Measles Cases In The US Rise To 1,046: Indiana Outbreak Concludes
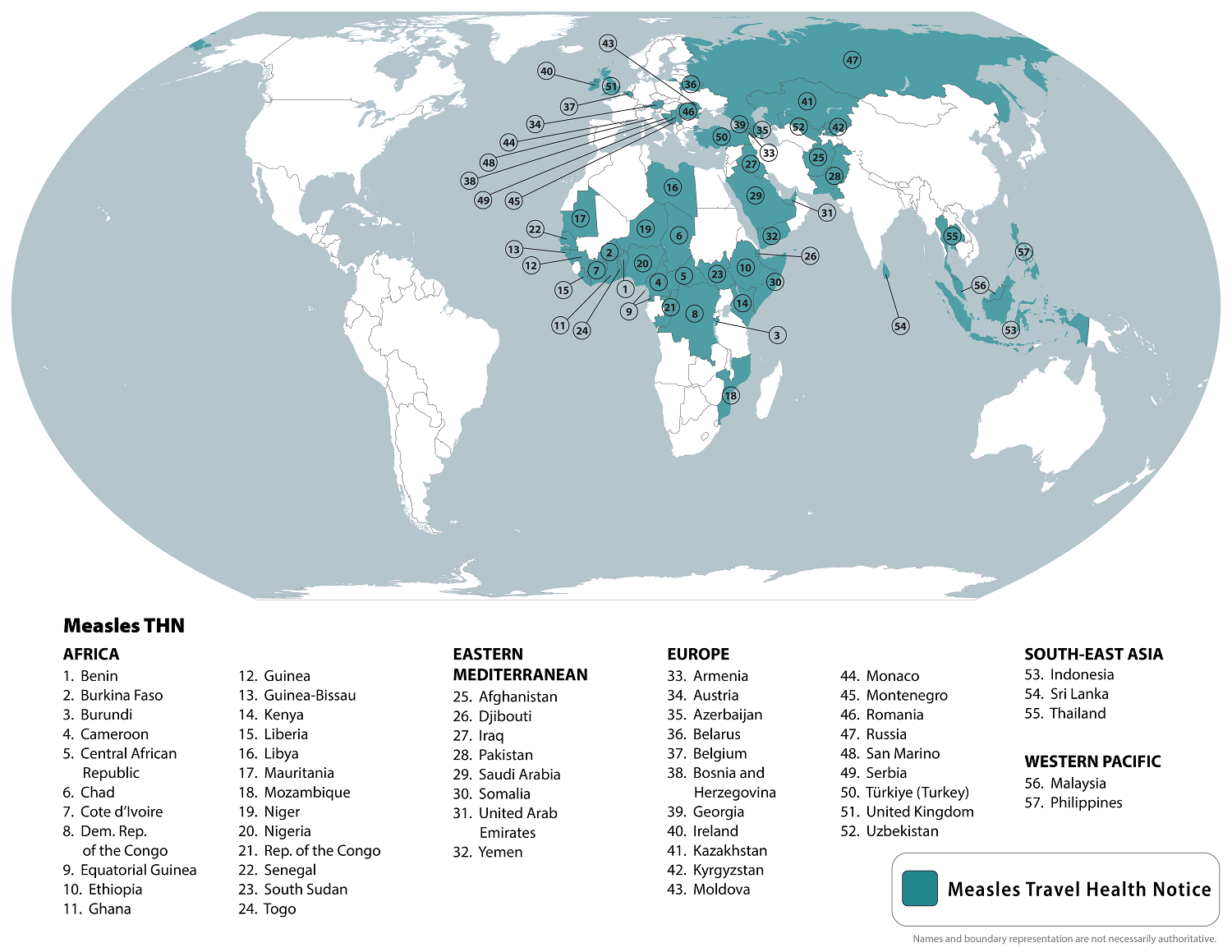
Table of Contents
The Indiana Measles Outbreak: A Case Study
The Indiana measles outbreak serves as a stark reminder of the rapid spread and potential severity of this preventable disease. This outbreak, characterized by community spread and impacting various demographics, provides valuable lessons for future prevention strategies.
- Number of cases in Indiana: While the exact final number may vary slightly, the Indiana outbreak resulted in a substantial number of confirmed measles cases, significantly impacting several counties.
- Key demographics affected: The outbreak disproportionately affected unvaccinated children and adults, highlighting the vulnerability of those without adequate immunity. Cases were also observed across different age groups and socioeconomic backgrounds.
- Public health measures implemented to control the outbreak: Swift action by public health officials was critical. This included quarantine measures for infected individuals, aggressive contact tracing to identify and vaccinate those exposed, and widespread public health announcements urging vaccination.
- Successes and challenges encountered during outbreak response: The rapid implementation of quarantine and contact tracing proved effective in containing the spread, however challenges included vaccine hesitancy in some communities and difficulty in reaching all potentially exposed individuals.
- Lessons learned from the Indiana outbreak: The Indiana experience emphasized the importance of high vaccination rates to achieve herd immunity and the need for proactive public health interventions to swiftly contain outbreaks before they spread widely. Effective communication strategies and community engagement were also highlighted as crucial for success.
Factors Contributing to the Rise in Measles Cases Nationwide
The increase in US measles cases extends beyond the Indiana outbreak. Several factors contribute to this concerning resurgence, creating a significant public health crisis.
