Ohio Train Derailment Aftermath: Prolonged Presence Of Toxic Chemicals In Buildings
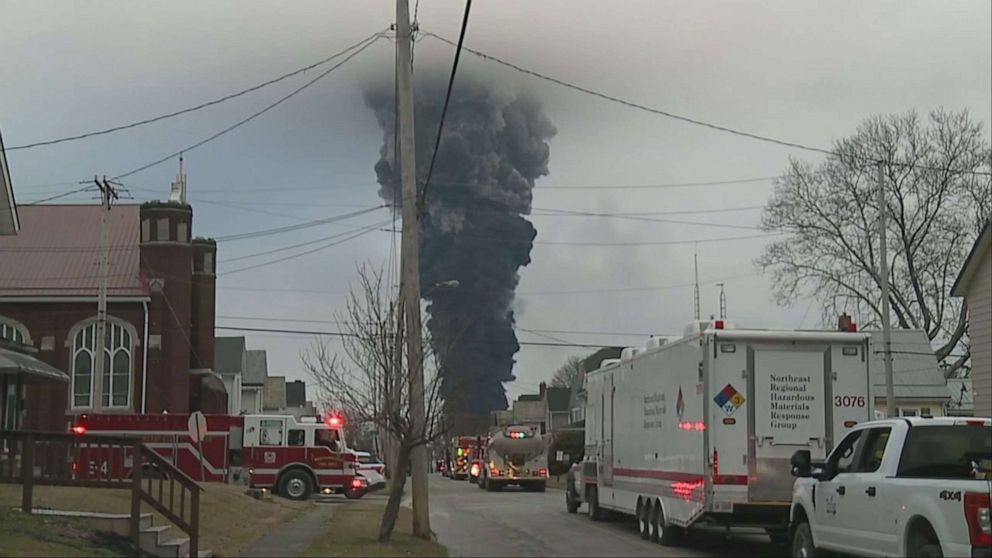

Table of Contents
Types of Toxic Chemicals and Their Persistence
The derailment released a cocktail of hazardous materials, including vinyl chloride, butyl acrylate, and ethylene glycol monobutyl ether. These chemicals, due to their specific properties, exhibit varying degrees of persistence within building materials. Many are volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that can readily absorb into porous surfaces like drywall, carpeting, and insulation. Their persistence is further influenced by factors such as the material's composition, temperature, and humidity.
- Vinyl chloride: Known for its carcinogenic properties, vinyl chloride readily seeps into porous building materials, potentially releasing toxic fumes for extended periods.
- Butyl acrylate: This chemical is prone to long-term off-gassing, meaning it slowly evaporates, releasing harmful vapors into the air inside buildings.
- Weather conditions: Rain and wind can influence the spread of these chemicals, potentially contaminating a wider area and impacting more buildings than initially anticipated. The degradation rate of these chemicals is also affected by environmental factors.
Health Risks Associated with Prolonged Exposure
Prolonged exposure to the toxic chemicals released from the Ohio train derailment poses significant short-term and long-term health risks. Exposure can lead to a range of adverse health effects, impacting various organ systems. Vulnerable populations, including children, the elderly, and individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions, are at a particularly heightened risk.
- Respiratory issues: Asthma, bronchitis, and other respiratory problems are common consequences of inhaling these toxic chemicals.
- Increased cancer risk: Many of the chemicals released are known carcinogens, significantly increasing the risk of various cancers over time.
- Neurological and developmental effects: Children are especially vulnerable to neurological and developmental damage from exposure to these toxins.
Methods for Detecting and Removing Toxic Chemicals from Buildings
Identifying and removing toxic chemicals from affected buildings requires a multi-pronged approach, combining advanced testing methodologies with specialized remediation techniques. The process involves careful assessment, thorough decontamination, and often, the demolition of severely affected structures.
- Air quality testing: Advanced air quality monitoring techniques are employed to detect the presence and concentration of various chemicals in the air.
