Should You Take Creatine? A Guide To Creatine Supplementation

Table of Contents
What is Creatine and How Does it Work?
Creatine is a naturally occurring organic compound found primarily in skeletal muscle. Your body produces a small amount of creatine, but supplementing with creatine monohydrate increases its levels, leading to various performance enhancements. Creatine's primary function is to improve the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the body's primary energy currency. Increased ATP availability translates to enhanced energy for muscle contractions, resulting in improved strength, power, and endurance.
While several forms of creatine exist (e.g., creatine ethyl ester, creatine hydrochloride), creatine monohydrate remains the most extensively researched and recommended form due to its proven efficacy and safety.
- Increased strength and power output: Creatine supplementation leads to significant improvements in strength and power, particularly during high-intensity activities.
- Improved muscle growth (hypertrophy): Creatine facilitates muscle protein synthesis, promoting muscle growth and hypertrophy.
- Enhanced high-intensity exercise performance: Creatine enhances performance in short bursts of intense activity, making it ideal for sports like weightlifting, sprinting, and HIIT.
- Potential cognitive benefits: Some studies suggest that creatine may offer cognitive benefits, including improved memory and reasoning.
Benefits of Creatine Supplementation
The benefits of creatine supplementation extend across various populations, from athletes to older adults. Let's delve deeper into the specific advantages:
Strength and Power Gains
Numerous studies have demonstrated significant increases in one-rep max (1RM) strength and overall power output following creatine supplementation. These gains are attributed to creatine's ability to increase ATP availability, enabling muscles to generate more force during contractions.
Muscle Growth
Creatine plays a crucial role in muscle protein synthesis, the process by which muscle tissue is built and repaired. By increasing cellular hydration and promoting anabolic signaling, creatine contributes to significant muscle growth and hypertrophy.
Improved Exercise Performance
Creatine's impact on high-intensity interval training (HIIT) and short-duration, high-intensity activities is particularly noteworthy. The increased ATP stores allow athletes to perform more repetitions and sets with greater intensity, leading to faster gains in strength and power.
Cognitive Function
Although further research is needed, some studies suggest potential benefits for cognitive function, including improved memory and reasoning, particularly in individuals with cognitive impairments.
Potential Side Effects and Risks of Creatine
While generally safe and well-tolerated, creatine supplementation can come with some potential side effects. Most of these are mild and temporary:
- Water retention (weight gain): Creatine attracts water into muscle cells, leading to temporary weight gain. This is usually not a cause for concern.
- Muscle cramps: Muscle cramps can occur, often due to dehydration. Proper hydration is crucial to mitigate this risk.
- Gastrointestinal upset (nausea, diarrhea): High doses of creatine can sometimes cause nausea or diarrhea. Starting with a lower dose can help.
- Kidney issues: While rare, creatine can pose a risk to individuals with pre-existing kidney conditions. Consult your doctor before using creatine if you have any kidney problems.
How to Take Creatine Effectively
To maximize the benefits of creatine supplementation, follow these guidelines:
- Dosage: A typical dosage is 3-5 grams of creatine monohydrate per day.
- Loading phase: Some individuals opt for a loading phase of 20 grams per day for the first week, followed by a maintenance phase. However, a maintenance phase alone is equally effective.
- Hydration: Maintain adequate hydration throughout the day, especially during and after workouts.
- Timing: Creatine can be taken pre-workout, post-workout, or at any convenient time of day. Combine with carbohydrates and protein for better absorption.
Creatine vs. Other Supplements
Creatine works synergistically with other supplements like protein powder and pre-workout. While protein powder supports muscle growth and repair, and pre-workout enhances energy and focus, creatine uniquely boosts ATP production for improved strength and power. Creatine is not a magic bullet; consistent training and a healthy diet remain crucial for optimal results.
Conclusion: Should You Take Creatine? Making the Informed Decision
Creatine monohydrate offers significant benefits for strength, power, muscle growth, and high-intensity exercise performance. While some mild side effects are possible, they are usually temporary and easily managed. However, individuals with pre-existing kidney conditions should consult their doctor before starting creatine supplementation. If you're looking to enhance your strength, muscle growth, and athletic performance, learn more about creatine supplementation and its potential benefits for you. Consult your doctor before starting any new supplement regimen. For further information, refer to reputable sources on sports nutrition and supplementation.

