Negative Inflation In Thailand: A Boon For Monetary Policy?
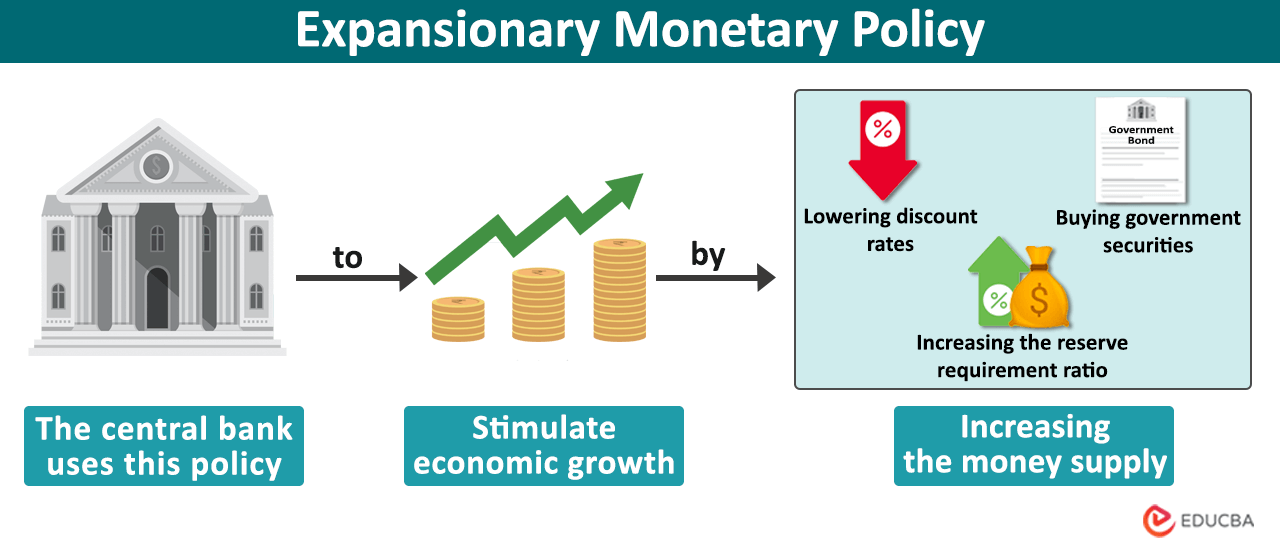
Table of Contents
Causes of Negative Inflation in Thailand
Negative inflation, or deflation, occurs when the general price level of goods and services in an economy decreases. In Thailand, several interconnected factors have contributed to this concerning trend.
-
Decreased Consumer Spending: A slowdown in Thai consumer spending, fueled by factors such as subdued wage growth and uncertainty about the global economic outlook, has reduced demand for goods and services. This decreased demand puts downward pressure on prices. Understanding the dynamics of Thai consumer spending is crucial to comprehending the deflationary pressures.
-
Overcapacity in Certain Sectors: Some sectors within the Thai economy suffer from overcapacity, leading to intense competition and price wars. This is particularly true in manufacturing and certain agricultural sectors. This oversupply translates to lower prices to attract customers, further contributing to the deflationary trend.
-
Global Economic Slowdown Impacting Exports: Thailand's export-oriented economy is significantly affected by global economic slowdowns. Reduced global demand for Thai exports, such as electronics and automobiles, leads to lower production and reduced prices. The impact of export decline in Thailand on the overall economy is significant.
-
Stronger Thai Baht Affecting Import Prices: The relative strength of the Thai Baht against other currencies makes imported goods cheaper. While beneficial for consumers in terms of access to affordable products, it also puts downward pressure on domestic prices, intensifying deflationary pressures. Analyzing the currency strength in Thailand is essential to grasp this factor.
-
Technological Advancements Leading to Lower Prices: Technological advancements constantly drive down the cost of production for many goods. This increased efficiency translates to lower prices for consumers, a positive aspect but also a contributor to the broader deflationary picture.
The Impact of Negative Inflation on the Thai Economy
While lower prices might seem appealing, negative inflation in Thailand carries both benefits and significant drawbacks.
-
Positive Impacts:
- Increased Purchasing Power: Deflation increases the purchasing power of consumers, allowing them to buy more goods and services with the same amount of money.
- Lower Borrowing Costs: Lower inflation typically leads to lower interest rates, making borrowing cheaper for businesses and individuals.
-
Negative Impacts:
- Delayed Consumption: Consumers might delay purchases anticipating further price drops, reducing aggregate demand and exacerbating deflation.
- Debt Burden Increase: Deflation increases the real value of debt, making it harder for borrowers to repay their loans. This can lead to increased defaults and financial instability. The impact of debt burden in Thailand is a crucial concern.
- Deflationary Spiral Risk: A deflationary spiral is a dangerous cycle where falling prices lead to reduced spending, further price drops, and ultimately economic recession. This risk is a significant concern for policymakers.
