South Africa-Tanzania Agricultural Trade: Progress On Import Restrictions

Table of Contents
The agricultural sector holds immense potential for boosting economic growth and development in both South Africa and Tanzania. However, the current state of agricultural trade between these two nations is significantly hampered by a complex web of import restrictions. This article delves into the historical context of this trade relationship, examines the current import barriers affecting South African agricultural products in Tanzania, highlights the progress made in reducing these restrictions, and finally, explores the remaining challenges and future prospects for enhancing agricultural trade between these two important African economies.
Historical Context of Agricultural Trade Between South Africa and Tanzania
The agricultural trade relationship between South Africa and Tanzania has a long and complex history, characterized by periods of both substantial growth and significant decline. Early trade patterns were largely dictated by colonial legacies, often resulting in an unequal exchange where South Africa served as a primary supplier of agricultural goods to Tanzania. This created dependencies and imbalances that persist to some degree even today. The formation of the Southern African Development Community (SADC) aimed to foster greater regional integration and facilitate smoother trade flows. However, despite these efforts, numerous obstacles continued to hinder the full potential of agricultural trade between the two nations.
- Early trade patterns: Primarily focused on South Africa exporting processed foods, agricultural inputs like fertilizers and machinery, and some staple crops.
- Impact of colonial legacies: Created asymmetrical trade relations, hindering the development of Tanzania's domestic agricultural sector.
- Establishment of SADC: While SADC aimed to promote regional integration, it did not fully resolve the persistent import restriction issues impacting bilateral trade.
Current Import Restrictions Affecting South African Agricultural Products in Tanzania
Tanzania currently imposes various import restrictions on several South African agricultural products. The rationale behind these restrictions often centers on the protection of domestic farmers and addressing food safety concerns. However, these measures often result in higher prices for consumers in Tanzania and reduced market access for South African producers.
- Tariffs and duties: High tariffs on specific agricultural goods significantly increase the cost of South African imports, making them less competitive compared to domestically produced alternatives.
- Non-tariff barriers: Sanitary and phytosanitary (SPS) measures and technical barriers to trade (TBT) impose stringent requirements on imported agricultural products, often creating significant hurdles for South African exporters to navigate. These can include complex documentation, certification processes, and stringent quality standards.
- Quota systems: Import quotas limit the quantity of specific South African agricultural products that can enter the Tanzanian market, reducing market access for South African producers.
- Licensing requirements: Complex licensing procedures and bureaucratic hurdles add to the overall cost and time needed to export agricultural goods from South Africa to Tanzania, deterring many businesses.
Progress Made in Reducing Import Restrictions
Despite the significant challenges, there has been some progress in recent years toward improving the trade relationship between South Africa and Tanzania. Both governments have engaged in bilateral negotiations to address specific concerns and simplify trade procedures. Efforts to harmonize food safety standards and regulations, drawing upon regional initiatives, have also yielded some positive outcomes.
- Bilateral trade negotiations: These talks have resulted in some reductions in tariffs and more streamlined customs procedures for certain agricultural products.
- WTO dispute settlement mechanisms: While not yet fully utilized, the WTO framework offers a potential avenue to address any unfair or discriminatory trade practices.
- Regional trade agreements (e.g., EAC): The East African Community (EAC) offers a platform for broader regional integration, potentially leading to harmonized regulations and reduced trade barriers.
- Initiatives to improve food safety standards and compliance: Collaborative efforts to improve food safety standards and compliance processes are helping reduce non-tariff barriers and enhance consumer protection.
Remaining Challenges and Future Prospects for South Africa-Tanzania Agricultural Trade
While progress has been made, significant challenges continue to hinder the full potential of South Africa-Tanzania agricultural trade. Infrastructure limitations, particularly in transportation and storage, contribute to increased costs and reduced competitiveness. Furthermore, complexities within phytosanitary certification processes and a lack of capacity building to ensure compliance with regulations remain persistent issues.
- Infrastructure limitations: Inadequate transportation networks, limited storage facilities, and unreliable power supply all increase the cost of moving and preserving agricultural products, reducing the profitability of exports.
- Phytosanitary certification processes: These processes need simplification and increased transparency to reduce delays and improve efficiency for South African exporters.
- Capacity building for compliance with regulations: Providing training and technical assistance to South African exporters will help them effectively meet the Tanzanian regulations, thereby increasing successful exports.
- Potential for increased investment and collaboration in agriculture: Joint ventures, technology transfer, and knowledge sharing can foster greater productivity and create more efficient and mutually beneficial trade relationships.
Strengthening South Africa-Tanzania Agricultural Trade: A Call to Action
Strengthening agricultural trade between South Africa and Tanzania requires a multifaceted approach. Continued high-level dialogue between the two governments is crucial, along with focused efforts toward regulatory harmonization, significant investment in infrastructure development, and capacity building initiatives to ensure compliance with standards. By addressing import restrictions effectively and promoting a more transparent and efficient trade environment, both South Africa and Tanzania can unlock the immense potential of their agricultural sectors, fostering economic growth and creating a more prosperous future for their citizens. Collaborative efforts are key to navigating the challenges and realizing the full potential of South Africa-Tanzania agricultural trade.

