The Complex Legacy Of Trump's Tariffs: A Study Of US Manufacturing.
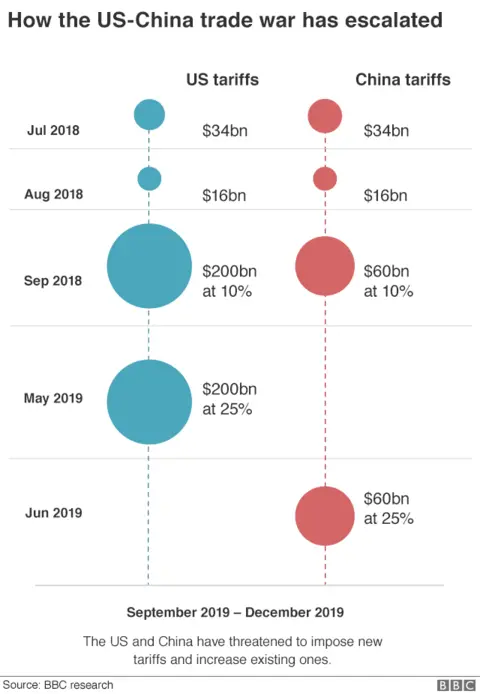
Table of Contents
The Initial Aims of Trump's Tariffs and Their Economic Rationale
The Trump administration justified its tariff policies as a necessary measure to protect American industries from unfair trade practices and to revive domestic production. The stated goals were multifaceted, encompassing both defensive and offensive strategies.
Protecting Domestic Industries
The core rationale was to safeguard specific sectors deemed vital to the US economy. This protectionist approach targeted industries struggling with foreign competition, particularly in steel and aluminum.
- Steel Tariffs: 25% tariffs were imposed on steel imports from various countries, aiming to protect domestic steel producers from cheaper foreign imports.
- Aluminum Tariffs: Similar 10% tariffs were levied on aluminum imports, citing national security concerns and unfair trade practices.
- Section 301 Tariffs on China: These tariffs, imposed under Section 301 of the Trade Act of 1974, targeted a wide range of Chinese goods, alleging intellectual property theft and forced technology transfer. These actions escalated into a full-blown trade war with significant repercussions. The stated aim was to force China to change its trade practices.
The keywords "trade war," "protectionism," and "American manufacturing" were central to the administration's justification. The underlying economic rationale was based on the theory of protectionism, arguing that shielding domestic industries from foreign competition would allow them to grow stronger, leading to job creation and increased economic activity.
Reciprocity and Negotiation Tactics
A key element of Trump's tariff strategy was using them as leverage in trade negotiations. The administration aimed to achieve more favorable trade agreements by threatening or imposing tariffs on other countries.
- Negotiations with Canada and Mexico: Tariffs were used as a bargaining chip in renegotiating the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), resulting in the new USMCA agreement.
- Trade Disputes with the European Union: Tariffs were imposed on various EU goods, leading to retaliatory tariffs from the EU, further exacerbating the trade war.
- Tariffs on Chinese Goods: The tariffs on Chinese goods were explicitly intended to force concessions from China on issues such as intellectual property rights and trade imbalances. The outcome, however, was inconclusive and resulted in prolonged trade tensions.
The administration believed that its aggressive use of tariffs would increase its "negotiating power," forcing other countries to accept more favorable terms in trade agreements. The strategy, however, often resulted in retaliatory measures and further complicated global trade relations. The keywords "trade agreements," "bilateral trade," and "negotiating power" highlight the strategic element of this approach.
Short-Term Impacts on US Manufacturing: Winners and Losers
The immediate impact of Trump's tariffs was far from uniform across the US manufacturing sector. Some industries thrived while others suffered significant setbacks.
Industries Benefiting from Tariffs
Certain sectors saw a boost in domestic demand and production due to increased import costs.
- Steel and Aluminum: Domestic producers in these sectors benefited from the reduced foreign competition, leading to increased production and, in some cases, job creation. However, this came at the expense of higher costs for downstream industries that rely on these inputs.
- Some Agricultural Sectors: While some agricultural exports suffered, certain sectors that competed with imports experienced a temporary boost in domestic demand.
These examples highlight how the tariffs provided a short-term boost to "domestic production" and contributed to a temporary "economic stimulus" in select sectors. Increased "job growth" was claimed in certain areas, though the long-term sustainability of these gains remains questionable.
