The Impact Of European Shipyards On Russia's Arctic Gas Deliveries
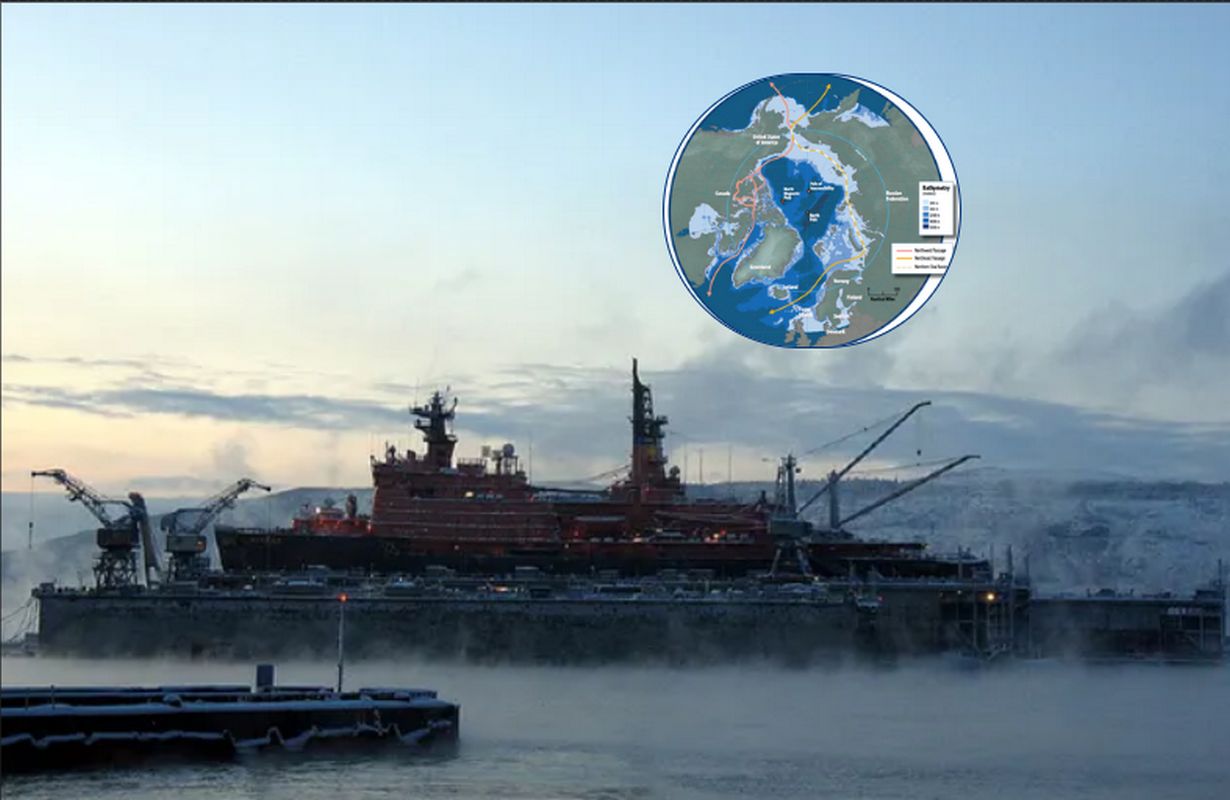

Table of Contents
The Role of Specialized Ice-Class Vessels
Sub-heading: The Necessity for Advanced Shipbuilding Technology
The unique challenges of navigating Arctic waters necessitate specialized ice-class vessels, capable of withstanding extreme conditions like thick ice floes, freezing temperatures, and unpredictable weather patterns. These vessels are not merely modified standard ships; they require sophisticated design and construction incorporating reinforced hulls, powerful propulsion systems, and advanced icebreaking capabilities. This is where European shipyards play a critical role.
- The unique challenges of navigating Arctic waters necessitate specialized ice-class vessels, capable of withstanding extreme conditions. These conditions demand vessels built to withstand immense pressure and impact from ice, requiring specialized materials and construction techniques.
