Russia's Economy Under Putin: Total War Mobilization
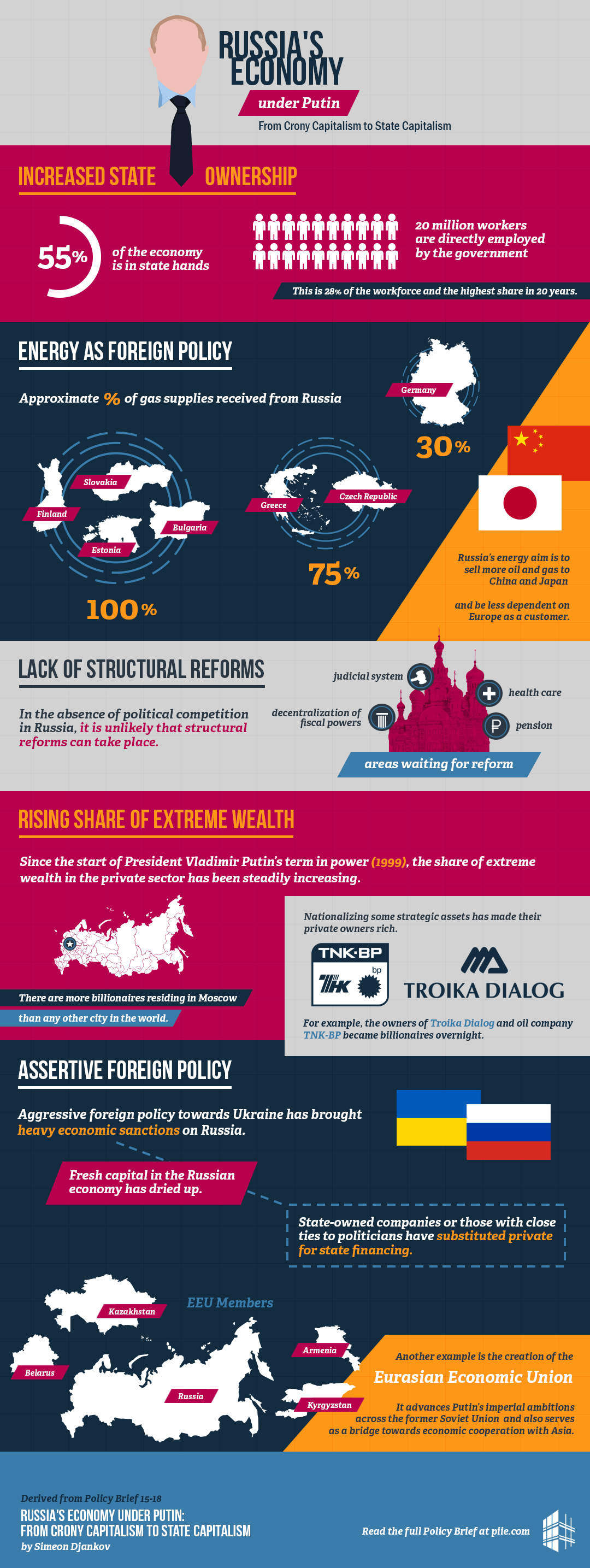
Table of Contents
Sanctions and Their Economic Impact
The West's response to the invasion has involved a barrage of sanctions designed to cripple the Russian economy. These sanctions represent a significant challenge to Putin's economic strategy and have profoundly altered the landscape of the Russian economy.
Financial Sanctions and Capital Flight
Financial sanctions have targeted major Russian banks, freezing assets and limiting access to the SWIFT international payment system. This has led to a significant capital flight, as wealthy individuals and businesses moved their assets out of the country to protect them from seizure.
- Specific Sanctions: The US, EU, UK, and Canada have imposed numerous sanctions, including asset freezes on prominent individuals and entities, restrictions on access to foreign currency, and limitations on investment in Russian assets.
- Impact on the Ruble: The ruble initially experienced a sharp devaluation, though it later stabilized due to government intervention and the demand for rubles to pay for Russian energy exports. However, this stability masks underlying vulnerabilities. Inflation remains a significant concern, impacting the purchasing power of ordinary citizens.
- Limited Access to International Markets: Sanctions have significantly restricted Russia's access to international financial markets, making it more difficult to borrow money and invest in new projects. This hampers economic growth and development.
Trade Restrictions and Supply Chain Disruptions
Beyond financial sanctions, sweeping trade restrictions have disrupted Russia's import and export sectors. These restrictions have impacted key industries, particularly energy, technology, and manufacturing.
- Disrupted Supply Chains: Sanctions have severely limited Russia's access to crucial imported goods, leading to shortages and increased prices for consumers. This is especially true for technological components and advanced machinery.
- Reliance on Foreign Technology: Russia's significant reliance on imported technology has been exposed, forcing the country to explore expensive and often less effective alternatives. This underscores the limitations of import substitution in a technologically advanced global economy.
- Import Substitution Strategies: The Kremlin has prioritized import substitution strategies, aiming to boost domestic production of essential goods and reduce dependence on Western countries. However, the success of these strategies remains highly debated, hampered by a lack of skilled labor and advanced technology.
