School Desegregation Order Terminated: A Turning Point For Education Equality?
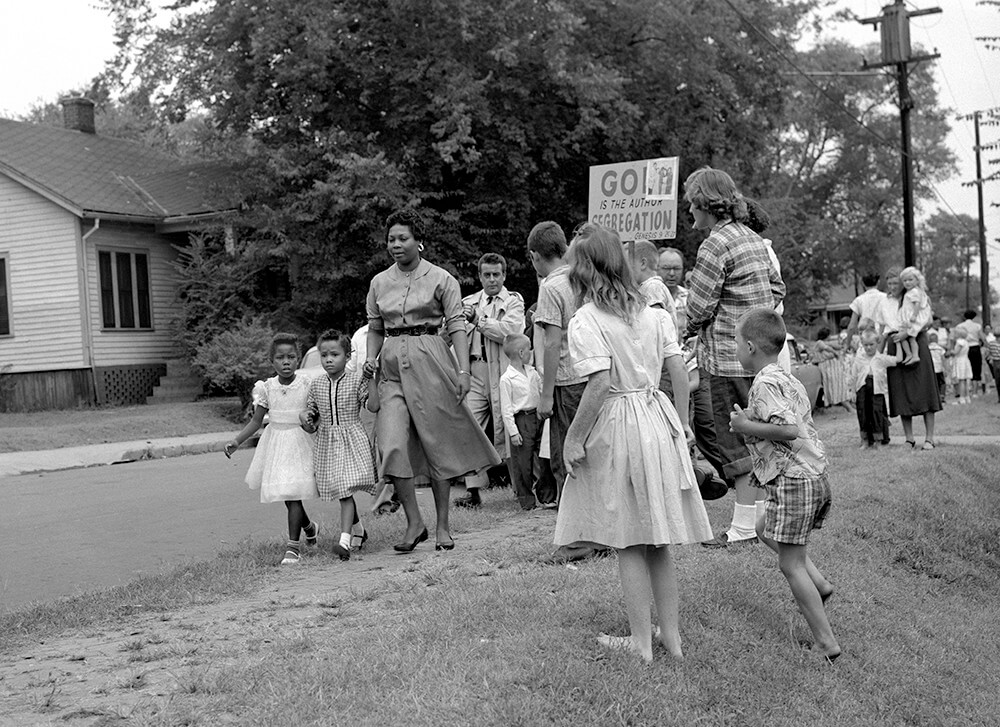
Table of Contents
Historical Context of the School Desegregation Order
The school desegregation order in question, implemented in [Insert Year], aimed to dismantle the system of de jure segregation – legally mandated racial separation – that had historically deprived minority students of equal educational opportunities. The order, based on the landmark Supreme Court case Brown v. Board of Education (1954), mandated the integration of schools within the [Insert affected region/state] school district. However, the path to integration proved far from smooth.
The implementation faced significant resistance, manifesting in various forms including:
- Active resistance: Protests, boycotts, and legal challenges attempted to thwart integration efforts.
- De facto segregation: Even after de jure segregation was outlawed, residential patterns and other factors led to de facto segregation – segregation in practice, even without legal mandate – perpetuating racial disparities in school populations.
- Funding disparities: Significant funding discrepancies between predominantly white and predominantly minority schools further exacerbated inequalities in educational resources and opportunities, hindering the progress of school integration.
- Achievement gaps: Persistent achievement gaps between racial groups highlighted the lasting impact of segregation and the need for continued intervention to address the systemic inequalities.
Key dates and events:
- [Insert Key Date]: Initial implementation of the desegregation order.
- [Insert Key Date]: Significant legal challenge to the order.
- [Insert Key Date]: Implementation of busing programs to achieve integration.
- [Insert Key Date]: Significant court ruling impacting the order.
Statistics: [Insert statistics illustrating progress or lack thereof in achieving integration over the years. For example: percentage of minority students in integrated schools, achievement gap data between racial groups over time].
Arguments for Terminating the School Desegregation Order
Proponents of terminating the desegregation order argue that it has become obsolete. They claim that the original problems of de jure segregation have been largely addressed, and that the order is no longer necessary or even beneficial. Key arguments include:
- Local control: Advocates for local control emphasize the importance of allowing individual school districts to manage their affairs and tailor their educational programs to meet the specific needs of their communities.
- School choice: The argument for school choice often accompanies calls for termination, suggesting that parents should have the freedom to choose the schools best suited to their children's needs, regardless of race or location.
- Resource allocation: Some argue that the resources dedicated to maintaining the desegregation order could be better allocated to other educational priorities.