- European shipyards possess advanced technologies and experience in constructing these specialized vessels. Decades of experience in building icebreakers and other Arctic-capable vessels have given European shipyards a technological edge.
- Russia's domestic shipbuilding capabilities lag behind in producing ice-class vessels at the scale and speed required. While Russia possesses shipbuilding expertise, its capacity to build the large number of sophisticated ice-class vessels needed for large-scale Arctic gas extraction and transport currently falls short.
- Dependence on European shipyards creates logistical bottlenecks and potential vulnerabilities. Reliance on foreign shipbuilders introduces potential delays, cost overruns, and susceptibility to geopolitical factors, including sanctions.
Further detail: Specific ice classes, such as Arc7 and Arc8, represent different levels of icebreaking capability. Arc7 vessels, for example, are designed to navigate the most challenging ice conditions in the Arctic. Finnish and Norwegian shipyards, notably, possess significant expertise and experience in constructing such vessels. The lack of equivalent domestic capacity in Russia creates a crucial dependency.
Geopolitical Implications and Sanctions
Sub-heading: The Impact of Western Sanctions on Russian Access to Shipbuilding
International sanctions imposed on Russia following its invasion of Ukraine have significantly impacted its access to European shipbuilding technology and expertise. These sanctions extend beyond simple trade restrictions; they affect access to crucial components, software, and even financing for new vessel construction.
- International sanctions imposed on Russia have significantly impacted its access to European shipbuilding technology and expertise. This includes restrictions on the export of key technologies and materials necessary for ice-class vessel construction.
- Sanctions may limit the availability of crucial components, software, and financing for new vessel construction. This makes it significantly harder for Russian companies to commission new icebreakers and LNG carriers from European shipyards.
- This reliance on foreign technology creates vulnerabilities to geopolitical shifts and potential disruptions in gas delivery. The sanctions highlight the risks associated with such dependencies, potentially impacting the reliability and timeliness of Arctic gas shipments.
- The sanctions could accelerate the development of Russia's domestic shipbuilding industry, but with uncertain timelines. While sanctions might spur domestic investment in shipbuilding technology, building this capability from the ground up is a lengthy process.
Further detail: The specific sanctions imposed vary, targeting different aspects of shipbuilding, from the export of specialized steel alloys to the provision of advanced navigation and communication systems. Russia may attempt to circumvent these restrictions through various means, but the overall impact is a significant hurdle to its Arctic gas ambitions.
Economic Considerations and Costs
Sub-heading: The Price of Reliance: Economic Factors and Competition
The economic implications of relying on European shipyards are multifaceted. While European shipbuilders possess the required expertise, commissioning vessels from them can be considerably more expensive than utilizing domestic builders – if those builders had the capability. Moreover, sanctions and potential delays add further costs.
- Commissioning vessels from European shipyards can be significantly more expensive than utilizing domestic builders (if capable). This cost differential needs to be factored into the overall profitability of Arctic gas projects.
- The cost implications of sanctions and potential delays in construction need to be considered. Sanctions create uncertainty and potential delays, adding to the overall expenses.
- Competition from other Arctic gas producers, who may have more reliable access to shipbuilding, could impact Russia's market share. Competitors with less reliance on sanctioned countries may gain a significant advantage in the market.
- The overall economic viability of Russian Arctic gas projects is influenced by the costs associated with vessel procurement. The high cost of ice-class vessels is a major factor in the long-term sustainability of Russian Arctic gas operations.
Further detail: A detailed comparative cost analysis between European and (hypothetically capable) Russian shipbuilding would highlight the economic impact. This analysis would need to consider factors like labor costs, material costs, and construction timelines. The findings would directly influence the economic feasibility of future Arctic gas projects.
Alternative Solutions and Future Outlook
Bullet points:
- Russia's investment in domestic shipbuilding capabilities: Russia is actively investing in developing its own ice-class vessel building capabilities, although progress is likely to be gradual.