- Material sampling: Samples of building materials are collected and analyzed to determine the extent of contamination within porous surfaces.
- Remediation techniques: Methods range from air scrubbing systems to remove volatile compounds from the air, to complete decontamination of surfaces and materials, to the more drastic measure of demolition and disposal of severely contaminated buildings.
The Role of Government Agencies and Environmental Regulations
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), along with other relevant state and local agencies, plays a crucial role in overseeing the cleanup efforts, monitoring the contamination levels, and enforcing environmental regulations. The adequacy of current regulations in handling this type of widespread, long-term contamination remains a subject of intense scrutiny and debate. Future regulations should incorporate lessons learned from this incident to prevent similar catastrophes. Improved protocols for the transportation and handling of hazardous materials are also critical.
Long-Term Impacts on Property Values and Community Wellbeing
The prolonged presence of toxic chemicals has far-reaching consequences that extend beyond immediate health concerns. Property values in the affected areas are likely to plummet, causing significant economic hardship for residents. The psychological and social impacts on the community are equally devastating.
- Economic losses: Decreased property values lead to significant economic losses, impacting the financial stability of affected families and the community as a whole.
- Community displacement: Some residents might be forced to relocate due to the health risks and economic instability.
- Long-term mental health concerns: The uncertainty and anxiety surrounding long-term contamination can significantly impact the mental health of residents.
Conclusion
The Ohio train derailment's legacy of toxic chemical contamination poses a severe and long-lasting threat to buildings and the surrounding communities. The persistent nature of these chemicals, coupled with the associated health risks and economic consequences, highlights the urgent need for thorough cleanup efforts, ongoing monitoring, and significant improvements in safety regulations to prevent future incidents. Continued vigilance and advocacy are crucial to ensure the safety and wellbeing of affected residents. We must prioritize preventing future chemical spills and protecting communities from environmental hazards by demanding stronger regulations and responsible handling of hazardous materials. Stay informed about the ongoing situation and advocate for stronger environmental protections regarding the Ohio Train Derailment Toxic Chemicals.

Featured Posts
-
 The Implications Of Newsoms Toxic Democrats Statement
Apr 25, 2025
The Implications Of Newsoms Toxic Democrats Statement
Apr 25, 2025 -
 Hollywood Strike Actors Join Writers Bringing Production To A Halt
Apr 25, 2025
Hollywood Strike Actors Join Writers Bringing Production To A Halt
Apr 25, 2025 -
 Trumps Attack On Currency Manipulation Implications For The Krw Usd Exchange Rate
Apr 25, 2025
Trumps Attack On Currency Manipulation Implications For The Krw Usd Exchange Rate
Apr 25, 2025 -
 Meteorologist Josh Fitzpatrick A Deep Dive Into The Sextortion Allegations
Apr 25, 2025
Meteorologist Josh Fitzpatrick A Deep Dive Into The Sextortion Allegations
Apr 25, 2025 -
 Dope Thief Episode 6 Will The Series Recover Before The Finale
Apr 25, 2025
Dope Thief Episode 6 Will The Series Recover Before The Finale
Apr 25, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Implementing A Robust System For Corrections And Clarifications
Apr 30, 2025
Implementing A Robust System For Corrections And Clarifications
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Mastering Corrections And Clarifications Best Practices For Journalists And Writers
Apr 30, 2025
Mastering Corrections And Clarifications Best Practices For Journalists And Writers
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Kaba Shooting Jury Delivers Not Guilty Verdict For Met Police Officer
Apr 30, 2025
Kaba Shooting Jury Delivers Not Guilty Verdict For Met Police Officer
Apr 30, 2025 -
 How To Issue Corrections And Clarifications Effectively
Apr 30, 2025
How To Issue Corrections And Clarifications Effectively
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Aaj Ka Love Rashifal 14 March 2025
Apr 30, 2025
Aaj Ka Love Rashifal 14 March 2025
Apr 30, 2025
