Rio Tinto's Pilbara Project: Addressing Environmental Concerns And Criticisms

Table of Contents
Water Management in the Pilbara
Water Usage and Depletion
The Pilbara region is arid and semi-arid, making water a precious resource. Rio Tinto's iron ore mining operations in the Pilbara consume significant quantities of water, raising concerns about potential depletion of local water resources. Precise figures vary depending on the year and specific operations, but it's undeniable that substantial water usage is a key environmental challenge. This impacts both surface water sources and groundwater aquifers.
- Water conservation strategies: Rio Tinto has implemented several water conservation strategies, including:
- Improved water efficiency in mining processes.
- Rainwater harvesting and storage.
- Leak detection and repair programs.
- Investment in technologies to reduce water usage per tonne of iron ore produced.
- Challenges and Future Plans: Despite these efforts, challenges remain, particularly in managing water usage during periods of drought. Rio Tinto is continuing to invest in research and development to further improve water efficiency and explore alternative water sources.
Water Recycling and Reuse Initiatives
Rio Tinto has invested heavily in water recycling and reuse technologies to minimize its reliance on fresh water sources. These initiatives play a crucial role in reducing the overall water footprint of the Pilbara operations.
- Examples of recycled water usage: Recycled water is used extensively in dust suppression, mine site operations, and even in some instances for process water.
- Effectiveness of Initiatives: The effectiveness of these initiatives is constantly monitored and evaluated. Data on the percentage of water recycled and reused is regularly reported, demonstrating the progress made in reducing the overall water demand.
Impact on Local Ecosystems
The extraction of water from the Pilbara's ecosystem has potential consequences for local flora and fauna. Changes in water availability can affect the distribution and abundance of plant and animal species.
- Mitigation Strategies: Rio Tinto has implemented several mitigation strategies to minimize the ecological impacts of water extraction, including:
- Environmental flow requirements in water management plans.
- Habitat restoration projects.
- Monitoring programs to track the health of local ecosystems.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Climate Change
Carbon Footprint of Pilbara Operations
Iron ore mining and transportation are energy-intensive activities, contributing significantly to greenhouse gas emissions. Rio Tinto's Pilbara operations have a substantial carbon footprint, with CO2 emissions primarily stemming from energy consumption in mining, processing, and transportation.
- Emission Reduction Targets and Strategies: Rio Tinto has set ambitious targets for reducing its greenhouse gas emissions. Strategies include:
- Transitioning to renewable energy sources (solar, wind).
- Investing in energy-efficient technologies.
- Exploring carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies.
Efforts to Reduce Emissions
Rio Tinto is actively pursuing various initiatives to reduce its emissions and improve its environmental performance.
- Examples of successful emission reduction projects: The company has made significant investments in renewable energy projects, resulting in a reduction of emissions from its operations. Specific examples can be found in their sustainability reports.
- Challenges in Achieving Emission Reduction Goals: Transitioning to a low-carbon future poses significant challenges, including the high capital cost of renewable energy infrastructure and the technological hurdles associated with CCS.
Future Strategies for Climate Change Mitigation
Rio Tinto's long-term strategy involves further decarbonization of its operations and a commitment to achieving net-zero emissions.
- Potential Future Technologies and Strategies: Future strategies may involve exploring hydrogen-powered vehicles for transportation, further advancements in renewable energy technologies, and wider adoption of CCS technology.
Biodiversity and Habitat Loss
Impact on Native Flora and Fauna
Mining activities can lead to habitat loss and fragmentation, impacting local biodiversity. The Pilbara region is home to a variety of unique flora and fauna, many of which are vulnerable to disturbance.
- Examples of Endangered Species Affected: Specific examples of affected species should be mentioned, and information regarding their conservation status can be found in environmental impact assessments.
- Habitat Restoration Efforts: Rio Tinto is involved in habitat restoration projects aimed at mitigating the impact of mining on biodiversity.
Biodiversity Conservation Programs
Rio Tinto implements various biodiversity conservation programs to offset the impact of its operations.
- Specific Examples of Successful Conservation Programs: Details about these programs and their effectiveness should be included, referencing any published case studies or reports.
- Areas for Improvement: Continuous improvement is essential, and areas where further efforts are needed should be acknowledged.
Collaboration with Conservation Organizations
Rio Tinto collaborates with several conservation organizations and government agencies to enhance its biodiversity conservation efforts.
