Staying Informed: The Latest On The Measles Outbreak In The United States
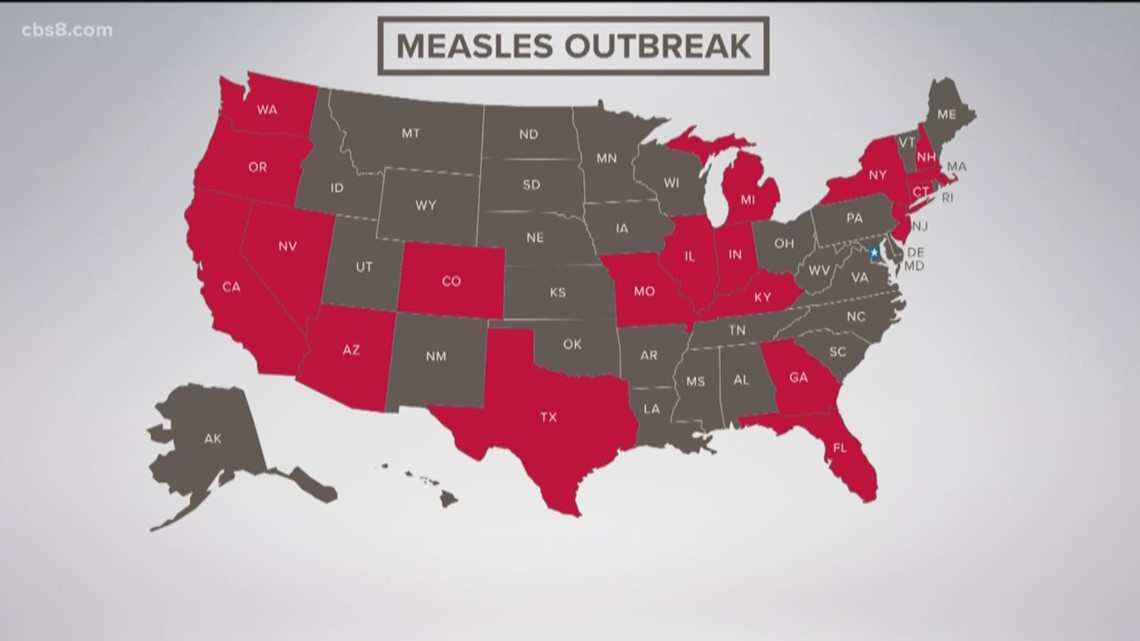
Table of Contents
Current Statistics and Geographic Spread of the Measles Outbreak
The measles outbreak in the United States continues to be a significant public health challenge. While precise, up-to-the-minute numbers fluctuate, reliable sources like the CDC should be consulted for the most current data. However, we can look at trends. In recent years, we've seen a concerning rise in measles cases, often clustered in specific regions.
The spread of measles is not uniform across the country. Certain states have experienced significantly higher case counts than others. For instance, outbreaks have been particularly notable in [Insert State A] and [Insert State B], often linked to specific communities or events. Using interactive maps provided by public health organizations is essential for visualizing the geographic distribution of the measles outbreak.
- Total number of cases: [Insert most recent data from a reliable source, such as the CDC]. This number is dynamic and requires frequent updates.
- States with highest case counts: [List the states with the highest number of reported cases, citing your source].
- Age demographics of affected individuals: [Provide data on the age groups most affected; often, unvaccinated children and young adults are disproportionately impacted].
- Any identified clusters or outbreaks: [Mention any specific locations or events associated with increased measles transmission].
Understanding the Causes and Risk Factors of the Outbreak
Measles is a highly contagious disease caused by a virus that spreads through the air through respiratory droplets produced from coughing or sneezing. Direct contact with an infected individual can also lead to transmission. The virus is exceptionally efficient at spreading, making it a significant public health threat, especially in areas with low vaccination rates.
One of the primary drivers of the current measles outbreak is low vaccination rates. "Vaccine hesitancy," fueled by misinformation and distrust of vaccines, has resulted in decreased herd immunity—the protection provided to a population when a sufficient percentage is vaccinated. This leaves vulnerable individuals unprotected and allows the virus to spread rapidly.
Other factors contribute to outbreaks, including:
- Transmission pathways: Airborne transmission is the most common, but direct contact with respiratory secretions also plays a role.
- Importance of high vaccination rates: Achieving high vaccination rates (typically above 95%) is crucial for establishing herd immunity and preventing outbreaks.
