The Magnificent Seven's Fall: Analyzing A $2.5 Trillion Market Value Decline
Table of Contents
Rising Interest Rates and Inflationary Pressures
The Federal Reserve's aggressive monetary policy, implemented to combat persistent inflation, has significantly impacted the Magnificent Seven and the broader tech industry. This section analyzes the twin pressures of rising interest rates and inflation on the market value decline.
The Impact of Monetary Policy
The Federal Reserve's interest rate hikes aim to cool the economy by increasing borrowing costs. This has several detrimental effects on tech companies:
- Reduced Investment: Higher borrowing costs make it more expensive for tech companies to invest in expansion projects, research and development (R&D), and acquisitions, hindering future growth. This impacts long-term market capitalization prospects.
- Lower Valuations: Higher interest rates make future earnings less valuable in present-day terms, directly impacting the discounted cash flow models used to determine a company's market capitalization. This effect is particularly pronounced for growth stocks, which are heavily reliant on future earnings.
- Dampened Revenue Growth: Increased interest rates lead to higher mortgage rates and loan costs, reducing consumer discretionary spending. This directly impacts the revenue streams of many tech companies, from reduced smartphone sales to lower subscription rates for online services.
Inflation's Squeeze on Consumer Spending
Rampant inflation has eroded consumer purchasing power, leading to a noticeable decline in demand for non-essential goods and services, including many tech products.
- Reduced Demand for Tech Products: Consumers are delaying purchases of smartphones, laptops, and other tech gadgets as they prioritize essential expenses.
- Impact on Subscription Services: Subscription services, a key revenue driver for many tech companies, are also feeling the pinch as consumers cut back on non-essential spending.
- Ripple Effect: This reduced consumer spending creates a ripple effect across the tech ecosystem, impacting everything from hardware manufacturers to software developers.
Overvaluation and Market Corrections
The meteoric rise in the market capitalization of the Magnificent Seven in recent years led to concerns about potential overvaluation, setting the stage for a significant market correction.
The Tech Bubble Burst?
Many analysts are questioning whether the previous valuations were sustainable, suggesting a tech bubble burst, or at least a necessary correction within a larger market cycle.
- Valuation Metrics: Analyzing Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratios and other valuation metrics reveals that some Magnificent Seven companies were trading at significantly higher multiples than historical averages, indicating potential overvaluation.
- Speculative Investment: A significant portion of the previous growth was fueled by speculative investment and exuberant investor sentiment, leading to a vulnerable market susceptible to a downturn.
- Historical Comparisons: The current decline can be compared to previous tech bubble bursts, like the dot-com crash of 2000, to better understand the scale and potential duration of the correction.
Profit Taking and Investor Sentiment Shift
A shift in investor sentiment, fueled by macroeconomic uncertainty and concerns about future growth, triggered substantial profit-taking, exacerbating the market value decline.
- Sell-Off Patterns: Analysis of sell-off patterns shows a significant exodus of capital from tech stocks, indicating a loss of investor confidence.
- Institutional Investor Behavior: Large institutional investors, often major players in the tech sector, have adjusted their portfolios, contributing to the sell-off.
- Negative Sentiment: Negative media coverage and widespread pessimism further fueled the decline, creating a self-reinforcing cycle of sell-offs and declining market capitalization.
Geopolitical Uncertainty and Supply Chain Disruptions
Geopolitical instability and persistent supply chain disruptions have also played a significant role in the Magnificent Seven's market value decline.
Geopolitical Risks and Their Economic Impact
The ongoing war in Ukraine, heightened US-China tensions, and other geopolitical events have created significant economic uncertainty, negatively impacting investor confidence.
- Impact of Sanctions: Sanctions and trade wars disrupt international trade and technological collaboration, impacting the global supply chains of many tech companies.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Geopolitical instability frequently leads to supply chain disruptions, increasing production costs and uncertainty about future production timelines.
- Market Growth Uncertainty: Uncertainty about future growth in key global markets, especially emerging markets, further dampens investor enthusiasm.
Supply Chain Bottlenecks and Inflationary Pressures
Supply chain disruptions, exacerbated by geopolitical events, have contributed to inflationary pressures and constrained production capacity.
- Chip Shortages: The ongoing semiconductor shortage, for example, has limited the production of numerous tech products, impacting revenue and profitability.
- Correlation with Market Value Decline: The correlation between supply chain issues and the decline in Magnificent Seven market values is undeniable, highlighting the interconnectedness of global economic factors.
- Mitigation Strategies: Tech companies are employing various strategies to mitigate supply chain risks, but these efforts are costly and take time to implement.
