Succession Planning For The Ultra-Wealthy: Challenges And Strategies
Table of Contents
The global population of ultra-high-net-worth individuals (UHNWIs) is rapidly expanding, presenting a crucial need for robust and comprehensive succession planning. This article focuses on Succession Planning for the Ultra-Wealthy, exploring the unique challenges faced by these families and outlining effective strategies to ensure a smooth and successful transfer of wealth and legacy across generations. We will delve into the complexities of managing diverse assets, navigating family dynamics, protecting wealth from volatility, and integrating philanthropic goals into long-term plans.
H2: Unique Challenges in Succession Planning for Ultra-High-Net-Worth Families:
H3: Complex Asset Structures:
Ultra-high-net-worth families typically own a diverse portfolio of assets far beyond simple stocks and bonds. These complex holdings present significant challenges for succession planning. The valuation and distribution of these assets can be incredibly intricate, requiring specialized expertise.
-
Difficulties in Valuation: Accurately valuing assets like real estate portfolios, private equity stakes, art collections, intellectual property rights, and other illiquid investments is challenging and requires specialized appraisers.
-
Tax Implications: International tax laws and estate taxes vary significantly, creating complexities in distributing assets across borders and minimizing tax liabilities. Careful tax planning is essential to mitigate these challenges.
-
Distribution Challenges: Dividing assets fairly and equitably among multiple heirs, while considering their individual circumstances and needs, is a significant hurdle.
-
Examples of Complex Assets and Their Specific Challenges:
- Private Equity: Illiquidity, valuation uncertainties, and potential disputes over management control.
- Real Estate: Varied market values across different locations and jurisdictions, potential for disputes over property division.
- Art Collections: Unique valuation complexities, requiring specialized expertise and potentially impacting inheritance tax calculations.
- Intellectual Property: Determining value, managing licensing agreements, and ensuring proper transfer to heirs.
H3: Family Dynamics and Conflicts:
Family dynamics play a crucial role in the success of succession planning. Disagreements among family members regarding wealth management, inheritance distribution, and philanthropic endeavors are common.
-
Sibling Rivalry: Competition and resentment among siblings can lead to significant disputes and legal battles.
-
Differing Financial Philosophies: Heirs may have vastly different investment approaches and risk tolerances, making it difficult to reach a consensus on wealth management strategies.
-
Lack of Communication: Open and honest communication is vital, but often lacking, leading to misunderstandings and mistrust.
-
Common Family Conflicts and Strategies for Conflict Resolution:
- Preemptive Mediation: Engaging a family therapist or mediator to facilitate open communication and address potential conflicts proactively.
- Family Governance Structures: Establishing clear rules, roles, and decision-making processes to minimize disputes.
- Professional Advisors: Utilizing financial advisors, lawyers, and other experts to provide neutral guidance and support.
H3: Protecting Assets from Volatility and Market Fluctuations:
Protecting accumulated wealth from market downturns and unforeseen circumstances is paramount for ultra-high-net-worth families. Implementing robust strategies is crucial for preserving capital and ensuring long-term financial security.
-
Diversification: Spreading investments across different asset classes reduces the impact of market volatility on the overall portfolio.
-
Risk Management: Implementing sophisticated risk management techniques to identify and mitigate potential threats.
-
Asset Protection Trusts: Utilizing trusts and other legal structures to safeguard assets from creditors and other potential liabilities.
-
Different Asset Protection Strategies and Their Benefits:
- Offshore Trusts: Protecting assets from domestic tax laws and creditors.
- Irrevocable Trusts: Providing asset protection and tax advantages.
- Insurance Strategies: Mitigating the risk of unforeseen events like lawsuits or catastrophic losses.
H3: Philanthropic Goals and Legacy Planning:
Many ultra-high-net-worth individuals wish to leave a lasting legacy through philanthropic activities. Integrating these goals into succession planning ensures that their values are carried forward.
-
Family Foundations: Establishing a family foundation provides a structured vehicle for charitable giving and allows for greater control over philanthropic initiatives.
-
Charitable Trusts: Offering tax advantages and allowing for long-term charitable giving.
-
Impact Investing: Investing in ventures aligned with philanthropic goals, generating both financial returns and social impact.
-
Examples of Philanthropic Initiatives and Their Incorporation into Succession Plans:
- Endowment Funds: Creating perpetual funds to support specific causes.
- Matching Gifts: Encouraging family members to participate in charitable giving.
- Grant Programs: Establishing grant programs to support specific charitable organizations or initiatives.
