Scientists Report Fewer Earthquakes On Santorini: What Does It Mean?
Table of Contents
Santorini's Volcanic History and Seismic Activity
Santorini, a breathtaking island in the Aegean Sea, is renowned for its stunning caldera, a geological formation resulting from past volcanic eruptions. Its history is punctuated by powerful volcanic events, most notably the Minoan eruption around 1600 BC, one of the largest volcanic eruptions in recorded history. This catastrophic event dramatically reshaped the island's landscape and is believed to have contributed to the decline of the Minoan civilization. Historically, Santorini has experienced a relatively high frequency of earthquakes, ranging in magnitude and intensity, reflecting its ongoing volcanic activity. These seismic events are a direct consequence of the underlying magmatic processes and tectonic movements in the region.
- Past major eruptions and their associated seismic activity: The Minoan eruption is the most well-known, but smaller, yet still significant, eruptions have occurred throughout Santorini's history, each accompanied by substantial seismic activity. These events provide valuable data for understanding the island's volcanic behavior and the relationship between volcanic activity and Santorini earthquakes.
- Ongoing monitoring of volcanic activity: Scientists continuously monitor Santorini's volcanic activity using a network of seismometers, GPS stations, and gas emission sensors. These tools provide crucial real-time data on ground deformation, seismic tremor, and gas composition, offering valuable insights into the state of the volcanic system.
- Relevant scientific resources: The National Observatory of Athens, the Institute of Geodynamics, and numerous international research teams contribute to the ongoing monitoring and research efforts on Santorini's volcanic activity. Their publications provide valuable data and insights into the frequency and patterns of Santorini earthquakes.
The Recent Decrease in Santorini Earthquakes
Over the past [Insert specific timeframe, e.g., six months, year], a notable decrease in the frequency of Santorini earthquakes has been observed. While the island still experiences seismic activity, the number of recorded events has significantly dropped compared to previous years. The magnitude of recent quakes has also generally been lower. The specific locations of these recent events are being carefully analyzed to identify any shifts in the patterns of seismic activity.
- Specific statistics on the reduction in earthquake frequency: [Insert specific data here, e.g., "A 30% decrease in the number of earthquakes recorded compared to the average of the previous five years."] This decrease is statistically significant and has prompted extensive scientific investigation.
- Observed changes in the type or pattern of seismic activity: Scientists are analyzing whether the recent seismic events are shallower or deeper than previously observed, providing clues about the changes occurring within the volcanic system. Any shift in the location or depth of these events could indicate alterations in magma pressure or tectonic stress.
- Source of data: This data is being compiled from various sources, including the National Observatory of Athens, the Institute of Geodynamics, and international seismic monitoring networks. These organizations provide publicly available datasets that inform the scientific community and the public.
Potential Interpretations of Reduced Seismic Activity
The decrease in Santorini earthquakes is prompting several hypotheses within the scientific community. These interpretations are not mutually exclusive and may be interconnected.
- Changes in magma pressure: A decrease in magma pressure within the volcanic system could lead to a reduction in seismic activity. This could be due to a slower rate of magma supply or changes in the pathways of magma movement beneath the island.
- Shifts in tectonic plates: The interplay between tectonic plates and the volcanic system plays a vital role in seismic activity. Minor shifts or adjustments in the tectonic stress field could temporarily reduce the frequency of earthquakes.
- Temporary lull in volcanic activity: The reduced seismic activity could be a temporary phenomenon, a lull before a potential increase in volcanic unrest. It is crucial to emphasize that this possibility, while scientifically plausible, requires continued monitoring and rigorous analysis to ascertain its likelihood. This possibility underscores the need for caution against drawing definite conclusions based on short-term observations.
Implications for Santorini and Future Monitoring
The observed reduction in Santorini earthquakes, though seemingly positive, carries significant implications for both the island's residents and its thriving tourism industry.
- Potential impact on tourism: A perceived decrease in seismic risk could lead to an increase in tourism, yet it is paramount to maintain a balanced approach to risk communication, highlighting the ongoing volcanic activity and the potential for future seismic events.
- Importance of ongoing seismic monitoring and volcanic surveillance: Continued and enhanced monitoring of volcanic activity is critical. This includes maintaining and upgrading existing monitoring networks and employing advanced techniques to provide real-time updates on volcanic status.
- Need for enhanced public awareness and preparedness programs: Educating the public about volcanic hazards and earthquake preparedness is crucial for mitigating potential risks. This includes developing effective emergency response plans and educating residents and tourists on what to do during seismic events.
