Strong Retail Sales Data Could Delay Bank Of Canada Rate Reduction
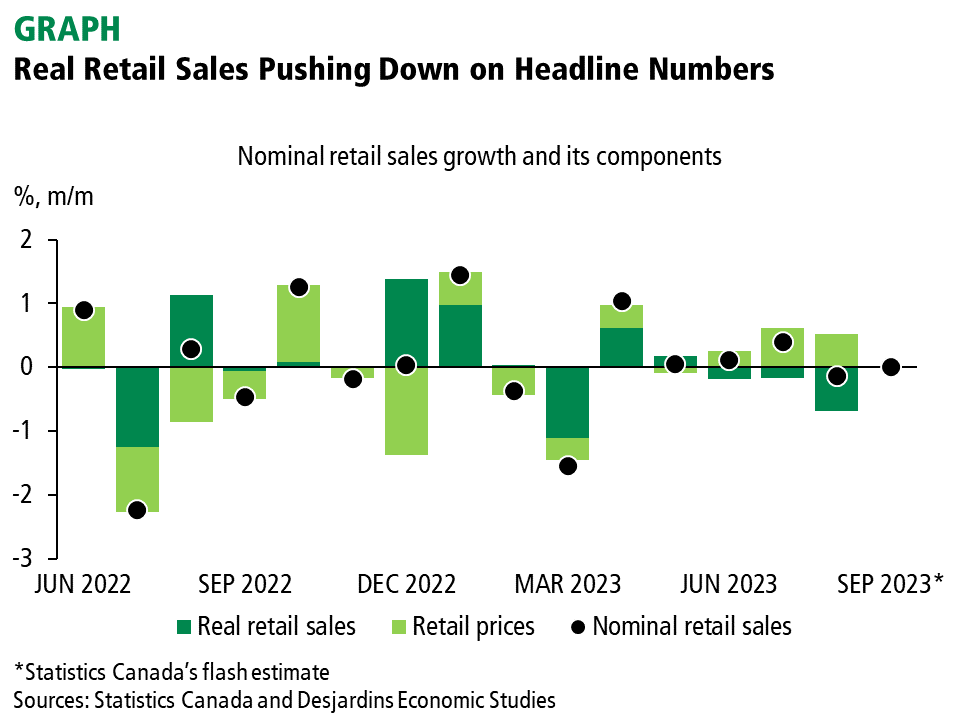
Table of Contents
The Current Economic Climate in Canada
Canada's economy is currently navigating a complex landscape. While retail sales have surged, a complete picture requires examining other key economic indicators. Inflation, though easing, remains above the BoC's target range, exerting upward pressure on interest rates. Unemployment, while relatively low, isn't providing sufficient slack to justify aggressive rate cuts. GDP growth projections remain moderate, suggesting a steady but not spectacular economic expansion.
- Recent inflation data: July's inflation rate, while lower than previous months, still exceeded the BoC's 2% target, adding to pressure to maintain interest rates at their current level.
- Current unemployment rate: The relatively low unemployment rate signals a tight labor market, potentially contributing to wage pressures and further inflation.
- Overall GDP growth projections: Analysts predict modest GDP growth for the remainder of 2023, suggesting continued, though not overly robust, economic expansion.
Impact of Strong Retail Sales on Interest Rate Decisions
Strong consumer spending, as reflected in robust retail sales data, typically indicates a healthy and resilient economy. This positive economic signal could lead the BoC to reconsider its plans for interest rate cuts. Robust retail sales might suggest that the economy doesn't require the stimulus of lower interest rates.
- Analysis of the data: The July retail sales surge was particularly strong in specific sectors like automotive and furniture sales, indicating sustained consumer confidence and spending.
- Potential reasons for strong retail sales: Pent-up demand following the pandemic, coupled with government stimulus measures implemented in previous years, might have contributed to this increased consumer spending.
- Concerns about inflationary pressures: The strong retail sales figures raise concerns that increased consumer spending might fuel inflationary pressures, potentially compelling the BoC to maintain or even slightly raise interest rates.
