Record-Breaking Forest Loss: Wildfires Intensify Global Deforestation
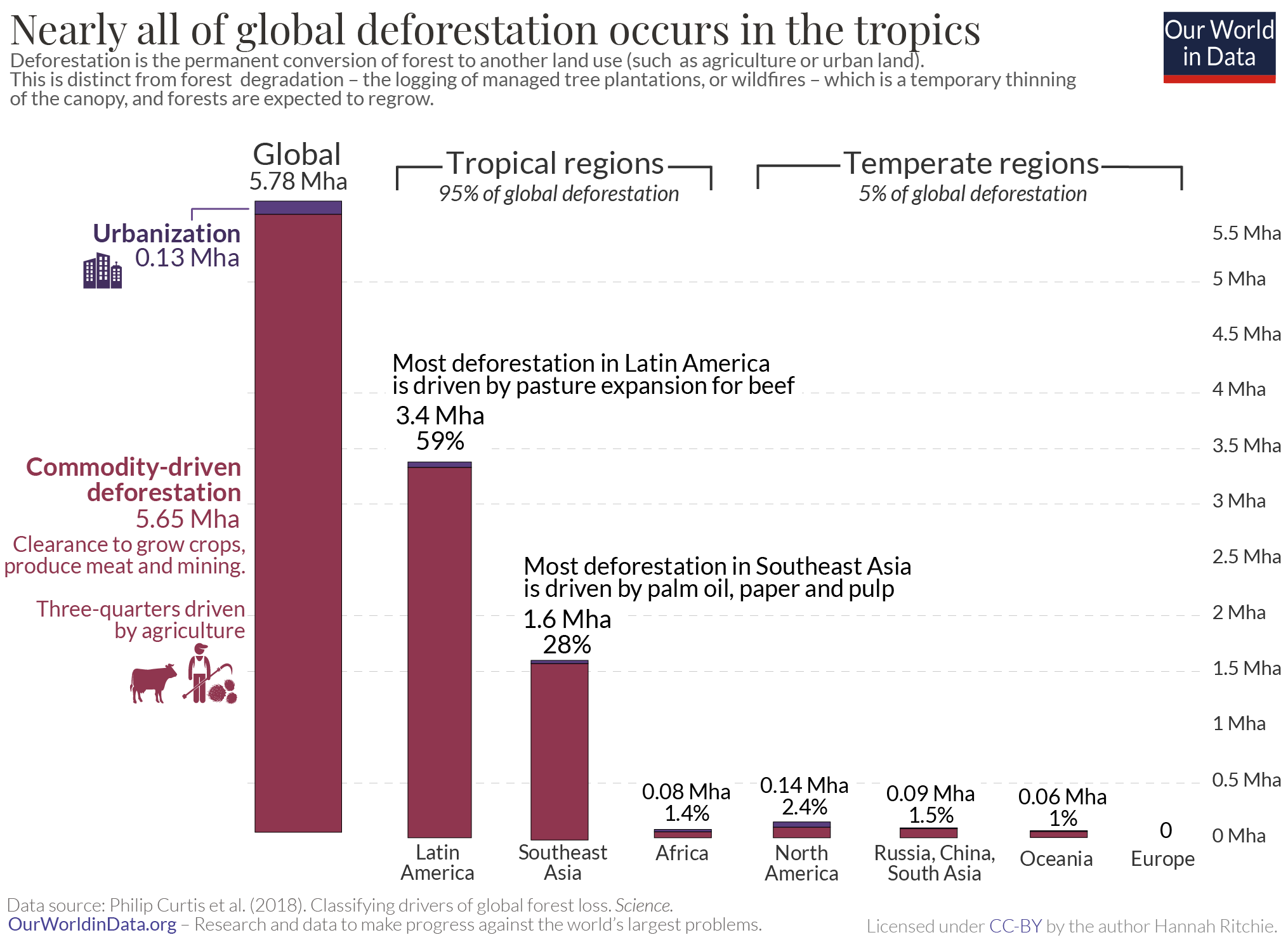
Table of Contents
The Devastating Impact of Wildfires on Forest Ecosystems
H3: Increased Frequency and Intensity of Wildfires:
Climate change is a primary driver behind the increased frequency and intensity of wildfires globally. Rising global temperatures create drier conditions, extending fire seasons and making forests more susceptible to ignition. This leads to larger, more destructive wildfires that burn hotter and faster.
