School Desegregation: Analyzing The Impact Of The Justice Department's Decision

Table of Contents
School desegregation refers to the dismantling of racially segregated school systems, a practice legally sanctioned for decades. Landmark Supreme Court cases, most notably Brown v. Board of Education (1954), declared state-sponsored segregation in public schools unconstitutional, marking a pivotal moment in the American civil rights movement. This ruling, however, was just the beginning of a long and arduous struggle for equal educational opportunity, a struggle in which the Justice Department played – and continues to play – a crucial role.
The Legal Foundation of School Desegregation
The Brown v. Board of Education decision provided the legal basis for challenging state-sponsored segregation. The Supreme Court's unanimous ruling declared that “separate educational facilities are inherently unequal,” fundamentally altering the legal landscape and setting the stage for the Justice Department to intervene in cases of resistance to desegregation. The Department’s role wasn't merely passive; it actively pursued litigation and secured court orders mandating desegregation across numerous school districts.
- Key Supreme Court cases following Brown v. Board of Education: Green v. County School Board (1968), Swann v. Charlotte-Mecklenburg Board of Education (1971), and Milliken v. Bradley (1974) further shaped the legal framework surrounding school desegregation, clarifying the responsibilities of school districts and the permissible remedies for achieving integration.
- Examples of Justice Department interventions: The Department filed numerous lawsuits against school districts resisting desegregation, employing various strategies, including court-ordered busing and the implementation of desegregation plans.
- Significant legal strategies: These included the use of statistical evidence to demonstrate discriminatory practices, challenging discriminatory school assignment policies, and advocating for equitable resource allocation across previously segregated schools.
The Impact of Desegregation on Educational Outcomes
The impact of school desegregation on educational outcomes remains a subject of ongoing debate. While integration aimed to create equal educational opportunities and improve academic achievement for all students, particularly African American students, the results have been complex and varied.
- Statistical data: While some studies show improved academic performance in integrated schools, particularly for minority students, others have found more modest effects or even negative outcomes in certain contexts. These variations often depend on factors beyond simply integration, such as resource allocation, teacher quality, and socioeconomic factors within the student population.
- Long-term effects: Long-term studies examining the effects of desegregation on educational attainment reveal a mixed picture. While some research suggests positive long-term impacts on educational attainment and future earnings for African American students, the benefits haven't been universally experienced, and disparities persist.
- Socioeconomic factors: Socioeconomic status significantly influences educational outcomes. Desegregation, while aiming to address racial disparities, doesn't automatically eliminate the impact of poverty or other socioeconomic disadvantages on student achievement.
The Evolving Role of the Justice Department in School Desegregation
The Justice Department's approach to school desegregation has evolved significantly over time, reflecting shifts in policy priorities and legal interpretations. While the early focus was on dismantling de jure segregation (segregation mandated by law), the later focus shifted towards addressing de facto segregation (segregation resulting from residential patterns and other factors).
- Recent Justice Department actions: Recent actions have involved investigating instances of discriminatory school practices, intervening in cases of disproportionate discipline of minority students, and addressing disparities in school funding.
- Current legal challenges: Contemporary challenges to school integration include ongoing residential segregation, the rise of charter schools (sometimes exacerbating segregation), and persistent achievement gaps.
- Effectiveness of current approaches: The effectiveness of current approaches to addressing these challenges remains a subject of ongoing discussion and research. The lack of a unified national strategy and the complexities of addressing de facto segregation pose considerable obstacles.
The Socioeconomic and Political Ramifications of School Desegregation
The societal impact of school desegregation has been profound, extending far beyond the classroom. The desegregation movement played a critical role in shaping race relations, social mobility, and the political landscape.
- Social and political consequences: Desegregation ignited intense social and political conflict, with resistance often leading to violence and social upheaval. The long-term effects on community relations have been varied, with some communities experiencing improved relations while others remain deeply divided along racial lines.
- White flight and re-segregation: The phenomenon of "white flight," where white families moved from integrated schools to more segregated ones, contributed significantly to the persistence of de facto segregation and hampered efforts to achieve truly integrated schools.
- Long-term effects on community relations: The long-term effects on community relations are complex and varied, influenced by local contexts, policies, and social dynamics.
Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of School Desegregation
The Justice Department's role in school desegregation has been pivotal, yet the journey towards achieving racial equity in education remains incomplete. The legal battles, societal shifts, and evolving challenges highlight the complexities inherent in dismantling deeply entrenched systems of inequality. While significant progress has been made, persistent disparities in school resources, academic achievement, and disciplinary practices demand continued attention.
Continue the fight for effective school desegregation. Advocate for equitable school desegregation policies. Research the ongoing impact of school desegregation. Learn more about this critical issue by visiting organizations like the NAACP Legal Defense and Educational Fund and the ACLU. Together, we can work towards creating truly integrated and equitable schools for all students.

Featured Posts
-
 Sardou Et Macron Tensions Au Diner
May 03, 2025
Sardou Et Macron Tensions Au Diner
May 03, 2025 -
 Emek Ve Dayanisma Guenue Gecmisten Guenuemueze Arbede Oernekleri
May 03, 2025
Emek Ve Dayanisma Guenue Gecmisten Guenuemueze Arbede Oernekleri
May 03, 2025 -
 Fortnite Update 34 21 Server Downtime And Whats New
May 03, 2025
Fortnite Update 34 21 Server Downtime And Whats New
May 03, 2025 -
 Alastthmar Waltjart Wzyr Altjart Ybhth Afaq Alteawn Me Adhrbyjan
May 03, 2025
Alastthmar Waltjart Wzyr Altjart Ybhth Afaq Alteawn Me Adhrbyjan
May 03, 2025 -
 Joseph La Nouvelle Serie Policiere De Tf 1 Vaut Elle Le Detour
May 03, 2025
Joseph La Nouvelle Serie Policiere De Tf 1 Vaut Elle Le Detour
May 03, 2025
Latest Posts
-
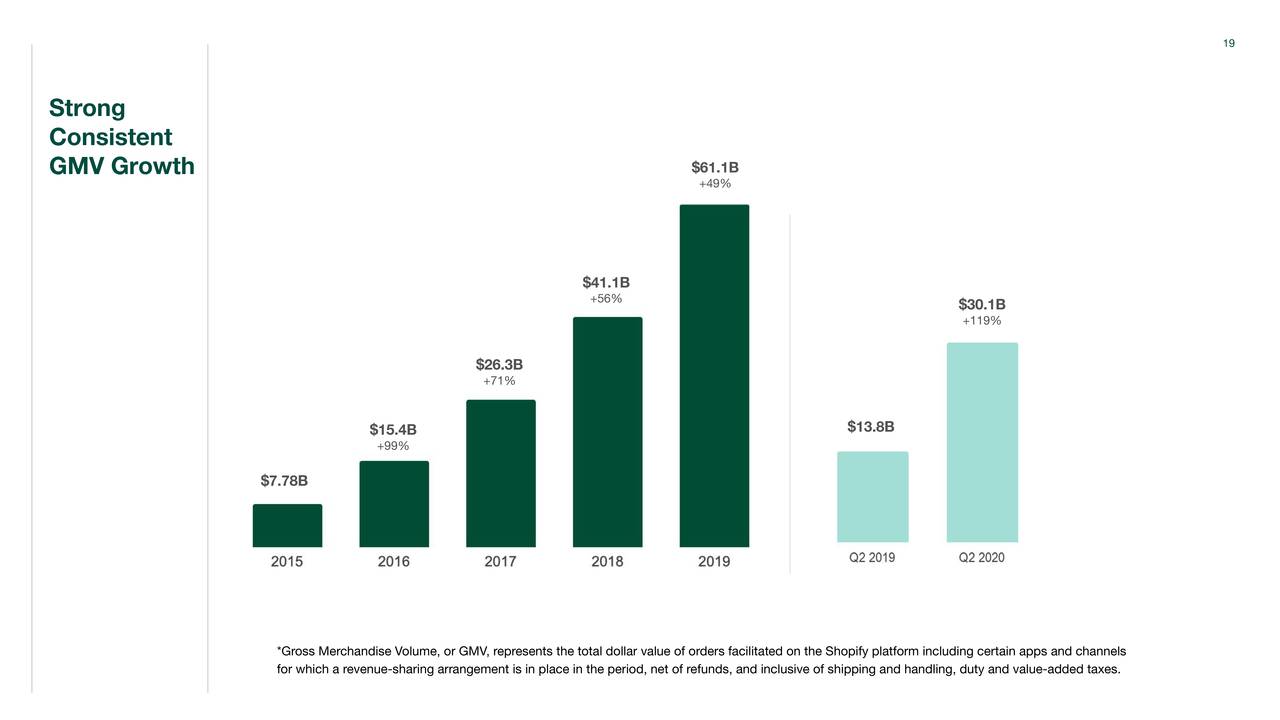 How The New Shopify Lifetime Revenue Share Affects Developers Earnings