- Impact of vaccine hesitancy on community health: Vaccine hesitancy undermines public health efforts and increases the risk for widespread outbreaks.
- Role of international travel in spreading the virus: Travel to areas with ongoing measles outbreaks can introduce the virus to communities with lower vaccination rates.
Prevention and Treatment Strategies for Measles
The most effective way to prevent measles is through vaccination. The MMR (measles, mumps, and rubella) vaccine is a safe and highly effective way to protect against measles. This vaccine is typically administered in two doses, offering robust protection against this highly contagious virus.
Addressing common misconceptions surrounding the MMR vaccine is crucial for increasing vaccination rates. The vaccine has a strong safety profile and is vital in protecting individuals and public health. There is extensive scientific evidence supporting its effectiveness and safety.
Unfortunately, there is no specific treatment for measles. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and preventing complications. This may include supportive care such as rest, fluids, and over-the-counter medications to alleviate symptoms. Serious complications of measles, particularly in young children and immunocompromised individuals, may require hospitalization. Early intervention is vital for minimizing these risks.
Public health measures play a crucial role in containing outbreaks. These measures often include:
- MMR vaccine schedule and effectiveness: The recommended schedule is two doses, with the first dose given at 6-12 months and the second dose at 4-6 years.
- Symptoms of measles and when to seek medical attention: Symptoms include fever, cough, runny nose, and a characteristic rash. Seek medical attention immediately if you suspect measles infection.
- Treatment options and supportive care: Treatment focuses on supportive care, alleviating symptoms, and preventing complications.
- Public health measures (e.g., quarantine, contact tracing): These measures are vital in limiting the spread of the virus.
Staying Informed and Protecting Yourself and Your Community
Staying up-to-date on the latest information regarding the measles outbreak is crucial. Reliable sources such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the World Health Organization (WHO) provide accurate and current data. Consulting these sources regularly can help individuals stay informed about the evolving situation.
Getting vaccinated is the single most effective way to protect yourself and your community from measles. Ensuring that you and your family are up-to-date on your MMR vaccinations is paramount in preventing further spread.
Beyond vaccination, practicing good hygiene plays a significant role in limiting the transmission of measles:
- Reliable sources for updates on the outbreak: CDC and WHO websites are excellent sources for current information.
- Importance of vaccination for individuals and community protection: Vaccination protects not only the individual but also contributes to herd immunity.
- Hygiene practices to reduce risk of infection: Frequent handwashing, covering coughs and sneezes, and avoiding close contact with infected individuals.
- Steps to take if you suspect measles infection: Seek immediate medical attention.
Conclusion: Staying Vigilant Against the Measles Outbreak
The measles outbreak in the United States highlights the critical importance of vaccination and public health measures. The contagious nature of the measles virus, coupled with vaccine hesitancy, has led to a concerning resurgence. Understanding the causes, prevention strategies, and available resources is essential for protecting ourselves and our communities.
Vaccination remains the most effective tool in preventing measles and reducing the severity of outbreaks. Staying informed about the latest updates, practicing good hygiene, and seeking medical advice when necessary are all vital steps in combating the spread of this highly contagious disease. Stay informed about the latest updates on the measles outbreak in the United States and take the necessary steps to protect yourself and your community. Get vaccinated today!

Featured Posts
-
 Emergency Red Tide Warning Cape Cod Beaches Closed
May 30, 2025
Emergency Red Tide Warning Cape Cod Beaches Closed
May 30, 2025 -
 Six New Measles Infections Confirmed In Kansas What You Need To Know
May 30, 2025
Six New Measles Infections Confirmed In Kansas What You Need To Know
May 30, 2025 -
 Beyond Bmw And Porsche The Broader Implications Of Chinas Automotive Market Dynamics
May 30, 2025
Beyond Bmw And Porsche The Broader Implications Of Chinas Automotive Market Dynamics
May 30, 2025 -
 Transfer Perfekt Garteig Verlaesst Ingolstadt Und Spielt Fortan Fuer Augsburg
May 30, 2025
Transfer Perfekt Garteig Verlaesst Ingolstadt Und Spielt Fortan Fuer Augsburg
May 30, 2025 -
 Deutsche Bank Depositary Receipts Virtual Investor Conference May 15 2025
May 30, 2025
Deutsche Bank Depositary Receipts Virtual Investor Conference May 15 2025
May 30, 2025