Specific arguments and evidence: [Insert specific arguments made by proponents of termination, supported by evidence or data].
Arguments Against Terminating the School Desegregation Order
Opponents of termination express serious concerns about the potential for a resurgence of segregation and increased racial disparities in education. They argue that the achievement gap persists, and that continued affirmative action and intervention are crucial to ensure equal educational opportunities for all students, regardless of race. Key concerns include:
- Re-segregation: The termination of the order could lead to a rapid increase in school segregation, potentially reversing decades of progress toward integration.
- Achievement gap: The persistent achievement gap between racial groups highlights the ongoing need for proactive measures to address systemic inequalities and ensure equal educational outcomes.
- Equity in education: Ending the order could undermine efforts to achieve true equity in education, leaving minority students at a significant disadvantage.
Specific concerns and evidence: [Insert specific concerns raised by opponents of termination, supported by evidence or data. This might include data showing increased segregation in other districts after similar orders were terminated].
Potential Consequences and Future Implications of the Termination
The termination of the school desegregation order carries significant long-term implications for student achievement, school funding, and community relations. Potential consequences include:
- Decreased student achievement: Re-segregation could lead to lower academic performance among minority students due to reduced access to resources and opportunities.
- Increased school funding disparities: The termination could exacerbate existing funding inequalities, further disadvantaging schools with predominantly minority populations.
- Strained community relations: Increased racial segregation in schools could negatively impact community relations and social cohesion.
Predicted outcomes and policy changes: [Insert predicted outcomes based on data and expert opinions. Suggest potential policy changes needed to mitigate negative consequences, such as increased funding for under-resourced schools or targeted interventions to address the achievement gap].
Future research and monitoring: [Suggest areas for future research and monitoring to track the effects of the termination on various aspects of education and community relations].
Conclusion: The Termination of School Desegregation Orders: A Call for Continued Vigilance
This article has explored the multifaceted issue of school desegregation in the context of the recent termination of a long-standing order. While proponents argue for local control and resource reallocation, opponents raise valid concerns about re-segregation and the perpetuation of racial disparities in education. The potential for negative consequences necessitates close monitoring and evaluation of the impact of this decision. Continued vigilance and proactive measures are crucial to ensure that all students have equal access to quality education, regardless of race or socioeconomic background. The fight for school integration and equity in education is far from over; further research, policy discussions, and community engagement are essential to ensure that this turning point does not represent a setback in the pursuit of true educational equality for all. Let's continue the conversation about school desegregation and strive for truly integrated and equitable educational systems.
Featured Posts
-
 Wednesday April 9th Lotto Results Check The Winning Jackpot Numbers
May 03, 2025
Wednesday April 9th Lotto Results Check The Winning Jackpot Numbers
May 03, 2025 -
 Algerie Reactions Politiques A La Reforme De La Loi Sur Les Partis Pt Ffs Rcd Jil Jadid
May 03, 2025
Algerie Reactions Politiques A La Reforme De La Loi Sur Les Partis Pt Ffs Rcd Jil Jadid
May 03, 2025 -
 Farages Future Should Rupert Lowe Take The Helm Of Reform Uk
May 03, 2025
Farages Future Should Rupert Lowe Take The Helm Of Reform Uk
May 03, 2025 -
 La Rencontre Emouvante D Emmanuel Macron Avec Les Victimes De L Armee Israelienne
May 03, 2025
La Rencontre Emouvante D Emmanuel Macron Avec Les Victimes De L Armee Israelienne
May 03, 2025 -
 Macron Au Gabon La Fin De La Francafrique
May 03, 2025
Macron Au Gabon La Fin De La Francafrique
May 03, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 The Power Of Wind Innovative Solutions For Railway Electrification
May 04, 2025
The Power Of Wind Innovative Solutions For Railway Electrification
May 04, 2025 -
 Is A Leadership Change At Reform Necessary The Farage Lowe Debate
May 04, 2025
Is A Leadership Change At Reform Necessary The Farage Lowe Debate
May 04, 2025 -
 Sustainable Rail Exploring The Potential Of Wind Powered Trains
May 04, 2025
Sustainable Rail Exploring The Potential Of Wind Powered Trains
May 04, 2025 -
 Farages Future And The Reform Party A Case For Lowes Leadership
May 04, 2025
Farages Future And The Reform Party A Case For Lowes Leadership
May 04, 2025 -
 Harnessing The Wind The Future Of Eco Friendly Train Travel
May 04, 2025
Harnessing The Wind The Future Of Eco Friendly Train Travel
May 04, 2025
