New US Duties On Solar Panels From Southeast Asia: A Detailed Analysis

Table of Contents
The Rationale Behind the New US Duties
The US government justified the imposition of these tariffs primarily on allegations of circumvention of previous anti-dumping and countervailing duties levied on Chinese solar panel manufacturers. The argument centers on the claim that Southeast Asian companies are acting as fronts for Chinese producers, effectively bypassing existing trade restrictions. National security concerns have also been cited, emphasizing the importance of a robust domestic solar manufacturing industry for energy independence. Furthermore, the administration aimed to protect the US solar industry from what it considered unfair competition.
The investigation process leading to the tariff imposition involved a detailed examination of trade practices, including an analysis of supply chains, production processes, and ownership structures. This investigation, conducted under Section 301 of the Trade Act of 1974, led to the determination that the circumvention of prior duties warranted the imposition of new tariffs.
Key arguments presented by the US government included:
- Significant increase in solar panel imports from Southeast Asia following the imposition of tariffs on Chinese imports.
- Evidence suggesting close ties between Southeast Asian manufacturers and Chinese companies, including shared ownership and technology transfer.
- Concerns about the potential disruption to the domestic US solar manufacturing sector.
[Link to relevant government document 1] [Link to relevant government document 2] [Link to relevant news article 1]
Impact on Southeast Asian Solar Panel Manufacturers
The new US duties have dealt a severe blow to Southeast Asian solar panel manufacturers, particularly in Vietnam, Cambodia, and Malaysia, which are major exporters to the US market. These tariffs have led to:
- Reduced export volumes: A significant decline in sales to the US market is impacting revenue streams.
- Potential job losses: Manufacturing plants may face closures or downsizing, resulting in job losses across the region.
- Economic slowdown: The solar industry contributes significantly to the economies of these countries; the tariffs threaten economic growth.
The reactions from Southeast Asian governments have ranged from diplomatic protests to exploring alternative export markets. However, the disruption to established trade relationships and the potential for further retaliatory measures pose significant challenges.
(Insert chart/graph visualizing production data before and after tariffs, if available)
Implications for the US Solar Energy Sector
While intended to protect the domestic solar industry, the new tariffs present a mixed bag of consequences for the US solar energy sector. The tariffs will likely:
- Increase solar panel prices: Higher prices will likely slow down the adoption of solar energy by consumers and businesses.
- Impact the growth of the US solar energy industry: Higher costs could hinder the expansion of solar energy projects.
- Potentially create jobs in domestic manufacturing: However, this effect might be limited, as the US domestic solar manufacturing capacity remains relatively small.
The long-term impact on achieving renewable energy goals remains uncertain. While the tariffs may provide short-term protection for some domestic manufacturers, they could ultimately hinder the overall growth of the US solar energy market in the long run.
Global Trade Implications and International Responses
The US tariffs have triggered concerns about escalating trade disputes and retaliatory measures from Southeast Asian countries. This situation adds another layer of complexity to already strained international trade relations. The World Trade Organization (WTO) could become involved if affected countries challenge the legality of the tariffs.
The impact on global solar panel supply chains is significant, creating uncertainty and potentially leading to disruptions. The US may need to explore alternative sourcing options, potentially impacting relationships with other countries and increasing reliance on other regions, potentially increasing transportation costs.
- Increased risk of trade wars and further protectionist measures.
- Potential for supply chain disruptions and increased costs.
- Uncertainty for investors in the global solar industry.
Conclusion: Understanding the Ramifications of New US Duties on Solar Panels from Southeast Asia
The new US duties on solar panels from Southeast Asia present a complex picture with significant ramifications for various stakeholders. The tariffs aim to protect the domestic US solar industry but risk harming the growth of renewable energy, increasing costs for consumers, and potentially triggering trade disputes. Southeast Asian manufacturers face significant economic challenges, while the global solar supply chain faces increased uncertainty. The economic and geopolitical complexities of this situation highlight the intricate interplay between national interests and global trade.
To stay informed on the ongoing developments regarding New US Duties on Solar Panels from Southeast Asia and their cascading effects, we encourage you to monitor relevant government announcements, industry reports, and news articles from credible sources. Further research into the WTO's potential role in resolving the trade disputes will be vital in understanding the long-term consequences of these tariffs on the global energy market and international trade relations.

Featured Posts
-
 Programma Tileorasis Savvatoy 3 5 Odigos Gia Tis Kalyteres Ekpompes
May 30, 2025
Programma Tileorasis Savvatoy 3 5 Odigos Gia Tis Kalyteres Ekpompes
May 30, 2025 -
 Sierra Leone Journalists Silenced Over Bolle Jos Drug Trafficking Investigation
May 30, 2025
Sierra Leone Journalists Silenced Over Bolle Jos Drug Trafficking Investigation
May 30, 2025 -
 Sacramento County Wastewater Surveillance Detects Measles What You Need To Know
May 30, 2025
Sacramento County Wastewater Surveillance Detects Measles What You Need To Know
May 30, 2025 -
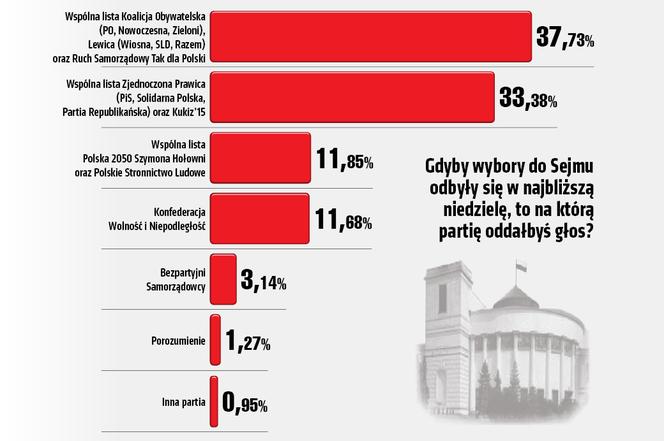 Prezydenckie Wybory 2025 Nowy Kurs Polityczny Wedlug Mentzena
May 30, 2025
Prezydenckie Wybory 2025 Nowy Kurs Polityczny Wedlug Mentzena
May 30, 2025 -
 Legenda Tenisului Andre Agassi Juca Pickleball
May 30, 2025
Legenda Tenisului Andre Agassi Juca Pickleball
May 30, 2025