- Examples: Australia experienced devastating bushfires in 2019-2020, burning millions of hectares. The western United States has seen record-breaking wildfire seasons in recent years, with significant acreage lost in California, Oregon, and Washington. The Amazon rainforest, a crucial carbon sink, has also suffered extensive damage from increasingly frequent and intense wildfires.
- Scientific Data: Numerous scientific studies correlate rising global temperatures with increased wildfire activity, demonstrating a clear link between climate change and wildfire intensity. Data from NASA and other organizations show a marked increase in the area burned globally each year.
- Keyword integration: "Climate Change," "wildfire intensity," "arid conditions," "fire seasons," "global warming".
H3: The Scope of Forest Loss Due to Wildfires:
The scale of forest loss due to wildfires is staggering. Millions of hectares of forests are destroyed annually, releasing vast amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere and contributing significantly to global warming.
- Statistics: According to the Global Forest Watch, millions of hectares of forest were lost to wildfires in 2023 alone, representing a significant increase compared to previous years. Specific data for different regions should be included here, citing reputable sources like the FAO or WWF.
- Regional Impacts: The impacts are not evenly distributed. Regions with unique ecosystems, like boreal forests and tropical rainforests, are particularly vulnerable, suffering disproportionate losses.
- Keyword integration: "hectares lost," "deforestation statistics," "forest fire damage," "carbon emissions from wildfires".
H3: Long-Term Ecological Consequences:
The ecological consequences of wildfire-driven deforestation extend far beyond the immediate destruction. These events have profound and long-lasting impacts on biodiversity, soil health, and carbon sequestration.
- Biodiversity Loss: Wildfires destroy habitats, leading to species extinction and population decline. Endangered species are particularly vulnerable, as their already limited habitats are further fragmented and destroyed.
- Soil Degradation: Intense heat from wildfires can destroy soil structure, leading to erosion, nutrient loss, and reduced fertility. This impacts long-term forest regeneration.
- Disruption of Carbon Cycles: Forests act as crucial carbon sinks, absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere. Wildfires release this stored carbon, contributing to climate change and creating a vicious cycle of escalating environmental damage.
- Keyword integration: "biodiversity loss," "carbon emissions," "soil degradation," "ecological damage," "habitat destruction".
Beyond Wildfires: Other Contributing Factors to Global Deforestation
H3: Illegal Logging and Deforestation:
Illegal logging and unsustainable forestry practices are significant drivers of deforestation, often working in conjunction with wildfires to accelerate forest loss. These practices often target valuable timber species, leaving behind degraded landscapes susceptible to wildfires.
- Statistics: Reports from organizations like Interpol and the UN highlight the scale of illegal logging globally, estimating the value of illegally harvested timber in the billions of dollars annually.
- Regional Focus: Specific regions like the Amazon, Southeast Asia, and parts of Africa are particularly hard-hit by illegal logging, fueling deforestation and biodiversity loss.
- Keyword integration: "illegal logging," "unsustainable forestry," "timber industry," "deforestation drivers".
H3: Agricultural Expansion and Land Conversion:
The expansion of agriculture, driven by the growing global demand for food and commodities, is a major cause of deforestation. Land conversion for agriculture, including palm oil plantations, soy farms, and cattle ranching, leads to widespread forest clearing.
- Examples: The expansion of palm oil plantations in Southeast Asia is a prime example of agriculture-driven deforestation, resulting in the loss of vast tracts of rainforest and significant biodiversity. Similarly, cattle ranching in the Amazon is a significant contributor to deforestation.
- Urbanization: Urban sprawl also encroaches on forested areas, contributing to deforestation and habitat loss.
- Keyword integration: "agricultural expansion," "land conversion," "urban sprawl," "palm oil deforestation," "cattle ranching".
H3: Mining and Infrastructure Development:
Mining operations and infrastructure development projects, such as road construction and dam building, often involve significant deforestation. These activities fragment forest landscapes, making them more vulnerable to wildfires and disrupting ecological processes.
- Examples: Mining for minerals and precious metals often leads to clear-cutting of forests to access resources. The construction of roads opens up previously inaccessible areas to logging and agriculture.
