School Desegregation Order Terminated: Analysis And Potential Impact
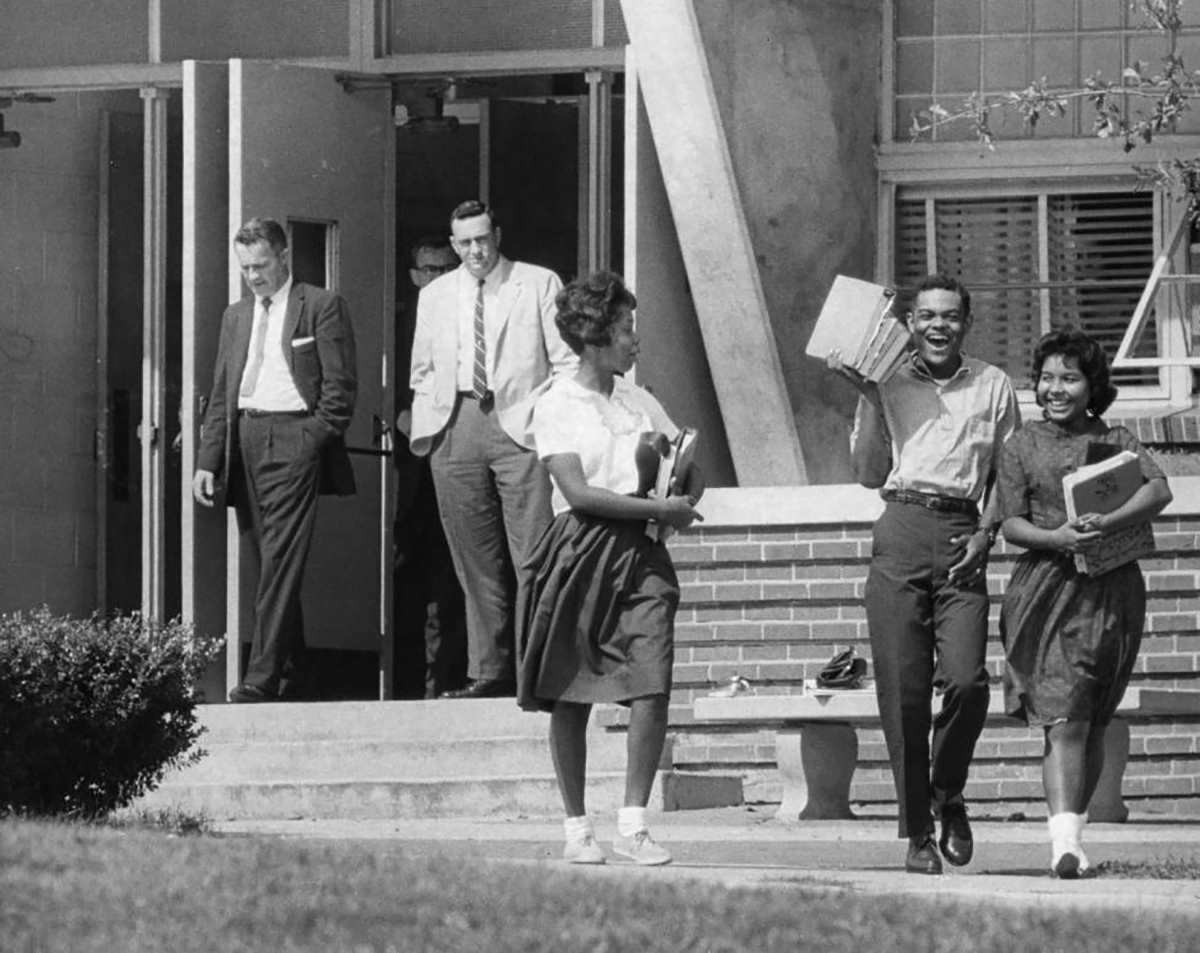

Table of Contents
Historical Context of the School Desegregation Order
The termination of this desegregation order cannot be understood without examining its historical context. The landmark Supreme Court case Brown v. Board of Education (1954) declared state laws establishing separate public schools for black and white students to be unconstitutional. This ruling, however, did not immediately lead to widespread desegregation. Resistance was significant, leading to protracted legal battles and social unrest across the nation. Many school districts, particularly in the South, actively resisted integration, employing various tactics to delay or circumvent the ruling.
-
Timeline of key events:
- 1954: Brown v. Board of Education
- 1964: Civil Rights Act prohibits discrimination in public education
- [Insert Year]: Initial desegregation order implemented in [School District Name]
- [Insert Year]: Significant milestones in desegregation efforts (e.g., busing programs, court-ordered integration plans)
- [Insert Year]: Challenges and setbacks encountered during implementation (e.g., white flight, resistance from communities)
-
Achievements and setbacks: While the initial desegregation order brought about some progress in integrating schools, significant challenges persisted. These included resistance from some communities, the phenomenon of "white flight" to suburban schools, and persistent achievement gaps between racial groups.
-
Social and political climate: The social and political climate surrounding the desegregation order was (and remains) highly charged. The issue remains deeply intertwined with broader questions of racial justice, equality, and access to opportunity.
Reasons for the Termination of the Desegregation Order
The termination of the desegregation order likely resulted from a confluence of factors. Legal arguments presented for termination might have centered on claims of the school district achieving unitary status—meaning that the vestiges of past segregation have been eliminated. However, this claim frequently overlooks the persistent racial and socioeconomic disparities that continue to shape educational outcomes.