Military Spending and Resource Reallocation
The war in Ukraine has necessitated a massive increase in military spending, diverting resources away from other crucial sectors of the Russian economy.
Increased Defense Budget and Economic Prioritization
The Russian defense budget has seen a dramatic increase, consuming a significant portion of the GDP. This has resulted in a reallocation of resources, with social programs and infrastructure development often taking a backseat.
- GDP Allocation to Defense: The precise allocation of GDP to defense is a subject of debate, with varying figures reported by different sources. However, it's clear that defense spending has risen substantially, crowding out other priorities.
- Opportunity Cost: The opportunity cost of prioritizing military spending over social programs such as healthcare, education, and infrastructure development is considerable, potentially impacting Russia's long-term economic growth and human capital development.
- Government Spending Priorities: The shift in government spending priorities reflects the Kremlin's prioritization of military security over broader societal well-being, signaling a significant economic trade-off.
Mobilization and its Labor Market Effects
Partial mobilization has further strained the Russian economy, creating labor shortages and impacting productivity across multiple sectors.
- Effects on Various Sectors: The mobilization of reservists has affected various sectors, including agriculture, manufacturing, and transportation, leading to workforce shortages and disruptions in production.
- Impact on Internal Migration: The mobilization has also influenced internal migration patterns, as individuals flee mobilization areas, leading to further labor market imbalances.
- Government Initiatives: The government has introduced measures to address the labor shortage, but their effectiveness remains limited.
Economic Diversification and Resilience Strategies
Facing Western sanctions, Russia is attempting to diversify its economy and reduce its dependence on Western countries.
Increased Focus on Domestic Production and Import Substitution
Russia is prioritizing domestic production and import substitution, aiming to develop its own industries and reduce reliance on foreign goods and technologies.
- Industries Targeted for Growth: Key industries targeted for growth include agriculture, energy (particularly natural gas), and manufacturing.
- Success of Strategies: The success of these strategies remains uncertain, facing challenges including technological backwardness, limited access to capital, and skilled labor shortages.
- Technological Dependence: Russia's continued dependence on foreign technology, particularly in high-tech sectors, remains a significant hurdle to effective diversification and import substitution.
Strengthening Ties with Emerging Economies
Russia is strengthening economic ties with emerging economies, particularly China, India, and other BRICS nations, to mitigate the effects of Western sanctions.
- Trade Agreements and Partnerships: Russia has actively pursued new trade agreements and partnerships with countries outside the West.
- Long-Term Implications: The long-term implications of this reorientation of trade relations are still unfolding, but it presents both opportunities and risks for the Russian economy.
- Potential Risks and Limitations: This strategy has inherent risks, including dependence on a limited number of trading partners and potentially less favorable trade terms.
Conclusion
Russia's economy under Putin faces unprecedented challenges due to the total war mobilization resulting from the invasion of Ukraine. The impact of Western sanctions, the enormous increase in military spending, and the resulting economic adjustments have created significant vulnerabilities. The Kremlin's attempts at diversification and strengthening ties with emerging economies are mitigating factors, but the long-term effects remain uncertain and the challenges are substantial. The interplay between political decisions, military conflict, and economic outcomes in Russia is complex and deserves further investigation. Learn more about Russia's economy under Putin and the effects of total war mobilization by exploring resources from reputable economic analysis organizations.

Featured Posts
-
 Space X Starbase Granted Official City Status In Texas
May 29, 2025
Space X Starbase Granted Official City Status In Texas
May 29, 2025 -
 Massive Cruise Ship Docks In Liverpool Today
May 29, 2025
Massive Cruise Ship Docks In Liverpool Today
May 29, 2025 -
 Understanding High Stock Valuations Insights From Bof A
May 29, 2025
Understanding High Stock Valuations Insights From Bof A
May 29, 2025 -
 Kondisi Cuaca Aktual And Prakiraan Sumatra Utara Medan Karo Nias Toba
May 29, 2025
Kondisi Cuaca Aktual And Prakiraan Sumatra Utara Medan Karo Nias Toba
May 29, 2025 -
 Winning With Probopass A Pokemon Tcg Pocket Deck Guide
May 29, 2025
Winning With Probopass A Pokemon Tcg Pocket Deck Guide
May 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Boxing Munguia Dominates Surace In Rematch Despite Limited Improvement
May 31, 2025
Boxing Munguia Dominates Surace In Rematch Despite Limited Improvement
May 31, 2025 -
 Munguias Positive Testosterone Test Surace Demands Win Overturned
May 31, 2025
Munguias Positive Testosterone Test Surace Demands Win Overturned
May 31, 2025 -
 Boxing Results Munguias Improved Performance Secures Rematch Victory
May 31, 2025
Boxing Results Munguias Improved Performance Secures Rematch Victory
May 31, 2025 -
 Jaime Munguia Avenges Ko Loss Dominant Decision Win Over Bruno Segura
May 31, 2025
Jaime Munguia Avenges Ko Loss Dominant Decision Win Over Bruno Segura
May 31, 2025 -
 Munguia Vs Surace Ii A Dominant Rematch Win
May 31, 2025
Munguia Vs Surace Ii A Dominant Rematch Win
May 31, 2025