The effects of deflation vary across sectors. The agricultural sector, for instance, might experience lower farm incomes, while the manufacturing sector could face reduced profitability due to lower prices. The tourism sector in Thailand could also suffer, depending on currency fluctuations and overall consumer sentiment.
Monetary Policy Responses to Negative Inflation
The Bank of Thailand (BOT) has several tools at its disposal to combat deflation.
-
Lowering Interest Rates: The BOT can lower interest rates to stimulate borrowing and investment, boosting aggregate demand. However, extremely low interest rates can have limited effectiveness and may not always prevent deflation. The effectiveness of interest rate adjustments in Thailand is constantly evaluated.
-
Quantitative Easing (QE): While not yet employed extensively in Thailand, QE involves the central bank injecting liquidity into the economy by purchasing government bonds or other assets. This is a powerful but potentially risky tool. The possibility of quantitative easing in Thailand is a topic of ongoing debate.
-
Government Spending Initiatives: Government spending on infrastructure projects or social programs can increase aggregate demand and help to counter deflationary pressures. Effective fiscal policy in Thailand plays a vital role in addressing the problem.
-
Exchange Rate Management: The BOT can intervene in the foreign exchange market to manage the value of the Thai Baht. A weaker Baht can boost exports and help to combat deflation, but it also carries risks.
The effectiveness and potential limitations of each strategy must be carefully considered. The BOT needs to strike a delicate balance between stimulating the economy and avoiding excessive inflation or other unintended consequences.
Comparing Thailand's Situation to Other Countries Experiencing Deflation
Several countries, notably Japan, have experienced prolonged periods of deflation. Japan's deflationary experience provides valuable lessons, highlighting the challenges of escaping a deflationary spiral and the importance of a coordinated approach involving monetary and fiscal policies. Studying the strategies employed by Japan and other countries grappling with deflation offers valuable insights and potential solutions for Thailand.
Conclusion: Navigating Negative Inflation in Thailand – A Path Forward
Negative inflation in Thailand presents a complex challenge for policymakers. While some benefits exist, the potential risks of delayed consumption, increased debt burdens, and a deflationary spiral are significant. The causes are multifaceted, stemming from weak consumer spending, global economic conditions, and sectoral imbalances. The Bank of Thailand's response needs a balanced and multifaceted approach, carefully utilizing monetary and fiscal tools while monitoring the impact on various economic sectors.
Further research and open discussion are crucial to understanding the full implications of negative inflation in Thailand and developing effective long-term strategies. We encourage readers to explore resources from the Bank of Thailand, the Ministry of Finance, and reputable economic research institutions to gain a deeper understanding of this pressing issue and its impact on the Thai economy. Addressing deflation in Thailand requires a collaborative effort between the government, the central bank, and the private sector.

Featured Posts
-
 7 Sezon Chernogo Zerkala Chto Izvestno O Date Vykhoda 13 Marta 2025
May 07, 2025
7 Sezon Chernogo Zerkala Chto Izvestno O Date Vykhoda 13 Marta 2025
May 07, 2025 -
 Provincial Spending Scrutinized Peis 500 000 Nhl Event Bill
May 07, 2025
Provincial Spending Scrutinized Peis 500 000 Nhl Event Bill
May 07, 2025 -
 Bitcoin Nears 100 000 Breaking 10 Week High
May 07, 2025
Bitcoin Nears 100 000 Breaking 10 Week High
May 07, 2025 -
 Cem Karaca Bati Ve Anadolu Mueziginin Essiz Bulusmasi
May 07, 2025
Cem Karaca Bati Ve Anadolu Mueziginin Essiz Bulusmasi
May 07, 2025 -
 The Karate Kid Part Ii Themes Characters And Legacy
May 07, 2025
The Karate Kid Part Ii Themes Characters And Legacy
May 07, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 First Look The Long Walk Trailer Reveals Intense Dystopian Action
May 08, 2025
First Look The Long Walk Trailer Reveals Intense Dystopian Action
May 08, 2025 -
 Can The Thunder Overcome Memphis Key Matchup To Watch
May 08, 2025
Can The Thunder Overcome Memphis Key Matchup To Watch
May 08, 2025 -
 March 7th Thunder Vs Trail Blazers Game Time Tv Broadcast And Live Stream Info
May 08, 2025
March 7th Thunder Vs Trail Blazers Game Time Tv Broadcast And Live Stream Info
May 08, 2025 -
 Stephen Kings The Long Walk New Trailer Analysis And Discussion
May 08, 2025
Stephen Kings The Long Walk New Trailer Analysis And Discussion
May 08, 2025 -
 Thunder Grizzlies Preview A Challenging Game On The Horizon
May 08, 2025
Thunder Grizzlies Preview A Challenging Game On The Horizon
May 08, 2025