Conclusion
The dramatic $2.5 trillion decline in the market value of the Magnificent Seven is a multifaceted issue stemming from a confluence of factors, including rising interest rates, high inflation, market corrections driven by overvaluation, and persistent geopolitical uncertainties and supply chain disruptions. Understanding these interconnected challenges is crucial for investors, policymakers, and the tech industry itself. The future trajectory of these tech giants will depend heavily on their ability to adapt to the shifting economic landscape and navigate the ongoing challenges to maintain and grow their market capitalization. To stay informed about the dynamic situation with the Magnificent Seven and their impact on the global economy, continue to monitor market trends and economic indicators closely. Further research into the long-term implications of this significant market value decline is critical for informed decision-making.

Featured Posts
-
 Hungary Defies Us Pressure Maintaining Strong Economic Ties With China
Apr 29, 2025
Hungary Defies Us Pressure Maintaining Strong Economic Ties With China
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Blue Origin Scraps Launch Due To Vehicle Subsystem Problem
Apr 29, 2025
Blue Origin Scraps Launch Due To Vehicle Subsystem Problem
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Actors And Writers Strike The Impact On Hollywood
Apr 29, 2025
Actors And Writers Strike The Impact On Hollywood
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Russias Military Strategy And Its Impact On European Security
Apr 29, 2025
Russias Military Strategy And Its Impact On European Security
Apr 29, 2025 -
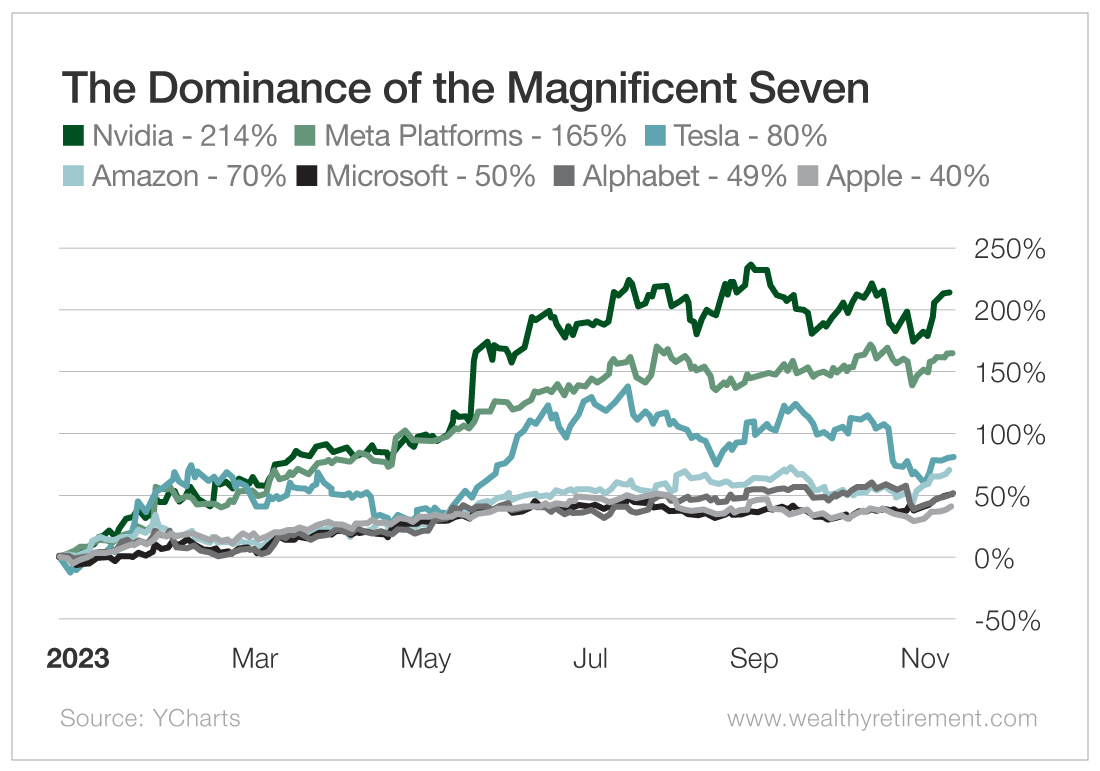 Magnificent Seven Stocks 2 5 Trillion In Lost Market Value This Year
Apr 29, 2025
Magnificent Seven Stocks 2 5 Trillion In Lost Market Value This Year
Apr 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Willie Nelsons 4th Of July Picnic Texas Comeback
Apr 29, 2025
Willie Nelsons 4th Of July Picnic Texas Comeback
Apr 29, 2025 -
 New Documentary Willie Nelson Celebrates Legendary Roadie
Apr 29, 2025
New Documentary Willie Nelson Celebrates Legendary Roadie
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Get To Know Willie Nelson A Collection Of Fast Facts
Apr 29, 2025
Get To Know Willie Nelson A Collection Of Fast Facts
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Willie Nelsons 4th Of July Picnic Returns To Texas
Apr 29, 2025
Willie Nelsons 4th Of July Picnic Returns To Texas
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Willie Nelson Pays Tribute To His King Of The Road Crew In New Documentary
Apr 29, 2025
Willie Nelson Pays Tribute To His King Of The Road Crew In New Documentary
Apr 29, 2025
