Toxic Chemical Contamination: Ohio Train Derailment's Lingering Impact On Buildings
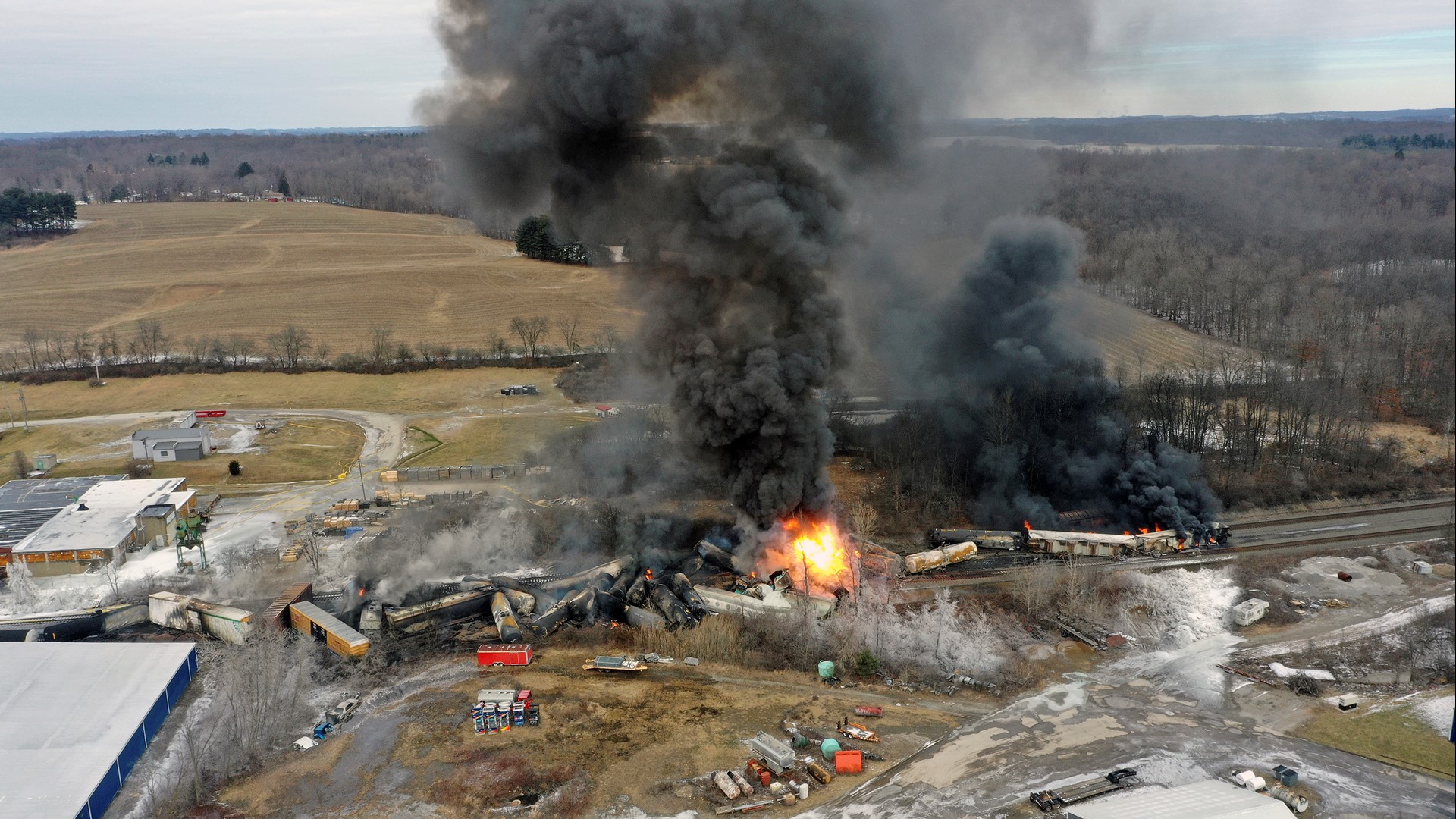

Table of Contents
Assessing the Extent of Toxic Chemical Contamination in Buildings
Types of Chemicals and Their Impact
The derailment released a cocktail of hazardous substances, including vinyl chloride, butyl acrylate, and ethylene glycol monobutyl ether. These chemicals pose significant risks to both human health and building materials.
- Vinyl Chloride: A known carcinogen, vinyl chloride can cause liver damage, respiratory problems, and increased cancer risk. It can degrade many building materials over time, leading to structural weakening.
- Butyl Acrylate: This chemical is an irritant to the skin, eyes, and respiratory system. Long-term exposure can cause allergic reactions and potential damage to building materials, especially plastics and rubber components.
- Ethylene Glycol Monobutyl Ether: This solvent can cause headaches, nausea, and dizziness. Prolonged exposure may lead to kidney and liver damage. It can also affect the integrity of certain paints and coatings within buildings.
These chemicals can infiltrate various building materials:
- Wood: Absorption of these chemicals can weaken wood structures, making them prone to rot and insect infestation.
- Concrete: While concrete is relatively resistant, prolonged exposure to certain chemicals can cause cracking and deterioration over time.
- Insulation: Many insulation materials are susceptible to chemical degradation, compromising their thermal efficiency and potentially releasing harmful particles into the air.
Methods for Detecting Contamination
Accurately assessing the extent of toxic chemical contamination requires employing rigorous testing methods.
- Air Sampling: This involves collecting air samples from inside buildings to measure the concentration of airborne chemicals. This method helps determine the level of immediate risk to occupants.
- Material Sampling: This technique involves collecting samples of building materials (e.g., drywall, insulation) for laboratory analysis to determine the extent of chemical penetration and material degradation.