H2: Effective Strategies for Ultra-High-Net-Worth Succession Planning:
H3: Engaging a Multidisciplinary Team of Professionals:
Building a strong team of experienced professionals is essential for effective succession planning. This collaborative approach ensures a holistic and comprehensive approach.
-
Estate Planning Attorneys: Drafting legally sound wills, trusts, and other estate planning documents.
-
Tax Advisors: Minimizing tax liabilities through effective tax planning.
-
Financial Advisors: Developing and managing investment strategies that align with family goals.
-
Family Therapists: Facilitating communication and resolving family conflicts.
-
Roles and Responsibilities of Each Professional: Clearly defined roles ensure coordinated efforts and minimize potential conflicts.
H3: Developing a Comprehensive Succession Plan Document:
A well-structured succession plan document is crucial for guiding the transfer of wealth and legacy. This document must be clear, concise, and legally binding.
-
Asset Inventory: A detailed list of all assets, including their valuation and location.
-
Distribution Plan: A clear outline of how assets will be distributed to heirs.
-
Family Governance Structure: Guidelines for family decision-making and conflict resolution.
-
Philanthropic Goals: Details of charitable giving and legacy initiatives.
-
Key Components of a Comprehensive Succession Plan Document: All components should be comprehensive, easily understood, and legally sound.
H3: Implementing a Family Governance Structure:
A family governance structure provides a framework for family decision-making, particularly regarding wealth management and philanthropic activities.
-
Family Councils: Regular meetings to discuss family matters and make collective decisions.
-
Family Boards: Formal structures with specific roles and responsibilities for managing family assets and overseeing philanthropic activities.
-
Mediation Processes: Establishing clear procedures for resolving disputes.
-
Examples of Family Governance Structures and Their Benefits: Tailored structures depend on family size, complexity, and goals.
H3: Regular Review and Updates:
Succession plans should not be static documents. Regular review and updates are crucial to adapt to changing circumstances, family needs, and economic conditions.
-
Market Fluctuations: Adjusting investment strategies based on market performance.
-
Family Changes: Addressing changes in family structure, such as births, deaths, or marriages.
-
Legal and Tax Changes: Keeping abreast of changes in relevant laws and regulations.
-
Reasons for Reviewing and Updating a Succession Plan: Ensuring the plan remains relevant and effective.
3. Conclusion:
Succession Planning for the Ultra-Wealthy presents unique challenges, including managing complex assets, navigating family dynamics, and protecting wealth from volatility. However, with proactive planning and the engagement of a multidisciplinary team of professionals, UHNW families can successfully transfer their wealth and legacy across generations. A comprehensive succession plan, incorporating a well-defined family governance structure and regular reviews, is crucial. Don't wait until it's too late. Secure your family's future and protect your legacy today. Plan your family's future with effective Succession Planning for the Ultra-Wealthy by contacting a reputable wealth management firm or estate planning lawyer for a consultation.

Featured Posts
-
 Karin Polman Nieuwe Directeur Hypotheken Bij Abn Amro Florius En Moneyou
May 22, 2025
Karin Polman Nieuwe Directeur Hypotheken Bij Abn Amro Florius En Moneyou
May 22, 2025 -
 Wtt Star Contender Chennai 2025 Kamals Loss And Farewell
May 22, 2025
Wtt Star Contender Chennai 2025 Kamals Loss And Farewell
May 22, 2025 -
 Todays Nyt Wordle Hints Answer And Help For March 18 1368
May 22, 2025
Todays Nyt Wordle Hints Answer And Help For March 18 1368
May 22, 2025 -
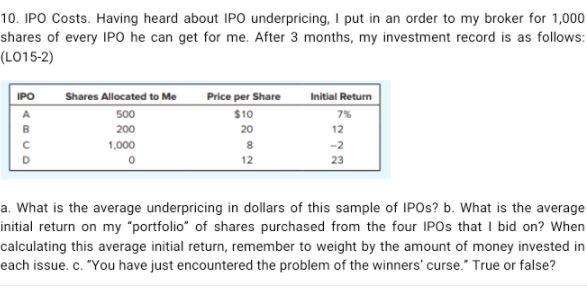 Core Weave Sets Ipo Price At 40 Below Projected 51 Midpoint
May 22, 2025
Core Weave Sets Ipo Price At 40 Below Projected 51 Midpoint
May 22, 2025 -
 Cest La Petite Italie De L Ouest Architecture Toscane A Nom De La Ville
May 22, 2025
Cest La Petite Italie De L Ouest Architecture Toscane A Nom De La Ville
May 22, 2025
