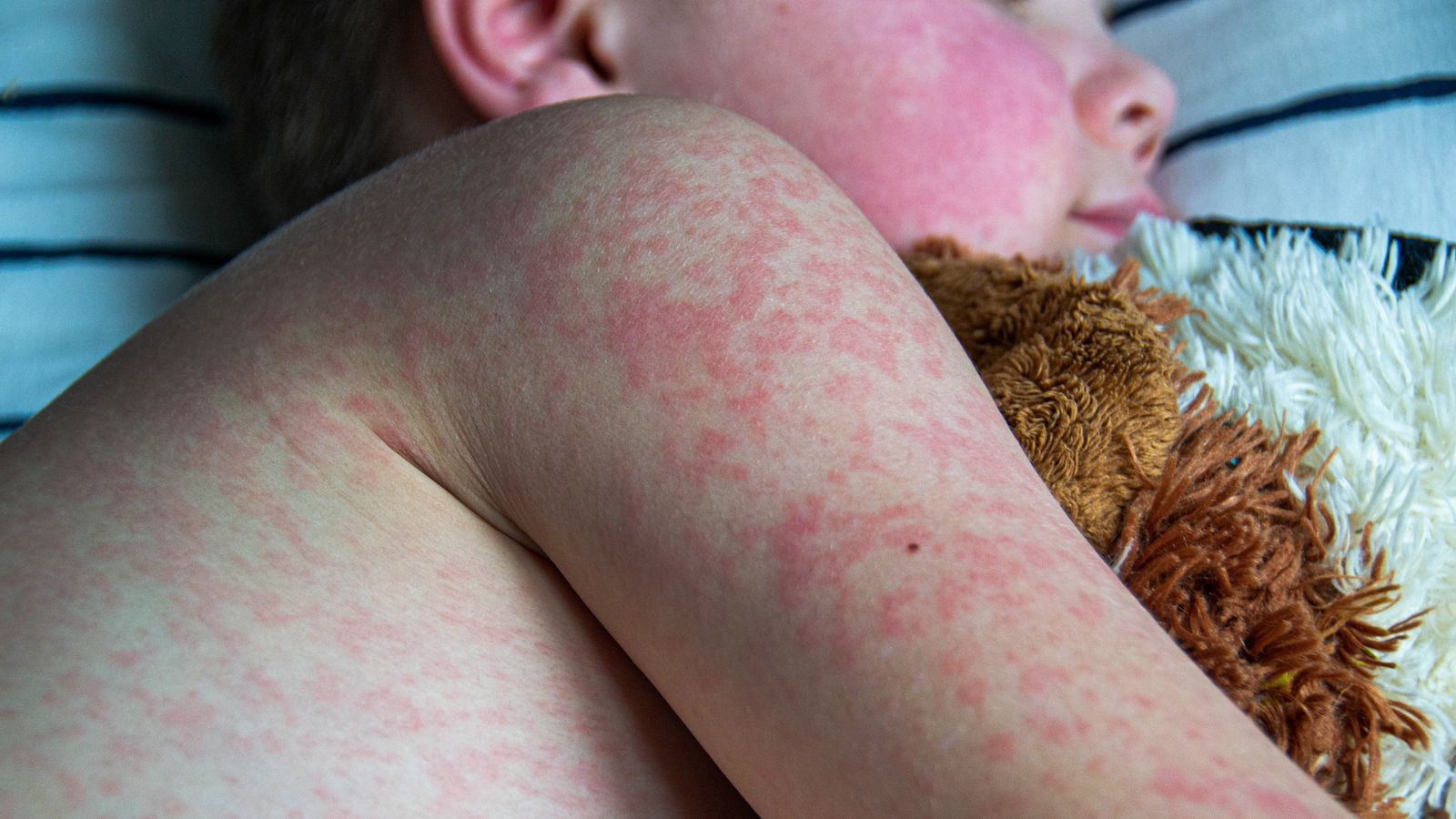
Table of Contents
Current Measles Case Numbers by State
Tracking measles cases in the U.S. requires diligent monitoring at both the state and national levels. Data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and individual state health departments provides the most accurate picture. While precise, real-time data fluctuates, we can analyze trends and identify areas of particular concern.
-
States with the Highest Number of Reported Cases: Historically, outbreaks have often been concentrated in specific regions, sometimes linked to specific communities with lower vaccination rates or international travel connections. Data analysis frequently reveals a non-uniform distribution, highlighting the need for targeted public health interventions. (Specific state data would be inserted here, drawn from the most recent CDC reports and state health department websites. This would need to be updated regularly to reflect current information.)
-
States with No Reported Cases: While some states may report zero cases in a given period, it's crucial to understand this might reflect temporary lows rather than complete elimination. Continuous vigilance and robust vaccination programs are essential in maintaining this status. (Specific state data would be inserted here. Again, this requires regularly updated data.)
-
States Experiencing Recent Outbreaks: Outbreaks often warrant immediate and focused response efforts. These events highlight the contagious nature of measles and the importance of rapid response protocols, including contact tracing and vaccination campaigns. (Specific state data would be inserted here, linking to relevant state health department websites for detailed outbreak information.)
-
Interactive Map: (An interactive map displaying measles case distribution across the U.S. would ideally be included here. This could link to the CDC's data visualization tools or a similar resource).
-
Data Visualization: (Charts and graphs showing trends in measles cases over time, both nationally and at the state level, would be included here. This visual representation would enhance understanding and emphasize the importance of ongoing surveillance.)