- Soil Sampling: Analyzing soil samples around buildings can reveal the extent of ground contamination and the potential for further infiltration.
Reputable environmental testing labs and agencies should be consulted to ensure accurate and reliable results.
Identifying Vulnerable Buildings
Certain buildings are more vulnerable to toxic chemical contamination than others.
- Proximity to the derailment site: Buildings closest to the derailment site are at the highest risk of exposure.
- Ventilation systems: Buildings with inadequate ventilation systems are more susceptible to chemical accumulation.
- Building age and materials: Older buildings with porous materials are more likely to absorb and retain contaminants than newer structures with more resistant materials.
Long-Term Effects of Toxic Chemical Contamination on Buildings
Structural Damage and Degradation
The long-term exposure to toxic chemicals can lead to significant structural damage and degradation.
- Weakening of foundations: Chemical infiltration can compromise the structural integrity of building foundations, leading to instability and potential collapse.
- Corrosion of metal components: Many chemicals are corrosive to metals, leading to rusting and weakening of structural steel and other metallic components.
- Degradation of other materials: Exposure can degrade various building materials including wood, plastics, and insulation, reducing their lifespan and effectiveness. Repair or replacement costs can be substantial.
Health Risks for Occupants
Continued exposure to low levels of toxic chemicals can pose significant health risks for building occupants.
- Respiratory problems: Exposure to airborne chemicals can trigger asthma, bronchitis, and other respiratory illnesses.
- Neurological effects: Certain chemicals can affect the nervous system, leading to headaches, dizziness, and cognitive impairment.
- Increased cancer risk: Exposure to known carcinogens, like vinyl chloride, significantly increases the risk of developing various cancers.
Regular air quality monitoring is crucial to protect the health of building occupants.
Economic Impacts
The economic consequences of toxic chemical contamination are far-reaching.
- Cost of testing and remediation: The process of assessing and remediating contamination can be extremely expensive.
- Decreased property values: Buildings affected by contamination often experience a significant decrease in property value, impacting homeowners and investors.
- Legal battles and insurance claims: Disputes over liability and insurance claims can further increase economic losses.
Remediation and Mitigation Strategies
Decontamination Processes
Several methods can be employed to decontaminate affected buildings.
- Air purification: High-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters and other air purification systems can remove airborne contaminants.
- Material removal/replacement: Severely contaminated materials may need to be removed and replaced with clean materials.
- Specialized cleaning techniques: Specialized cleaning methods may be required to remove surface contaminants from building materials.
Building Code Updates and Future Prevention
The Ohio train derailment underscores the urgent need for updated building codes and regulations.
- Improved safety regulations for the transportation of hazardous materials.
- Stricter building material standards that are more resistant to chemical damage.
- Enhanced emergency response protocols for handling chemical spills and releases.
Conclusion
The toxic chemical contamination resulting from the Ohio train derailment presents a severe and long-lasting threat to the structural integrity and habitability of affected buildings. The long-term health implications for residents, coupled with the significant economic burden of remediation, highlight the critical need for immediate action. The severity of this toxic chemical contamination demands a comprehensive response involving rigorous testing, effective decontamination, and significant improvements to safety regulations. Stay informed about ongoing developments, advocate for stronger environmental regulations, and seek professional assistance if you suspect toxic chemical contamination in your building. Understanding and addressing the ongoing dangers of toxic chemical contamination in your community is a crucial step in ensuring public health and safety. Contact your local environmental agencies for further information and support.

Featured Posts
-
 Manchester United Fan Poppy Family Shares Emotional Tribute Following Her Passing
May 02, 2025
Manchester United Fan Poppy Family Shares Emotional Tribute Following Her Passing
May 02, 2025 -
 The Prisoner Of Azkaban Why Chris Columbus Wasnt The Director
May 02, 2025
The Prisoner Of Azkaban Why Chris Columbus Wasnt The Director
May 02, 2025 -
 Remembering Ted Kotcheff Director Of Rambo First Blood 1982
May 02, 2025
Remembering Ted Kotcheff Director Of Rambo First Blood 1982
May 02, 2025 -
 Bila Je Prva Ljubav Zdravka Colica Kad Sam Se Vratio Ti Si Se Udala Zasto
May 02, 2025
Bila Je Prva Ljubav Zdravka Colica Kad Sam Se Vratio Ti Si Se Udala Zasto
May 02, 2025 -
 21 5 Million Seed Funding For Ahead Computing A Major Milestone
May 02, 2025
21 5 Million Seed Funding For Ahead Computing A Major Milestone
May 02, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Gaza Bound Aid Ship Attacked By Drones Ngo Account
May 03, 2025
Gaza Bound Aid Ship Attacked By Drones Ngo Account
May 03, 2025 -
 Sos From Gaza Bound Aid Ship Drone Attack Alleged Off Malta Coast
May 03, 2025
Sos From Gaza Bound Aid Ship Drone Attack Alleged Off Malta Coast
May 03, 2025 -
 Drones Attack Aid Ship Bound For Gaza Ngo Reports
May 03, 2025
Drones Attack Aid Ship Bound For Gaza Ngo Reports
May 03, 2025 -
 Malta Coast Aid Ship To Gaza Reports Drone Attack Issues Sos
May 03, 2025
Malta Coast Aid Ship To Gaza Reports Drone Attack Issues Sos
May 03, 2025 -
 Astwl Alhryt Alkhlfyt Walntayj Almtrtbt Ela Alhjwm Alisrayyly
May 03, 2025
Astwl Alhryt Alkhlfyt Walntayj Almtrtbt Ela Alhjwm Alisrayyly
May 03, 2025