Industries Negatively Impacted by Tariffs
Many other sectors faced significant challenges due to higher input costs, reduced exports, and retaliatory tariffs.
- Automotive Industry: The automotive industry suffered from higher costs of steel and aluminum, impacting profitability and competitiveness.
- Agricultural Exports: Retaliatory tariffs imposed by other countries significantly impacted agricultural exports, leading to losses for farmers and related businesses.
- Manufacturing relying on imported components: Companies reliant on imported components faced increased production costs, forcing some to reduce output or raise prices.
The negative consequences included "supply chain disruptions," increased "inflation," and significantly "reduced exports" for various sectors. These factors led to job losses and plant closures in several industries.
Long-Term Effects and Unintended Consequences
The long-term effects of Trump's tariffs continue to unfold, revealing unintended consequences that complicate the overall assessment.
Inflationary Pressures
The tariffs contributed to inflationary pressures, impacting consumer prices and the overall economy.
- Increased costs of imported goods were passed on to consumers, leading to higher prices for various products.
- The increase in prices for essential goods negatively impacted lower-income households disproportionately.
- The inflationary impact created uncertainty and hampered economic growth.
The "inflationary impact" on "consumer prices" and the broader "economic consequences" are still being analyzed and debated. The long-term effects are complex and intertwined with other economic factors.
Shifting Global Supply Chains
Tariffs contributed to a reshaping of global supply chains, but not necessarily in the way intended.
- Some companies chose "reshoring," bringing manufacturing back to the US, but this was often offset by the increased costs.
- Many companies opted for "nearshoring," shifting production to other countries closer to the US, avoiding the tariffs but still impacting American workers.
- The disruption and uncertainty led to complexity and inefficiencies in global trade.
The impact on "global supply chains" and the long-term success of "reshoring" strategies is yet to be fully determined.
The Role of Automation and Technological Change
Technological advancements in manufacturing influenced the impact of tariffs.
- Automation allowed some companies to mitigate job losses by automating certain production processes.
- Technological change allowed some companies to adapt more quickly to the changing trade environment.
The integration of "automation" and "technological change" into manufacturing processes played a significant, yet often overlooked, role in shaping the outcome of the tariff policies. Assessing the full impact requires careful consideration of these technological factors alongside economic and political developments.
Conclusion: Assessing the Lasting Impact of Trump's Tariffs on US Manufacturing
The legacy of Trump's tariffs on US manufacturing is complex and multifaceted. While some industries benefited from increased domestic demand and protection from foreign competition, many others faced significant challenges due to higher input costs, reduced exports, and retaliatory tariffs. The long-term effects, including inflationary pressures and the reshaping of global supply chains, are still unfolding. It's clear that the simplistic narrative of a straightforward boost to American manufacturing is inaccurate.
The key takeaway is that the overall impact was mixed, with both positive and negative consequences that varied greatly across sectors. While the intended goal of boosting domestic production had some success in specific areas, the wider economic ramifications, including inflation and supply chain disruptions, overshadowed many of these gains.
Understanding the complex legacy of Trump’s tariffs requires further investigation into the specific impacts on various sectors of US manufacturing. Continue your research to form your own informed opinion on the long-term effects of these trade policies, including exploring data on specific industries affected and examining the ongoing debates surrounding trade policy and its effects on American jobs and the global economy.

Featured Posts
-
 Discover Rihannas Wedding Night Lingerie Collection From Savage X Fenty
May 06, 2025
Discover Rihannas Wedding Night Lingerie Collection From Savage X Fenty
May 06, 2025 -
 Rozheve Merezhivo Ta Rianna Fotosesiya Scho Zapam Yatayetsya
May 06, 2025
Rozheve Merezhivo Ta Rianna Fotosesiya Scho Zapam Yatayetsya
May 06, 2025 -
 Tracee Ellis Ross On Marriage Regret And Self Love
May 06, 2025
Tracee Ellis Ross On Marriage Regret And Self Love
May 06, 2025 -
 Getting To Know Emilie Livingston Jeff Goldblums Wife Age And Family
May 06, 2025
Getting To Know Emilie Livingston Jeff Goldblums Wife Age And Family
May 06, 2025 -
 Gazze Ye Yardim Malzemesi Sevkiyati Guencel Bilgiler Ve Gelismeler
May 06, 2025
Gazze Ye Yardim Malzemesi Sevkiyati Guencel Bilgiler Ve Gelismeler
May 06, 2025
