The Federal Reserve And Interest Rates: Navigating Economic Uncertainty
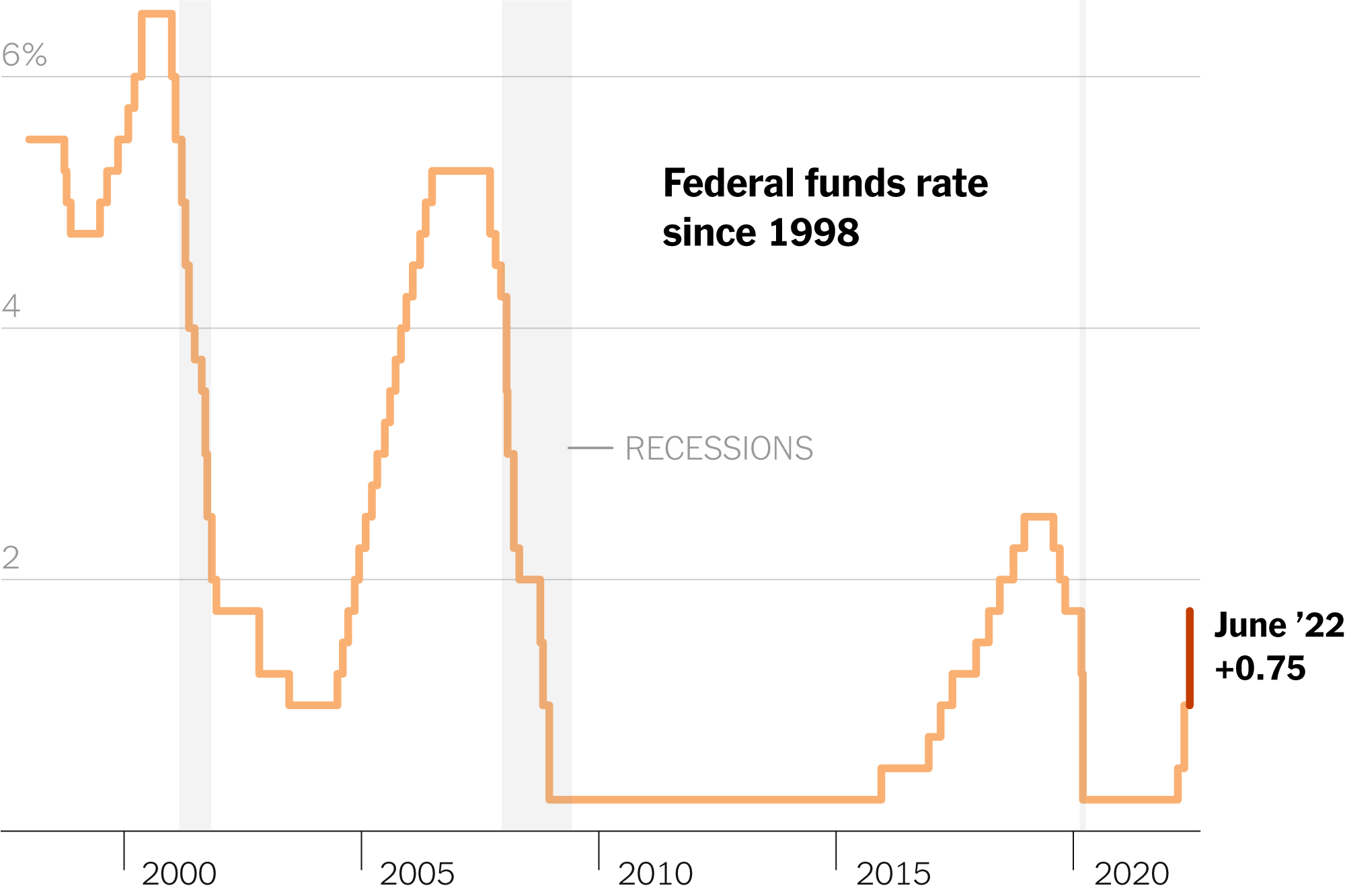
Table of Contents
The Federal Reserve's Role in Managing the Economy
The Federal Reserve operates under a dual mandate: maintaining price stability and achieving maximum employment. These seemingly straightforward goals often present a delicate balancing act. To influence the economy, the Fed employs several powerful tools, directly impacting interest rates and broader economic conditions:
- The federal funds rate: This is the target rate for overnight lending between banks. Adjusting this rate ripples through the entire financial system, influencing borrowing costs for other institutions and ultimately consumers. A higher federal funds rate generally leads to higher interest rates across the board.
- Reserve requirements: This refers to the percentage of deposits banks must hold in reserve, rather than lending out. Changes in reserve requirements affect the amount of money available for lending, influencing credit availability and interest rates.
- Quantitative easing (QE) and quantitative tightening (QT): QE involves the Fed buying government bonds to increase the money supply, lowering long-term interest rates and stimulating borrowing. Conversely, QT involves selling these bonds, reducing the money supply and potentially raising interest rates. These are powerful, albeit blunt, instruments for monetary policy.