- Exploration of alternative shipbuilding partnerships outside of Europe: Russia may seek to collaborate with Asian shipyards to reduce its reliance on European builders. This presents its own set of political and logistical challenges.
- Potential for technological advancements that reduce reliance on specialized ice-class vessels: Developments in icebreaker technology and alternative shipping routes could lessen the need for the most specialized vessels.
- The long-term impact of climate change on Arctic shipping routes and vessel requirements: Climate change is influencing Arctic ice conditions, potentially impacting the need for and type of ice-class vessels required.
Further detail: Specific Russian shipbuilding initiatives, including investments in new infrastructure and technology transfer programs, need to be examined to assess their effectiveness. The potential partnerships with Asian shipyards (e.g., China and South Korea) present both opportunities and risks for Russia.
Conclusion
The relationship between European shipyards and Russia's Arctic gas deliveries is complex and multifaceted, significantly influenced by geopolitical factors, economic constraints, and technological necessities. While European shipyards possess the expertise and capacity to build the specialized ice-class vessels required for Arctic operations, sanctions and economic considerations create significant challenges for Russia. The future of Russia's Arctic gas ambitions hinges on its ability to address these challenges, whether through enhanced domestic shipbuilding capabilities, alternative partnerships, or technological innovations. Understanding the intricate interplay between European shipyards and Russia's Arctic gas deliveries is crucial for predicting future energy market dynamics and geopolitical stability in the Arctic region. Further research into this critical relationship is needed to fully comprehend the long-term implications. The impact of sanctions and the ongoing development of Russian domestic shipbuilding capacity warrant continued monitoring to understand the future of Arctic gas delivery and its geopolitical implications.

Featured Posts
-
 Nyt Spelling Bee Puzzle 387 March 25 Complete Guide With Solutions
Apr 26, 2025
Nyt Spelling Bee Puzzle 387 March 25 Complete Guide With Solutions
Apr 26, 2025 -
 Shedeur Sanders Nfl Draft Prospects An Espn Analysts Perspective
Apr 26, 2025
Shedeur Sanders Nfl Draft Prospects An Espn Analysts Perspective
Apr 26, 2025 -
 Le Labo Du 8 Presente L Uvre Photographique De Pierre Terrasson
Apr 26, 2025
Le Labo Du 8 Presente L Uvre Photographique De Pierre Terrasson
Apr 26, 2025 -
 Is Gavin Newsoms Strategy A Gamble Analyzing The Fallout
Apr 26, 2025
Is Gavin Newsoms Strategy A Gamble Analyzing The Fallout
Apr 26, 2025 -
 Whistler Trip Chelsea Handlers Surprise Celebrity Companion
Apr 26, 2025
Whistler Trip Chelsea Handlers Surprise Celebrity Companion
Apr 26, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Ariana Grandes Hair And Tattoo Transformation Expert Opinion And Analysis
Apr 27, 2025
Ariana Grandes Hair And Tattoo Transformation Expert Opinion And Analysis
Apr 27, 2025 -
 Exploring Ariana Grandes New Look A Professional Assessment Of Her Tattoos And Hairstyle
Apr 27, 2025
Exploring Ariana Grandes New Look A Professional Assessment Of Her Tattoos And Hairstyle
Apr 27, 2025 -
 Understanding Ariana Grandes Latest Transformation A Professionals View
Apr 27, 2025
Understanding Ariana Grandes Latest Transformation A Professionals View
Apr 27, 2025 -
 Professional Commentary Ariana Grandes Bold Hair And Tattoo Changes
Apr 27, 2025
Professional Commentary Ariana Grandes Bold Hair And Tattoo Changes
Apr 27, 2025 -
 Ariana Grandes Style Evolution Professional Analysis Of Her New Look
Apr 27, 2025
Ariana Grandes Style Evolution Professional Analysis Of Her New Look
Apr 27, 2025