- Environmental Impact Assessments: While environmental impact assessments are often required, their effectiveness varies, and inadequate enforcement can lead to significant environmental damage.
- Keyword integration: "mining activities," "infrastructure development," "road construction," "environmental impact," "deforestation impacts".
Combating Global Deforestation: Solutions and Strategies
H3: Improved Wildfire Management and Prevention:
Effective wildfire management and prevention strategies are crucial in mitigating the impact of wildfires on forests. This includes investing in improved early warning systems, implementing controlled burns to reduce fuel loads, and improving community engagement in fire prevention efforts.
- Early Warning Systems: Advanced technology, such as satellite monitoring and weather forecasting, can help predict and respond to wildfires more effectively.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in fire prevention and suppression efforts is essential for effective wildfire management.
- Keyword integration: "wildfire prevention," "controlled burns," "early warning systems," "fire management".
H3: Sustainable Forestry Practices and Reforestation Efforts:
Sustainable forestry practices, including selective logging and reforestation initiatives, are vital for restoring and protecting forests. Certification schemes, such as the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC), help ensure that timber is sourced sustainably.
- Reforestation Projects: Large-scale reforestation projects can help restore degraded lands and increase carbon sequestration. Successful examples from around the world should be highlighted here.
- Sustainable Logging: Implementing sustainable logging practices minimizes the impact on forest ecosystems and ensures long-term forest health.
- Keyword integration: "sustainable forestry," "reforestation," "forest conservation," "FSC certification," "sustainable logging".
H3: Policy and International Cooperation:
Strong environmental policies and international cooperation are essential for tackling global deforestation. This includes enforcing laws against illegal logging, promoting sustainable land management practices, and supporting international agreements like the Paris Agreement.
- Policy Instruments: Government policies that incentivize sustainable forestry and penalize deforestation are crucial. Examples of successful policies from different countries should be mentioned.
- International Agreements: International collaboration and agreements are essential to address the transboundary nature of deforestation and climate change.