Factors Contributing to Measles Outbreaks
Several interconnected factors contribute to measles outbreaks in the U.S., many of which are preventable through increased vaccination rates and public health education.
-
Low Vaccination Rates in Certain Communities: Pockets of low vaccination coverage create vulnerabilities within populations, allowing the measles virus to spread more easily. This is often linked to misinformation and vaccine hesitancy.
-
Spread Through International Travel: International travel can quickly introduce the measles virus into communities with lower vaccination rates, leading to rapid transmission.
-
Clusters of Unvaccinated Individuals: The concentration of unvaccinated individuals, whether due to philosophical objections, religious exemptions, or lack of access to healthcare, increases the likelihood of outbreaks.
-
Misinformation and Vaccine Hesitancy: The spread of misinformation about vaccine safety and efficacy undermines public health efforts and fuels vaccine hesitancy, contributing to lower vaccination rates.
-
Impact of Healthcare Access: Limited access to healthcare can impede timely vaccination and diagnosis, making communities more susceptible to outbreaks.
State-Level Public Health Responses
State health departments play a crucial role in responding to and preventing measles outbreaks. Their strategies vary but often incorporate several key elements:
-
Vaccination Campaigns and Initiatives: Many states launch targeted vaccination campaigns to increase coverage rates, particularly in communities with low vaccination rates.
-
Public Health Advisories and Communication Strategies: Effective communication is key. Public health agencies utilize various platforms to inform the public about measles risks, symptoms, and prevention measures.
-
Outbreak Investigations and Contact Tracing: During outbreaks, thorough investigations help identify the source of infection and trace contacts to prevent further spread.
-
Quarantine Measures Where Necessary: In some cases, quarantine measures might be implemented to contain the spread of the virus.
-
Collaboration Between State and Federal Agencies: Effective collaboration between state and federal agencies, like the CDC, is critical for coordinating resources and sharing best practices.
The Importance of Measles Vaccination
Measles vaccination remains the most effective way to prevent measles outbreaks and protect individuals and communities.
-
Effectiveness of the MMR Vaccine: The MMR (measles, mumps, and rubella) vaccine is highly effective in preventing measles, offering strong protection against infection.
-
Addressing Common Vaccine Concerns and Myths: Addressing concerns and debunking myths surrounding vaccine safety is crucial in building public trust and increasing vaccination rates.
-
Importance of Herd Immunity: Herd immunity, achieved when a significant portion of a population is vaccinated, protects even those who cannot be vaccinated due to medical reasons.
-
Information on Where to Get Vaccinated: Information on where to access MMR vaccines, including local health departments and healthcare providers, should be readily available.
-
Long-Term Consequences of Measles Infection: Highlighting the potential for serious complications, such as pneumonia, encephalitis, and even death, reinforces the importance of vaccination.
Conclusion
This article has presented a state-by-state overview of the current measles situation in the U.S., highlighting the importance of vaccination and public health interventions in controlling outbreaks. Understanding the geographical distribution of measles cases and the contributing factors allows for the development of targeted strategies for prevention and control. The continuing rise in measles cases in the U.S. underscores the critical need for sustained public health efforts and community engagement.
Call to Action: Stay informed about measles cases in your state and ensure you and your family are up-to-date on your MMR vaccinations. Regularly check your state health department’s website and the CDC website for updates on measles cases in the U.S. Protect yourself and your community by preventing the spread of measles. Learn more about measles prevention and vaccination from your healthcare provider or your local health department.

Featured Posts
-
 Andre Agassis Pickleball Debut Performance Impact And Future Prospects
May 30, 2025
Andre Agassis Pickleball Debut Performance Impact And Future Prospects
May 30, 2025 -
 Invasive Seaweed A Growing Threat To Australias Coastal Ecosystems
May 30, 2025
Invasive Seaweed A Growing Threat To Australias Coastal Ecosystems
May 30, 2025 -
 Ai Driven Podcast Creation Analyzing And Transforming Repetitive Scatological Text
May 30, 2025
Ai Driven Podcast Creation Analyzing And Transforming Repetitive Scatological Text
May 30, 2025 -
 Google Vs Competition Bureau Constitutional Challenge Looms
May 30, 2025
Google Vs Competition Bureau Constitutional Challenge Looms
May 30, 2025 -
 Intet Er Besluttet Endnu Hvad Betyder Det For Fremtiden
May 30, 2025
Intet Er Besluttet Endnu Hvad Betyder Det For Fremtiden
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Munichs Bmw Open 2025 Zverev Battles Griekspoor In Quarter Finals
May 31, 2025
Munichs Bmw Open 2025 Zverev Battles Griekspoor In Quarter Finals
May 31, 2025 -
 May Day Rally In Kingston Images Show Strength And Solidarity Daily Freeman
May 31, 2025
May Day Rally In Kingston Images Show Strength And Solidarity Daily Freeman
May 31, 2025 -
 Bmw Open 2025 Zverev Griekspoor Quarter Final Showdown In Munich
May 31, 2025
Bmw Open 2025 Zverev Griekspoor Quarter Final Showdown In Munich
May 31, 2025 -
 Indian Wells Surprise Zverevs First Match Exit And His Honest Assessment
May 31, 2025
Indian Wells Surprise Zverevs First Match Exit And His Honest Assessment
May 31, 2025 -
 Trump Administration Loses Key Advisor Elon Musks Resignation Explained
May 31, 2025
Trump Administration Loses Key Advisor Elon Musks Resignation Explained
May 31, 2025