Conclusion
The recent decrease in Santorini earthquakes is a significant development requiring further investigation. While the reasons behind this change remain uncertain, several hypotheses are being explored, involving magma pressure, tectonic shifts, or a temporary lull in volcanic activity. It's crucial to avoid drawing premature conclusions and instead emphasize continued monitoring and research. Understanding the dynamics of Santorini earthquakes is essential for ensuring the safety and well-being of the island's community. Stay informed about the latest developments concerning Santorini earthquakes by following reputable scientific sources and supporting ongoing research in volcanology. The ongoing monitoring of seismic activity and volcanic processes is key to understanding future risks and ensuring the safety of both residents and visitors.

Featured Posts
-
 Kojak Itv 4 Full Episode Guide And Viewing Information
May 11, 2025
Kojak Itv 4 Full Episode Guide And Viewing Information
May 11, 2025 -
 Protecting Aaron Judge The Importance Of Cody Bellinger In The Yankees Batting Order
May 11, 2025
Protecting Aaron Judge The Importance Of Cody Bellinger In The Yankees Batting Order
May 11, 2025 -
 Canadas Top Natural Gas Producer A Growing Force In The Energy Sector
May 11, 2025
Canadas Top Natural Gas Producer A Growing Force In The Energy Sector
May 11, 2025 -
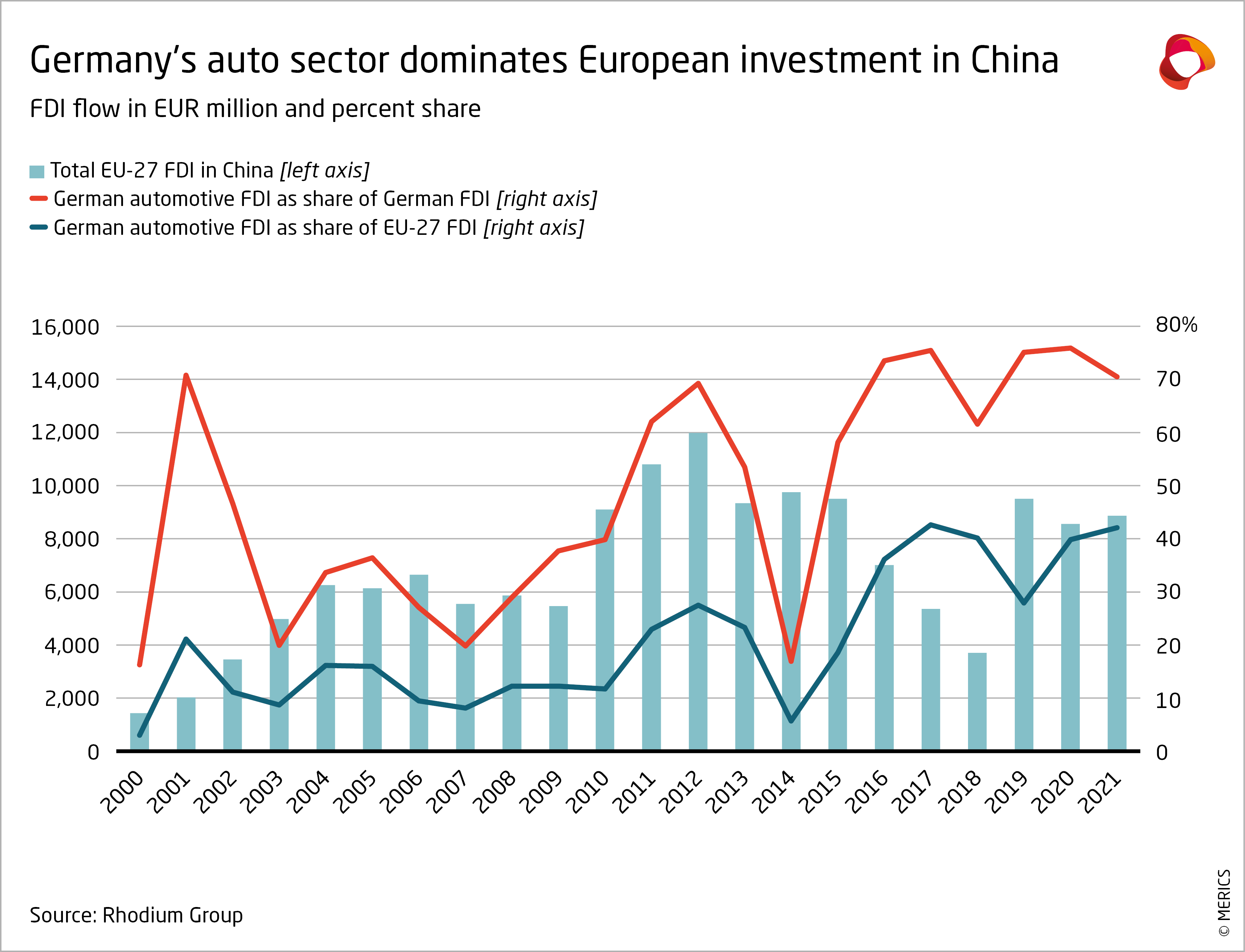 Bmw Porsche And The Future Of Automotive Sales In China A Complex Picture
May 11, 2025
Bmw Porsche And The Future Of Automotive Sales In China A Complex Picture
May 11, 2025 -
 Jay Kelly I Nea Tainia Poy Tha Sas Kratisei Se Paratetameno Gelio
May 11, 2025
Jay Kelly I Nea Tainia Poy Tha Sas Kratisei Se Paratetameno Gelio
May 11, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Iftar Programi Hakkari Deki Hakim Ve Savcilar Bir Arada
May 12, 2025
Iftar Programi Hakkari Deki Hakim Ve Savcilar Bir Arada
May 12, 2025 -
 Hakkari De Yueksek Mahkeme Hakim Ve Savcilarina Iftar Yemegi
May 12, 2025
Hakkari De Yueksek Mahkeme Hakim Ve Savcilarina Iftar Yemegi
May 12, 2025 -
 Hakkaride Duezenlenen Hakim Ve Savcilar Iftar Programi
May 12, 2025
Hakkaride Duezenlenen Hakim Ve Savcilar Iftar Programi
May 12, 2025 -
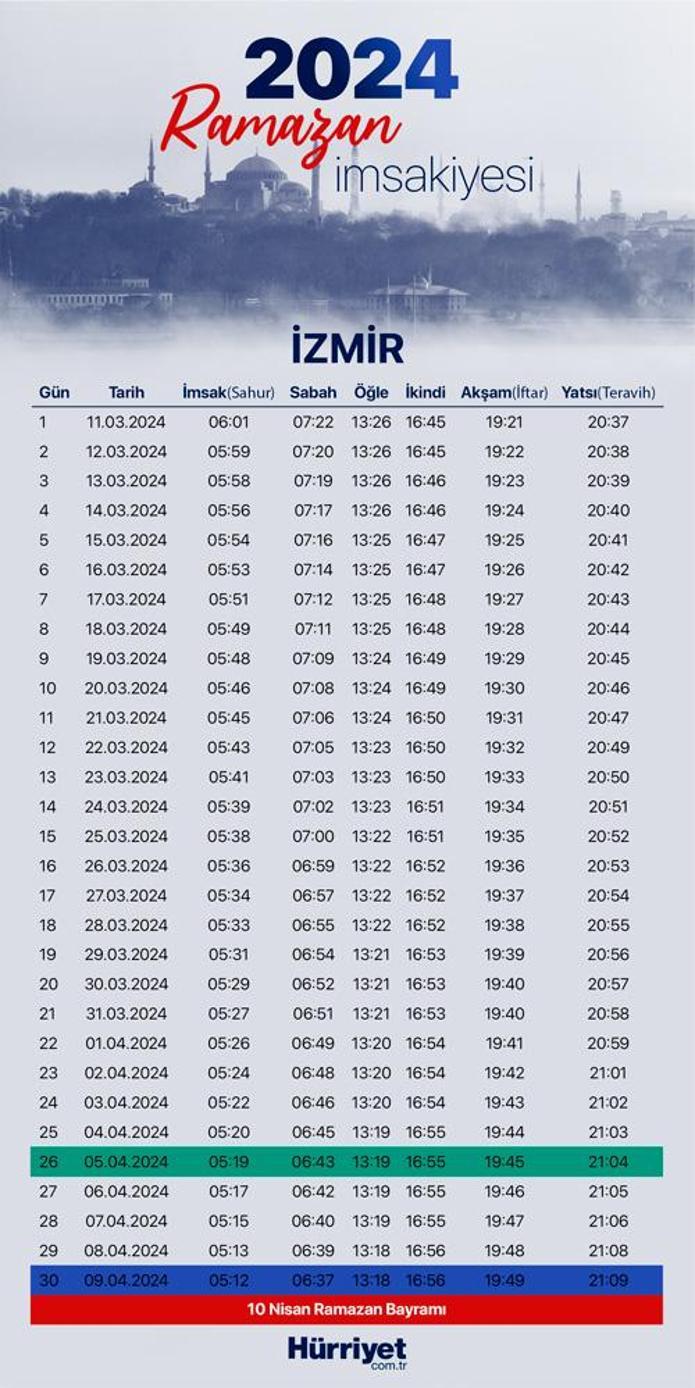 Hakimler Ve Savcilar Icin Iftar Programi Detayli Bilgi
May 12, 2025
Hakimler Ve Savcilar Icin Iftar Programi Detayli Bilgi
May 12, 2025 -
 Finding Zane Denton Update On The Former Tennessee Volunteers Baseball Player
May 12, 2025
Finding Zane Denton Update On The Former Tennessee Volunteers Baseball Player
May 12, 2025