- Key Partners and Collaborative Projects: Details about these partnerships and their collaborative projects should be listed.
Addressing Community Concerns and Stakeholder Engagement
Community Consultation and Dialogue
Rio Tinto engages with local communities and stakeholders through various consultation and dialogue mechanisms.
- Community Engagement Processes and Forums: Details of these engagement methods need to be clearly explained.
Transparency and Accountability
Rio Tinto is committed to transparency and accountability in its environmental performance.
- Reporting Mechanisms and External Audits: Transparency requires clear and publicly accessible reports, along with details of any external audits or verification processes.
Addressing Social and Economic Impacts
The Pilbara project has significant social and economic impacts on local communities.
- Highlighting Both Positive and Negative Impacts: A balanced perspective on both the benefits and drawbacks is crucial for a comprehensive understanding.
Conclusion
Rio Tinto's Pilbara Project presents significant environmental challenges, including water usage, greenhouse gas emissions, and biodiversity impacts. However, the company has implemented various strategies to mitigate these concerns, investing in water recycling, renewable energy, and biodiversity conservation. While progress has been made, ongoing challenges remain, and continued improvement is needed. Further transparency and robust community engagement are crucial for responsible mining practices. Learn more about Rio Tinto's commitment to sustainable mining in the Pilbara and explore the challenges and solutions related to Rio Tinto's Pilbara Project by visiting their website and accessing their sustainability reports.

Featured Posts
-
 Hai Lo Vuong Tren Dau Noi Usb Chuc Nang Va Giai Dap Thac Mac
May 22, 2025
Hai Lo Vuong Tren Dau Noi Usb Chuc Nang Va Giai Dap Thac Mac
May 22, 2025 -
 Core Weave Crwv Stock Soars Analyzing The Reasons For The Recent Increase
May 22, 2025
Core Weave Crwv Stock Soars Analyzing The Reasons For The Recent Increase
May 22, 2025 -
 Abn Amro Ziet Forse Groei In Occasionverkopen Impact Van Meer Autobezit
May 22, 2025
Abn Amro Ziet Forse Groei In Occasionverkopen Impact Van Meer Autobezit
May 22, 2025 -
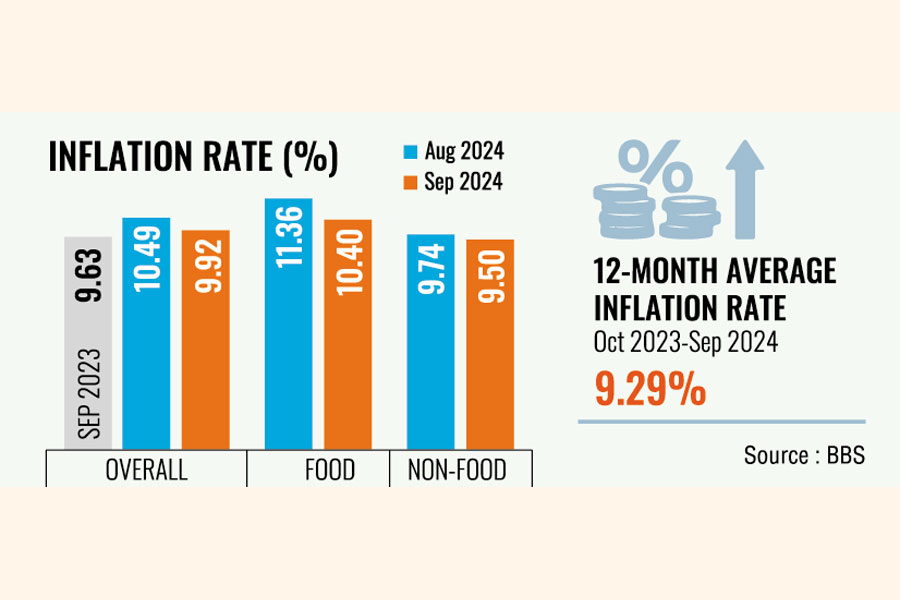 Food Prices Outpace Inflation For Third Consecutive Month
May 22, 2025
Food Prices Outpace Inflation For Third Consecutive Month
May 22, 2025 -
 Kenny Picketts Homecoming Game A Redemption Story For The Quarterback
May 22, 2025
Kenny Picketts Homecoming Game A Redemption Story For The Quarterback
May 22, 2025