May 04, 2025
How The New Shopify Lifetime Revenue Share Affects Developers Earnings
May 04, 2025 -
 Shopify Developer Program Overhaul Understanding The New Revenue Structure
May 04, 2025
Shopify Developer Program Overhaul Understanding The New Revenue Structure
May 04, 2025 -
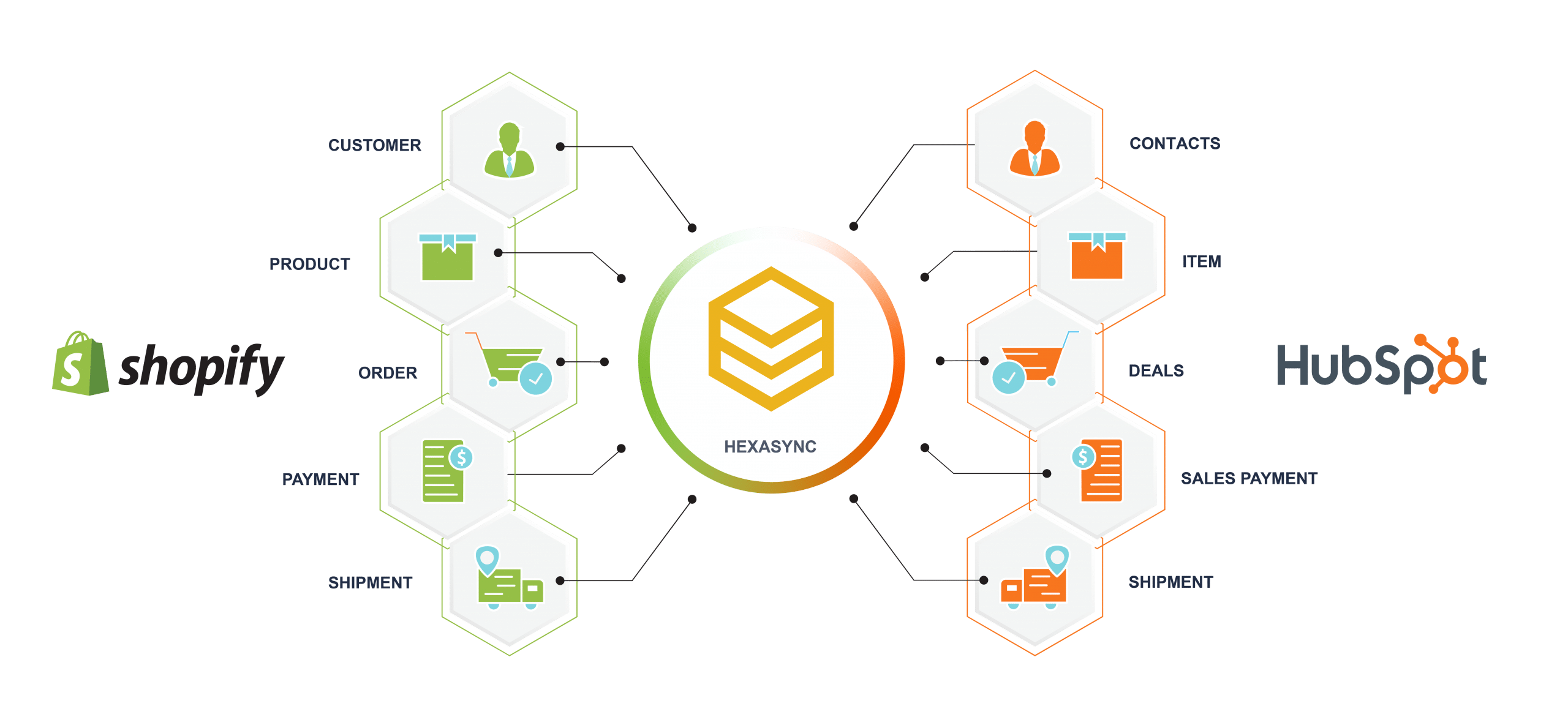 Analyzing The Shift Shopify Developer Programs Annual To Lifetime Revenue Share
May 04, 2025
Analyzing The Shift Shopify Developer Programs Annual To Lifetime Revenue Share
May 04, 2025 -
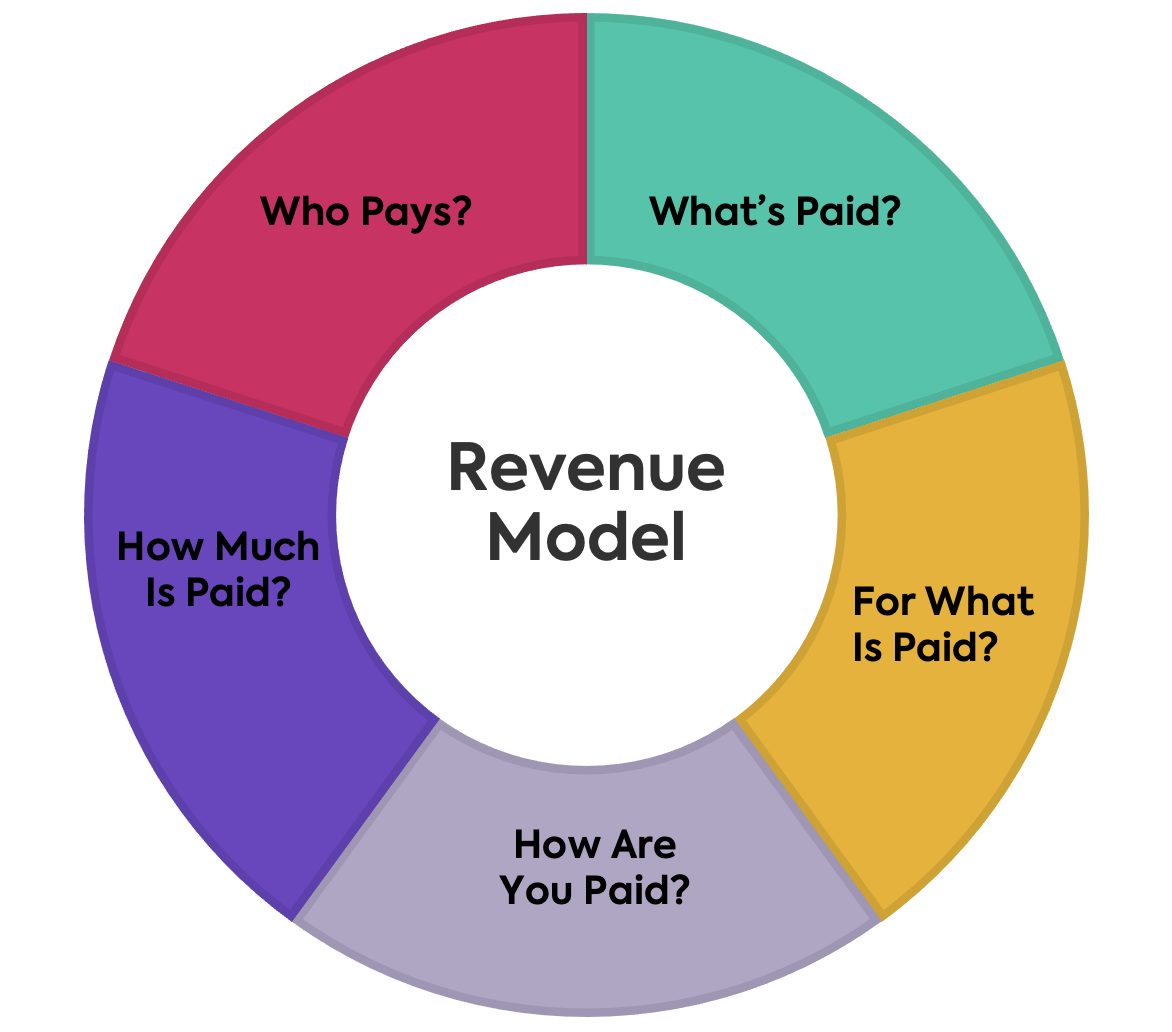 Shopifys New Lifetime Revenue Share Model Impact On Developers
May 04, 2025
Shopifys New Lifetime Revenue Share Model Impact On Developers
May 04, 2025 -
 Shopify Developers Lifetime Revenue Share Changes Explained
May 04, 2025
Shopify Developers Lifetime Revenue Share Changes Explained
May 04, 2025