Featured Posts
-
 Exec Office365 Breach Millions Made Through Email Hacks Fbi Reveals
Apr 27, 2025
Exec Office365 Breach Millions Made Through Email Hacks Fbi Reveals
Apr 27, 2025 -
 Canadas Election Carney Highlights Trumps Aggressive Trade Stance
Apr 27, 2025
Canadas Election Carney Highlights Trumps Aggressive Trade Stance
Apr 27, 2025 -
 Grand National 2025 A Complete Guide To The Runners At Aintree
Apr 27, 2025
Grand National 2025 A Complete Guide To The Runners At Aintree
Apr 27, 2025 -
 Ai And Human Creativity Insights From Microsofts Chief Designer
Apr 27, 2025
Ai And Human Creativity Insights From Microsofts Chief Designer
Apr 27, 2025 -
 El Sistema Alberto Ardila Olivares Garantia De Logro En El Futbol
Apr 27, 2025
El Sistema Alberto Ardila Olivares Garantia De Logro En El Futbol
Apr 27, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Yukon Politicians Cite Contempt Over Mine Managers Evasive Answers
Apr 28, 2025
Yukon Politicians Cite Contempt Over Mine Managers Evasive Answers
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Teslas Rise Leads Tech Driven Us Stock Market Gains
Apr 28, 2025
Teslas Rise Leads Tech Driven Us Stock Market Gains
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Tech Powerhouses Propel Us Stock Market Higher Teslas Impact
Apr 28, 2025
Tech Powerhouses Propel Us Stock Market Higher Teslas Impact
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Us Stock Market Rally Driven By Tech Giants Tesla In The Lead
Apr 28, 2025
Us Stock Market Rally Driven By Tech Giants Tesla In The Lead
Apr 28, 2025 -
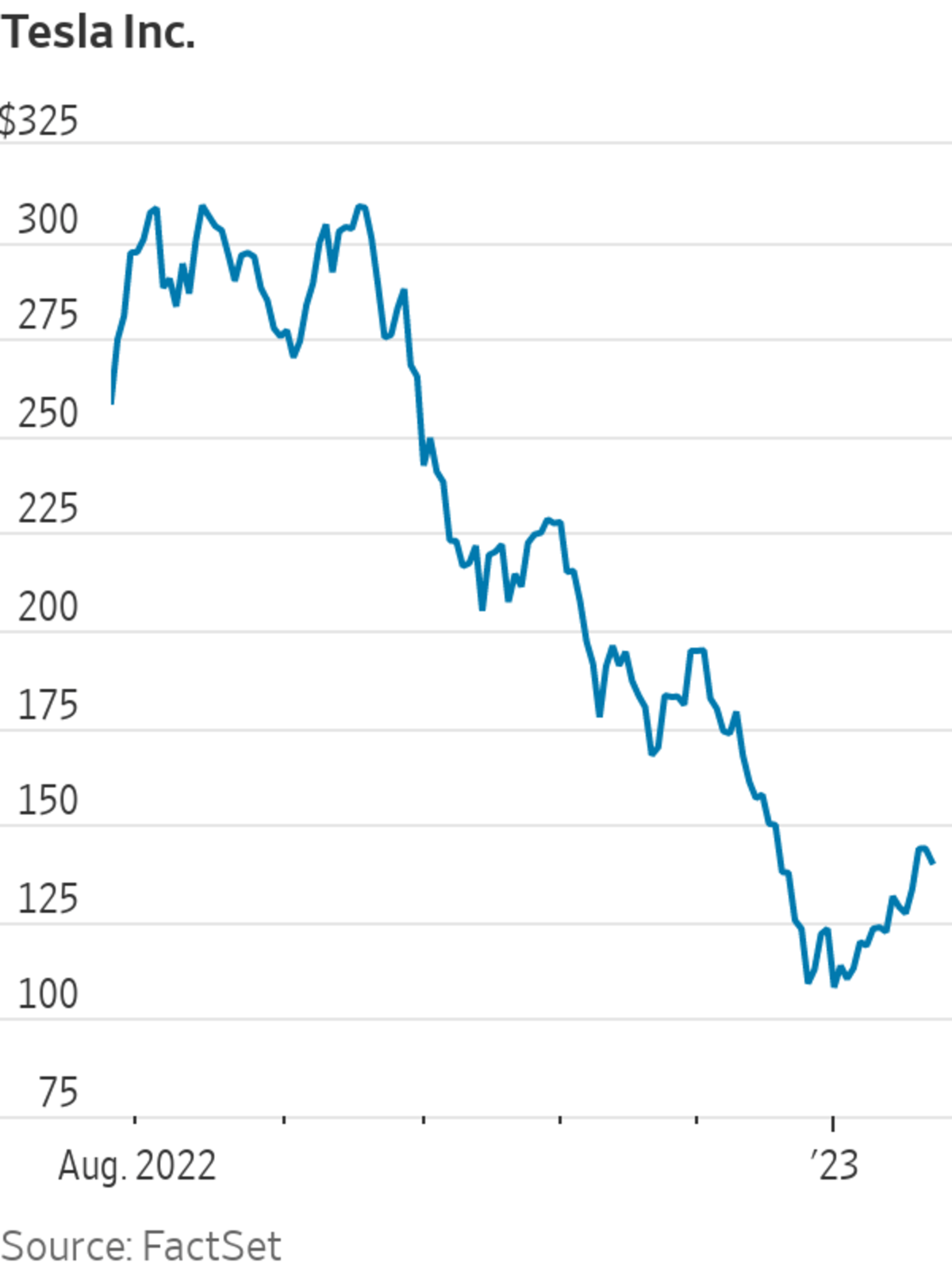 Tesla And Tech Fuel Us Stock Market Surge
Apr 28, 2025
Tesla And Tech Fuel Us Stock Market Surge
Apr 28, 2025