Featured Posts
-
 Angstcultuur Bij De Npo Getuigenissen Van Tientallen Medewerkers
May 15, 2025
Angstcultuur Bij De Npo Getuigenissen Van Tientallen Medewerkers
May 15, 2025 -
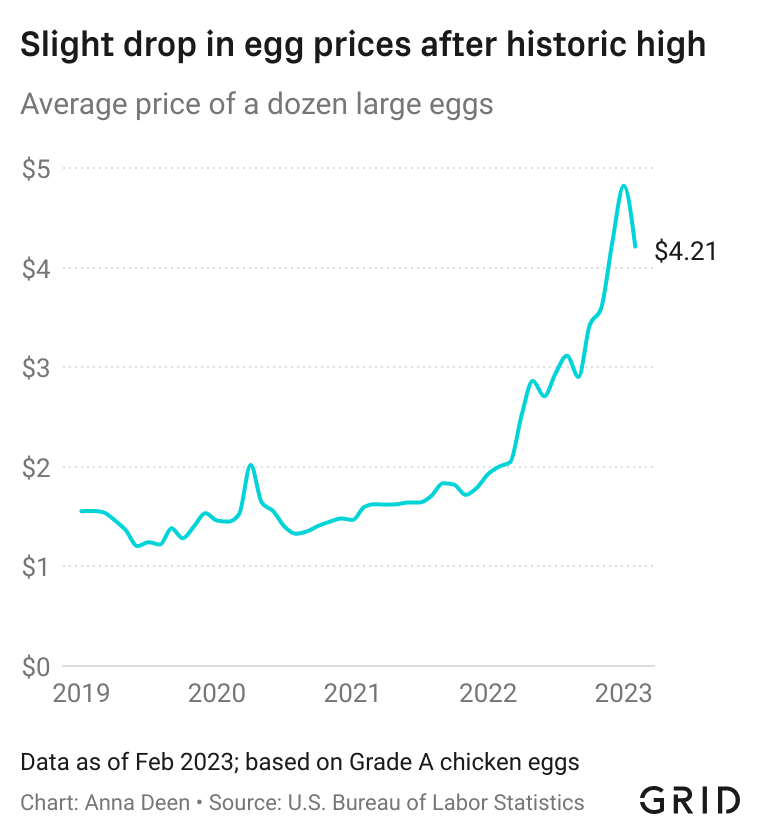 5 Dozen Eggs Us Egg Price Drop Explained
May 15, 2025
5 Dozen Eggs Us Egg Price Drop Explained
May 15, 2025 -
 Five Photos Summarizing Vont Weekend At 104 5 The Cat April 4 6 2025
May 15, 2025
Five Photos Summarizing Vont Weekend At 104 5 The Cat April 4 6 2025
May 15, 2025 -
 Times Kaysimon Kypros Breite Ta Fthinotera Pratiria
May 15, 2025
Times Kaysimon Kypros Breite Ta Fthinotera Pratiria
May 15, 2025 -
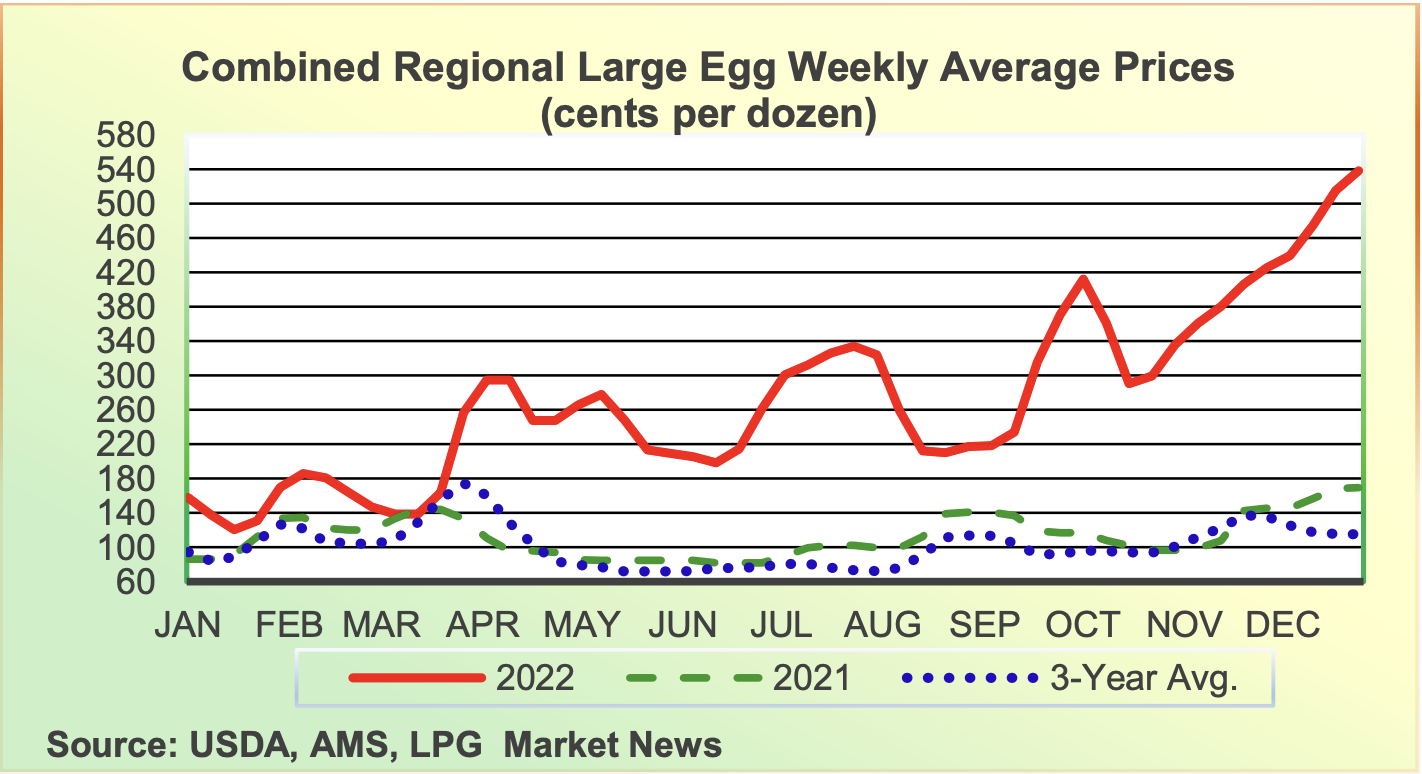 Record Egg Prices Fall A Dozen Now Costs 5 In The Us
May 15, 2025
Record Egg Prices Fall A Dozen Now Costs 5 In The Us
May 15, 2025