- Keyword integration: "environmental policy," "international cooperation," "climate agreements," "conservation policies," "forest protection policies".
Conclusion
Record-breaking forest loss, fueled by increasingly intense wildfires and other contributing factors, presents a significant global challenge. The consequences— biodiversity loss, climate change exacerbation, and disruption of crucial ecosystem services—are far-reaching and demand urgent action. We must act now to prevent global deforestation. Learn more about the issue and support organizations working to protect our planet's precious forests. Support sustainable practices, advocate for stronger policies, and join the fight against deforestation to ensure a healthier future for generations to come. Let's work together to combat global forest loss and preserve the vital role forests play in our world.

Featured Posts
-
 High Cost Of Living Impacts Canadian Auto Theft Prevention
May 24, 2025
High Cost Of Living Impacts Canadian Auto Theft Prevention
May 24, 2025 -
 11 Down Amsterdam Stock Exchange Experiences Third Day Of Heavy Losses
May 24, 2025
11 Down Amsterdam Stock Exchange Experiences Third Day Of Heavy Losses
May 24, 2025 -
 Philips Annual General Meeting Of Shareholders Key Highlights
May 24, 2025
Philips Annual General Meeting Of Shareholders Key Highlights
May 24, 2025 -
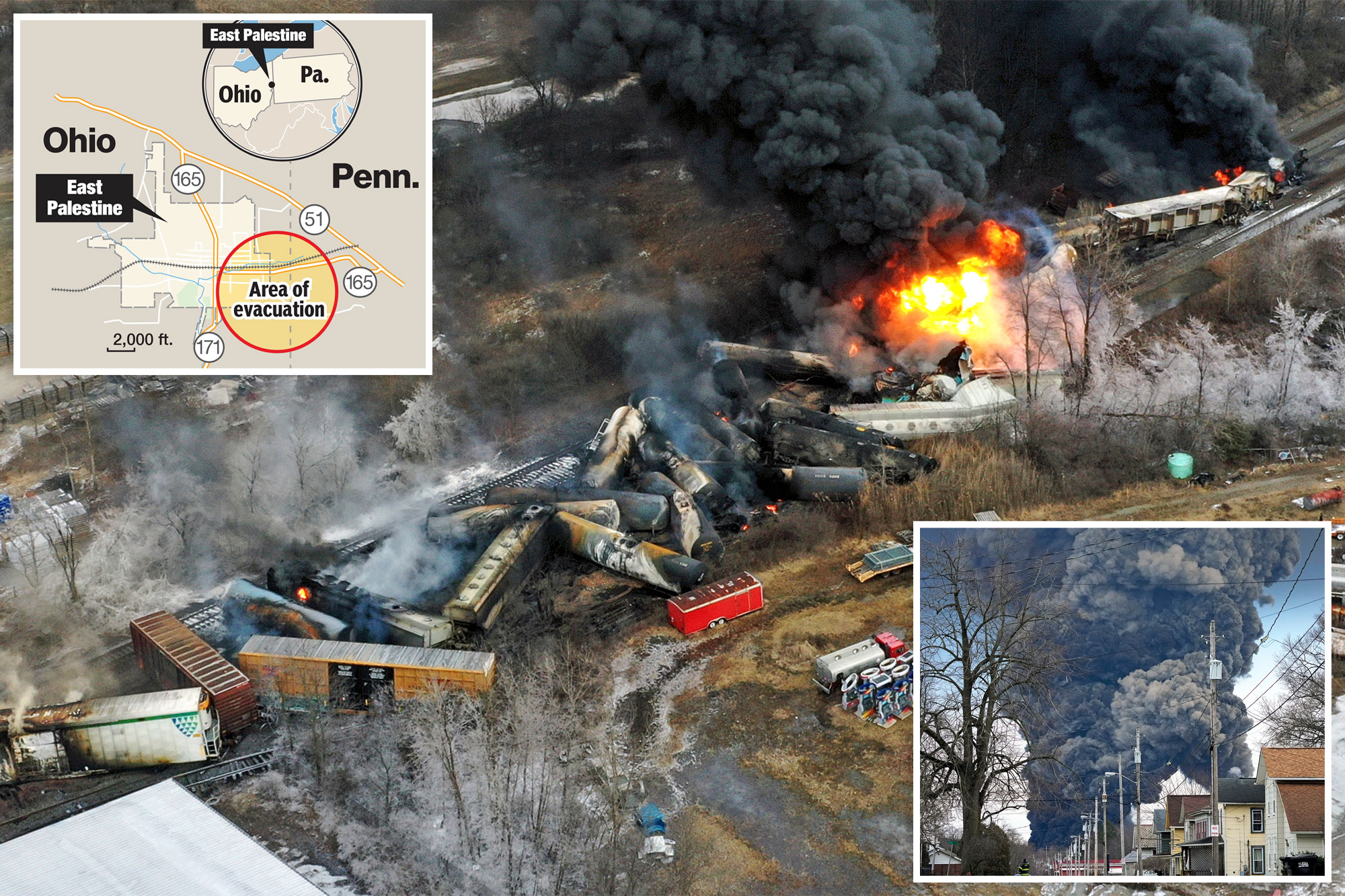 Long Term Effects Of Toxic Chemicals From Ohio Train Derailment On Buildings
May 24, 2025
Long Term Effects Of Toxic Chemicals From Ohio Train Derailment On Buildings
May 24, 2025 -
 Rayakan Seni Dan Otomotif Di Porsche Indonesia Classic Art Week 2025
May 24, 2025
Rayakan Seni Dan Otomotif Di Porsche Indonesia Classic Art Week 2025
May 24, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Kermit The Frog Commencement Speaker At University Of Maryland In 2025
May 24, 2025
Kermit The Frog Commencement Speaker At University Of Maryland In 2025
May 24, 2025 -
 Kermit The Frog 2025 University Of Maryland Graduation Speaker
May 24, 2025
Kermit The Frog 2025 University Of Maryland Graduation Speaker
May 24, 2025 -
 Kazakhstan Defeats Australia In Billie Jean King Cup Qualifying Tie
May 24, 2025
Kazakhstan Defeats Australia In Billie Jean King Cup Qualifying Tie
May 24, 2025 -
 Hi Ho Kermit University Of Marylands 2025 Commencement Speaker Announced
May 24, 2025
Hi Ho Kermit University Of Marylands 2025 Commencement Speaker Announced
May 24, 2025 -
 Kermit The Frog 2025 University Of Maryland Commencement Speaker
May 24, 2025
Kermit The Frog 2025 University Of Maryland Commencement Speaker
May 24, 2025