- Statistics on national vaccination rates: National vaccination rates for the MMR (measles, mumps, rubella) vaccine have plateaued or even declined in certain areas, leaving communities vulnerable to outbreaks.
- Role of social media and misinformation in spreading anti-vaccine sentiments: The spread of misinformation and anti-vaccine sentiments through social media platforms has fueled vaccine hesitancy and contributed significantly to the decline in vaccination rates. Misinformation campaigns often exploit parental anxieties and sow distrust in established medical science.
- Impact of declining vaccination rates on community immunity: Lower vaccination rates weaken herd immunity, making it easier for measles to spread within communities. Herd immunity protects vulnerable individuals who cannot be vaccinated.
- Geographic distribution of measles cases across the US: Measles cases are not uniformly distributed across the US. Outbreaks are often concentrated in areas with lower vaccination rates, highlighting the geographic disparities in immunity levels.
- The role of international travel in importing measles cases: International travel plays a significant role. Individuals infected with measles abroad can introduce the virus into communities with lower vaccination rates, potentially triggering widespread outbreaks.
The Importance of MMR Vaccination and Public Health Initiatives
The MMR vaccine is highly effective and safe in preventing measles, mumps, and rubella. Public health initiatives are crucial in promoting vaccination and addressing vaccine hesitancy.
- MMR vaccine effectiveness rate: The MMR vaccine is highly effective, with a very high rate of preventing measles infection.
- Addressing common concerns and myths surrounding vaccine safety: Openly addressing and debunking common misconceptions about vaccine safety, through credible sources and medical professionals, is paramount to building trust and improving vaccination rates.
- Strategies for increasing vaccination rates: Strategies include targeted educational campaigns, community outreach programs focused on engaging with hesitant parents, and making vaccines readily accessible and affordable.
- The role of healthcare providers in promoting vaccination: Healthcare providers are vital in advocating for vaccination and providing accurate information to patients, answering their questions, and addressing their concerns.
- Funding for public health programs to support vaccination efforts: Adequate funding for public health programs is necessary for effective vaccination campaigns, community outreach, and monitoring outbreaks.
Protecting Yourself and Your Community from Measles
Protecting yourself and your community from measles requires vigilance and proactive measures.
- Common symptoms of measles: Symptoms include high fever, cough, runny nose, and a characteristic red rash.
- Importance of early diagnosis and treatment: Early diagnosis and supportive care can minimize the severity of the illness.
- Steps to take if exposed to measles: If exposed, seek immediate medical attention. Post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) with the MMR vaccine can prevent the disease in some cases.
- How to protect vulnerable individuals: Ensure that vulnerable individuals (infants, pregnant women, immunocompromised) are protected through herd immunity.
- Resources for reliable information about measles and vaccination: Seek information from reputable sources like the CDC and WHO.
Conclusion
The significant rise in measles cases across the US, despite the conclusion of the Indiana outbreak, underscores a critical public health concern. Factors like declining vaccination rates, fueled by misinformation, have weakened herd immunity, making communities vulnerable. The effectiveness and safety of the MMR vaccine are well-established. Increased vaccination rates, coupled with strong public health initiatives to address vaccine hesitancy, are essential to prevent future measles outbreaks. Protect yourself and your community: get vaccinated against measles, consult your healthcare provider for vaccination information, and share accurate information about the importance of measles vaccination with your social networks. Let's work together to combat this preventable disease and ensure the health and safety of everyone.

Featured Posts
-
 Amanda Holdens Dog Grooming Habit Disgusts Heart Listeners
May 30, 2025
Amanda Holdens Dog Grooming Habit Disgusts Heart Listeners
May 30, 2025 -
 The Ultimate Guide To Paris Neighborhoods
May 30, 2025
The Ultimate Guide To Paris Neighborhoods
May 30, 2025 -
 New Twins For Amber Heard Is Elon Musk The Father
May 30, 2025
New Twins For Amber Heard Is Elon Musk The Father
May 30, 2025 -
 Israel Faces Measles Surge After Texas Outbreak
May 30, 2025
Israel Faces Measles Surge After Texas Outbreak
May 30, 2025 -
 Plires Programma Tileorasis Gia To Savvato 3 5
May 30, 2025
Plires Programma Tileorasis Gia To Savvato 3 5
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Munichs Bmw Open 2025 Zverev Battles Griekspoor In Quarter Finals
May 31, 2025
Munichs Bmw Open 2025 Zverev Battles Griekspoor In Quarter Finals
May 31, 2025 -
 May Day Rally In Kingston Images Show Strength And Solidarity Daily Freeman
May 31, 2025
May Day Rally In Kingston Images Show Strength And Solidarity Daily Freeman
May 31, 2025 -
 Bmw Open 2025 Zverev Griekspoor Quarter Final Showdown In Munich
May 31, 2025
Bmw Open 2025 Zverev Griekspoor Quarter Final Showdown In Munich
May 31, 2025 -
 Indian Wells Surprise Zverevs First Match Exit And His Honest Assessment
May 31, 2025
Indian Wells Surprise Zverevs First Match Exit And His Honest Assessment
May 31, 2025 -
 Trump Administration Loses Key Advisor Elon Musks Resignation Explained
May 31, 2025
Trump Administration Loses Key Advisor Elon Musks Resignation Explained
May 31, 2025
