The Impact Of Wildfires On Record Global Forest Loss
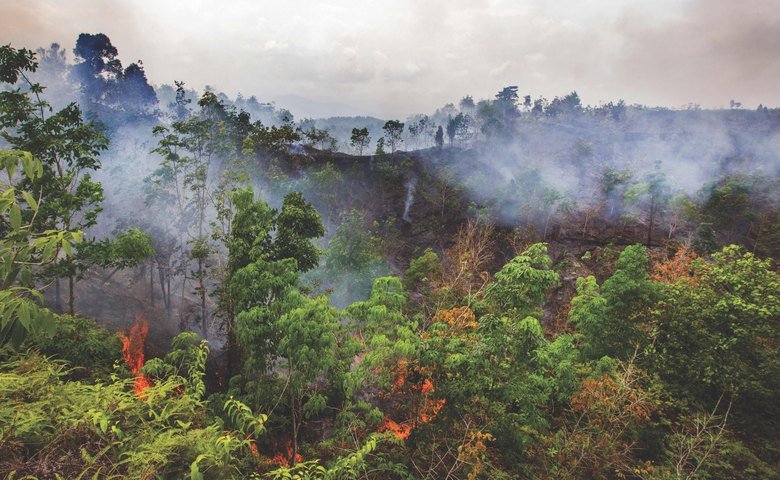

Table of Contents
The Devastating Scale of Wildfires and Their Contribution to Global Forest Loss
Wildfires are consuming vast swathes of forestland annually, contributing significantly to global deforestation. Millions of hectares burn each year, a number that has been steadily increasing in recent decades. This escalating trend is not merely a localized problem; it's a global crisis.
- Increased Wildfire Frequency and Intensity: Data reveals a concerning rise in both the frequency and intensity of wildfires globally, particularly in regions experiencing prolonged droughts and extreme heat.
- Geographically Affected Regions: The Amazon rainforest, boreal forests of Canada and Russia, and Mediterranean regions are among the areas most severely impacted by wildfires, experiencing catastrophic losses of forest cover.
- Vulnerable Forest Types: Coniferous forests, with their dense, flammable needles, are particularly vulnerable to intense and rapidly spreading wildfires. Dry scrublands and eucalyptus forests also pose significant fire risks.
- Climate Change's Role: Climate change is a key driver in this alarming trend. Rising global temperatures, prolonged droughts, and more frequent heatwaves create ideal conditions for wildfires to ignite and spread rapidly.
The Ecological Consequences: Biodiversity Loss and Habitat Destruction
The ecological consequences of wildfires are catastrophic, leading to significant biodiversity loss and widespread habitat destruction. The rapid destruction of entire ecosystems decimates plant and animal populations, disrupting delicate ecological balances.
- Endangered Species Affected: Numerous endangered species, including the koala in Australia and various bird species in California, face population decline and habitat loss due to increasingly frequent and intense wildfires.
- Ecosystem Disruption: Wildfires disrupt established food webs, leading to cascading effects throughout the ecosystem. The loss of key plant species affects herbivores, which in turn impacts predators and other species in the food chain.
- Long-Term Impacts on Regeneration: While some ecosystems possess natural resilience and can regenerate after a fire, the intensity and frequency of modern wildfires often exceed the capacity of forests to recover, leading to long-term ecosystem degradation.
- Loss of Genetic Diversity: Wildfires can eliminate entire populations of plants and animals, leading to a significant loss of genetic diversity, reducing the overall resilience and adaptability of ecosystems.
The Carbon Cycle and Climate Change: Wildfires as a Major Carbon Source
Forests act as crucial carbon sinks, absorbing significant amounts of atmospheric CO2. However, wildfires release massive quantities of this stored carbon back into the atmosphere, exacerbating climate change.
- Carbon Sequestration: Trees and other plants absorb CO2 during photosynthesis, storing carbon in their biomass and soil. This process, known as carbon sequestration, is vital for regulating the Earth's climate.
- Carbon Released Annually: Wildfires release billions of tons of CO2 into the atmosphere annually, contributing significantly to the greenhouse effect and accelerating global warming.
- Greenhouse Effect and Climate Change: The increased CO2 levels from wildfires contribute significantly to the greenhouse effect, trapping heat and further raising global temperatures, creating a dangerous feedback loop.
- Feedback Loops: Climate change increases the risk and intensity of wildfires, which in turn release more carbon into the atmosphere, further accelerating climate change. This creates a vicious cycle that must be addressed urgently.
Economic and Social Impacts: The Human Cost of Wildfires
The impact of wildfires extends beyond environmental damage, inflicting significant economic and social costs on communities worldwide.
- Economic Costs: Wildfires incur massive costs, including firefighting expenses, property damage, loss of timber resources, and disruption to tourism and other industries.
- Impact on Forestry Economies: Local economies heavily reliant on forestry suffer severe economic blows from wildfire damage, impacting jobs and livelihoods.
- Health Impacts of Smoke: Wildfire smoke poses serious health risks, causing respiratory illnesses, cardiovascular problems, and other health issues for exposed populations.
- Social and Psychological Consequences: The loss of homes, livelihoods, and community infrastructure from wildfires has profound social and psychological impacts, leading to displacement, trauma, and long-term mental health challenges.
Mitigation and Prevention Strategies: Addressing the Wildfire Crisis
Addressing the wildfire crisis requires a multi-pronged approach focused on prevention, mitigation, and international cooperation.
- Improved Forest Management: Implementing sustainable forest management practices, including controlled burns to reduce fuel loads and creating firebreaks, can significantly reduce wildfire risk.
- Early Warning Systems: Investing in advanced early warning systems and improved fire detection technologies is crucial for rapid response and effective wildfire suppression.
- Community-Based Preparedness: Empowering communities with wildfire preparedness programs, including evacuation plans and public awareness campaigns, is essential for minimizing human impacts.
- Addressing Climate Change: Mitigating climate change through reducing greenhouse gas emissions is crucial to reducing the frequency and intensity of wildfires in the long term.
- International Cooperation: International cooperation is essential for effective global forest conservation efforts, including sharing best practices and supporting reforestation initiatives.
Conclusion
Wildfires are a major driver of record global forest loss, resulting in devastating environmental, economic, and social consequences. The scale of this problem necessitates urgent action. We must invest in sustainable forest management, improve wildfire prevention and mitigation strategies, and aggressively tackle climate change to reduce the risk of future catastrophic wildfires. Learn more about global forest loss and support initiatives promoting forest conservation, sustainable forestry, and reforestation efforts. Advocate for policies that address climate change and support sustainable forest management practices. Together, we can combat the ongoing crisis of global forest loss due to wildfires.

Featured Posts
-
 Two Israeli Embassy Staff Members Dead In Washington Dc Shooting Ap Photo Coverage
May 22, 2025
Two Israeli Embassy Staff Members Dead In Washington Dc Shooting Ap Photo Coverage
May 22, 2025 -
 Impact Van Heffingen Op Voedselexport Naar Vs Abn Amro Rapport
May 22, 2025
Impact Van Heffingen Op Voedselexport Naar Vs Abn Amro Rapport
May 22, 2025 -
 Challenging The Trans Australia Runs World Record
May 22, 2025
Challenging The Trans Australia Runs World Record
May 22, 2025 -
 Saskatchewans Costco Campaign A Political Panel Analysis
May 22, 2025
Saskatchewans Costco Campaign A Political Panel Analysis
May 22, 2025 -
 Arrest Made In Killing Of Embassy Workers Lischinsky And Milgram
May 22, 2025
Arrest Made In Killing Of Embassy Workers Lischinsky And Milgram
May 22, 2025