Alternative Scenarios and Market Reactions
The economic outlook isn't static. If retail sales data weakens in subsequent months, the pressure on the BoC to lower interest rates might increase. Conversely, if the strong trend continues, a delay in rate reductions, or even a pause in the easing cycle, becomes more likely. Market reactions will heavily depend on the BoC's actions.
- Market predictions: Many market analysts predict a rate cut later this year, but the timing remains highly uncertain, given the conflicting signals from the strong retail sales data.
- Potential impact on the Canadian dollar: A delay in rate cuts could strengthen the Canadian dollar, impacting both imports and exports.
- Effect on borrowing costs: Continued high interest rates would maintain higher borrowing costs for both consumers and businesses, potentially impacting investment and economic growth.
Bank of Canada's Communication and Future Outlook
The BoC's recent communications have emphasized its commitment to price stability. Its upcoming announcements will likely incorporate the latest economic data, including the strong retail sales figures, when formulating its future monetary policy decisions.
- Summary of recent BoC statements: Recent press releases and monetary policy reports underscore the BoC's data-dependent approach to interest rate adjustments.
- Key considerations for the BoC: The BoC will carefully weigh inflation targets, unemployment levels, and overall economic growth when making its decision.
- Possible future policy adjustments: Besides interest rate changes, the BoC might employ other policy tools to manage inflation and economic growth.
Strong Retail Sales Data and the Bank of Canada's Next Move
In conclusion, the unexpectedly strong retail sales data presents a significant challenge to the anticipated Bank of Canada interest rate reductions. The resilience of consumer spending, while positive in some aspects, also raises concerns about persistent inflationary pressures. This strong data might lead the BoC to delay any further rate cuts, or even to pause its easing cycle. The BoC's future decisions will hinge on a careful balancing act between supporting economic growth and maintaining price stability. Stay informed about upcoming economic data releases and Bank of Canada statements to better understand how strong retail sales data might continue to impact interest rate decisions.

Featured Posts
-
 Crystal Palace Target Emanuel Emegha To Replace Mateta
May 27, 2025
Crystal Palace Target Emanuel Emegha To Replace Mateta
May 27, 2025 -
 The Nora Fatehi Rasha Thadani Feud Unpacking The 100 Noras Comment On Reddit
May 27, 2025
The Nora Fatehi Rasha Thadani Feud Unpacking The 100 Noras Comment On Reddit
May 27, 2025 -
 How To Stream 1923 Season 2 Episode 4 For Free Tonight
May 27, 2025
How To Stream 1923 Season 2 Episode 4 For Free Tonight
May 27, 2025 -
 Hailey Bieber I Njen Neocekivani Styling Plava Vintage Gucci Haljina
May 27, 2025
Hailey Bieber I Njen Neocekivani Styling Plava Vintage Gucci Haljina
May 27, 2025 -
 The Ultimate Paramount Showdown Which Show Reigns Supreme
May 27, 2025
The Ultimate Paramount Showdown Which Show Reigns Supreme
May 27, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 La Sentence De Marine Le Pen 5 Ans D Ineligibilite Reactions Et Debats
May 30, 2025
La Sentence De Marine Le Pen 5 Ans D Ineligibilite Reactions Et Debats
May 30, 2025 -
 Marine Le Pen Ineligible La Decision De Justice Et Ses Repercussions
May 30, 2025
Marine Le Pen Ineligible La Decision De Justice Et Ses Repercussions
May 30, 2025 -
 Le Jugement De Marine Le Pen 5 Ans D Ineligibilite Analyse Et Consequences
May 30, 2025
Le Jugement De Marine Le Pen 5 Ans D Ineligibilite Analyse Et Consequences
May 30, 2025 -
 Concert De Medine Subventionne En Grand Est Le Rn S Insurge
May 30, 2025
Concert De Medine Subventionne En Grand Est Le Rn S Insurge
May 30, 2025 -
 Condamnation De Marine Le Pen 5 Ans D Ineligibilite Et Une France Polarisee
May 30, 2025
Condamnation De Marine Le Pen 5 Ans D Ineligibilite Et Une France Polarisee
May 30, 2025