-
Legal arguments: The legal arguments for termination likely focused on demonstrating the district's compliance with desegregation mandates, highlighting demographic changes, and arguing that continued oversight is unnecessary.
-
Demographic shifts and social attitudes: Demographic shifts within the school district, potentially showing a more racially balanced student population, might have been presented as evidence of successful integration. Shifting social attitudes, though not necessarily indicative of a solved problem, could also have played a role in the court’s decision.
-
Political factors: Political influence, including shifts in judicial appointments and changes in local or state government priorities, cannot be ignored as potential contributing factors to the decision.
Potential Impact on Student Outcomes
The termination of the desegregation order carries significant risks for student outcomes. A return to de facto segregation—segregation in practice even without explicit legal mandates—could exacerbate existing achievement gaps and negatively impact social-emotional development.
-
Academic achievement: Research consistently shows a correlation between school diversity and improved academic outcomes for minority students. The termination could reverse this trend, potentially widening achievement gaps.
-
Social integration and intergroup relations: Integrated schools provide opportunities for students from diverse backgrounds to interact, fostering understanding and empathy. Re-segregation could limit these opportunities, potentially increasing prejudice and stereotypes.
-
Risk of re-segregation: Without continued oversight, the potential for re-segregation is significant. Factors such as housing patterns, school choice programs, and funding disparities can all contribute to the re-creation of racially and socioeconomically segregated schools.
The Role of Federal and State Oversight
Federal and state governments play a crucial role in ensuring equal educational opportunities for all students. The termination of the desegregation order raises concerns about the adequacy of current oversight mechanisms.
-
Federal and state laws: Existing federal and state laws, such as Title VI of the Civil Rights Act of 1964, prohibit discrimination in federally funded programs, including schools. However, enforcement varies significantly across jurisdictions.
-
Effectiveness of monitoring mechanisms: Current monitoring mechanisms may be insufficient to prevent re-segregation. More robust oversight, including regular assessments of school demographics and student outcomes, is needed.
-
Suggestions for improved oversight: Improved oversight should include stronger enforcement of anti-discrimination laws, increased funding for schools in underserved communities, and the development of evidence-based strategies to promote school diversity.
Community Response and Future Strategies
Community response to the termination of the desegregation order has been mixed, ranging from acceptance to outrage. Legal challenges and appeals are likely.
-
Public opinion: Community reactions are likely to be divided, reflecting differing views on the role of government in promoting school integration and the importance of diversity in education.
-
Legal challenges: Legal challenges to the termination could focus on arguments that the decision violates constitutional guarantees of equal protection and due process.
-
Strategies for promoting diversity and inclusion: Strategies to foster diverse and inclusive schools should include promoting equitable school funding, supporting innovative school choice models that foster integration, and implementing culturally responsive teaching practices. Community-based initiatives focused on building bridges between different groups are also crucial.
Conclusion
The termination of this school desegregation order presents both challenges and opportunities. The potential for increased school segregation necessitates proactive measures from all stakeholders—from policymakers to educators and community members—to ensure that all children receive a high-quality education, regardless of race or background. Continued advocacy and a commitment to equitable education are vital to prevent the resurgence of school segregation and uphold the principles of equal opportunity for all. We must remain actively involved in the ongoing conversation about school desegregation and work to protect the progress made towards inclusive education. We need to continue the fight for equal access to education and actively work towards dismantling the systemic barriers to school desegregation. The future of equitable education depends on it.

Featured Posts
-
 Boulangerie Normande Son Poids En Chocolat Pour Le Nouveau Ne De L Annee
May 02, 2025
Boulangerie Normande Son Poids En Chocolat Pour Le Nouveau Ne De L Annee
May 02, 2025 -
 Fortnite Matchmaking Error 1 A Comprehensive Guide
May 02, 2025
Fortnite Matchmaking Error 1 A Comprehensive Guide
May 02, 2025 -
 Syracuse Hazing Scandal 11 Players Surrender To Police
May 02, 2025
Syracuse Hazing Scandal 11 Players Surrender To Police
May 02, 2025 -
 Englands Last Minute Goal Seals Victory Against France
May 02, 2025
Englands Last Minute Goal Seals Victory Against France
May 02, 2025 -
 The Impact Of Airbus Tariffs On The Us Airline Industry
May 02, 2025
The Impact Of Airbus Tariffs On The Us Airline Industry
May 02, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Nigel Farage Takes On Conservatives In Shrewsbury Relief Road Debate And Local Observations
May 03, 2025
Nigel Farage Takes On Conservatives In Shrewsbury Relief Road Debate And Local Observations
May 03, 2025 -
 Reform Uk Leader Nigel Farage In Shrewsbury Local Pub Visit And Political Commentary
May 03, 2025
Reform Uk Leader Nigel Farage In Shrewsbury Local Pub Visit And Political Commentary
May 03, 2025 -
 Shrewsbury Visit Nigel Farage Criticizes Conservatives Enjoys Local Pub
May 03, 2025
Shrewsbury Visit Nigel Farage Criticizes Conservatives Enjoys Local Pub
May 03, 2025 -
 Nigel Farages Whats App Messages A Crisis Of Integrity For The Reform Party
May 03, 2025
Nigel Farages Whats App Messages A Crisis Of Integrity For The Reform Party
May 03, 2025 -
 Lawsuit Filed Rupert Lowe Accuses Nigel Farage Of Defamation
May 03, 2025
Lawsuit Filed Rupert Lowe Accuses Nigel Farage Of Defamation
May 03, 2025