- The discount rate: This is the interest rate at which commercial banks can borrow money directly from the Federal Reserve. It serves as a benchmark rate, influencing other interest rates within the banking system.
These tools, when utilized strategically, allow the Federal Reserve to influence short-term and long-term interest rates across the economy, impacting everything from mortgage rates to business loan costs.
Interest Rates and Their Impact on Economic Growth
Interest rates significantly impact borrowing costs for both businesses and consumers. This relationship forms a cornerstone of monetary policy:
- Higher interest rates: These discourage borrowing and spending, leading to decreased consumer demand and potentially slowing economic growth. Businesses might postpone investments due to higher borrowing costs. This can be a necessary tool to combat inflation, even if it leads to slower growth.
- Lower interest rates: These encourage borrowing and spending, boosting economic activity and potentially stimulating growth. Consumers are more likely to make large purchases (houses, cars), and businesses may invest more readily. However, excessively low interest rates can fuel inflation.
The effects on investment and consumer spending are substantial. Lower interest rates incentivize investment in new projects and capital expenditures, driving economic growth. Conversely, higher rates can curb investment and lead to decreased spending. The delicate balance the Fed aims for is crucial. Furthermore, higher interest rates can help to combat inflation by reducing demand.
Interest Rate Hikes and Economic Slowdowns
While interest rate hikes can effectively curb inflation, they also carry the risk of triggering a recession. The Fed walks a tightrope, attempting to manage inflation without stifling economic growth. Raising interest rates too aggressively can significantly reduce borrowing and investment, leading to job losses and a contraction in economic activity. This requires careful analysis of economic indicators and a nuanced understanding of the current economic climate. Historical examples, such as the Volcker shock in the early 1980s, demonstrate the potential for aggressive rate hikes to induce short-term pain for long-term gain, albeit at the cost of a recession.
Predicting Future Interest Rate Movements
Predicting future interest rate movements is challenging, yet crucial for investors and businesses. Several factors heavily influence the Fed's decisions:
- Inflation data (CPI, PCE): The Consumer Price Index (CPI) and Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) index are key measures of inflation. High inflation typically leads to interest rate hikes.
- Unemployment figures: Low unemployment often indicates a strong economy, potentially justifying interest rate increases to prevent overheating.
- Economic growth forecasts: Projections of future economic growth influence the Fed's decisions. Rapid growth might lead to rate hikes to prevent inflation, while slow growth may call for rate cuts to stimulate the economy.
Monitoring these key economic indicators is crucial, but even with precise data, predicting the Fed's actions remains inherently complex due to unforeseen economic shocks and changing global conditions.
Strategies for Navigating Economic Uncertainty
Navigating periods of interest rate volatility requires proactive strategies:
For investors, diversification of investment portfolios across different asset classes is vital. Hedging strategies can mitigate risks associated with interest rate fluctuations. A well-diversified portfolio can help to cushion the impact of changes in interest rates.
For businesses, careful financial planning and budgeting are essential. Understanding the potential impact of interest rate changes on borrowing costs and cash flow allows businesses to adapt their strategies. This could include securing long-term financing at favorable rates or adjusting pricing strategies in response to changing economic conditions.
- Diversification of investment portfolios: Spreading investments across various asset classes (stocks, bonds, real estate) reduces exposure to interest rate risk.
- Hedging strategies: Employing financial instruments to offset potential losses from interest rate changes can help to minimize risk.
- Careful financial planning and budgeting: Creating robust financial plans and budgets helps businesses and individuals better withstand economic shocks.
Conclusion
This article explored the intricate relationship between the Federal Reserve, interest rates, and economic uncertainty. Understanding the Fed's actions and their influence on interest rates is paramount for both individuals and businesses. The Fed's balancing act between price stability and maximum employment necessitates careful analysis of economic indicators, making precise predictions difficult. However, by staying informed about Federal Reserve decisions and economic data, you can improve your ability to navigate the dynamic landscape of interest rates and economic uncertainty. Regularly review your financial strategies and adapt to changing market conditions related to interest rates and the overall economic outlook. Understanding the Federal Reserve and its impact on interest rates is crucial for making sound financial decisions.

Featured Posts
-
 Colapinto Or Doohan Williams Team Principal Weighs In
May 09, 2025
Colapinto Or Doohan Williams Team Principal Weighs In
May 09, 2025 -
 Violences Conjugales A Dijon Le Boxeur Bilel Latreche Assigne En Aout
May 09, 2025
Violences Conjugales A Dijon Le Boxeur Bilel Latreche Assigne En Aout
May 09, 2025 -
 Massive Fentanyl Seizure Details From Pam Bondis Press Conference
May 09, 2025
Massive Fentanyl Seizure Details From Pam Bondis Press Conference
May 09, 2025 -
 Elon Musk And Dogecoin A Risky Investment Analyzing Teslas Stock Performance
May 09, 2025
Elon Musk And Dogecoin A Risky Investment Analyzing Teslas Stock Performance
May 09, 2025 -
 Doohans F1 Prospects Williams Assessment And Colapinto Links
May 09, 2025
Doohans F1 Prospects Williams Assessment And Colapinto Links
May 09, 2025
