U.S. Fed Holds Rates Amid Inflation And Unemployment Concerns
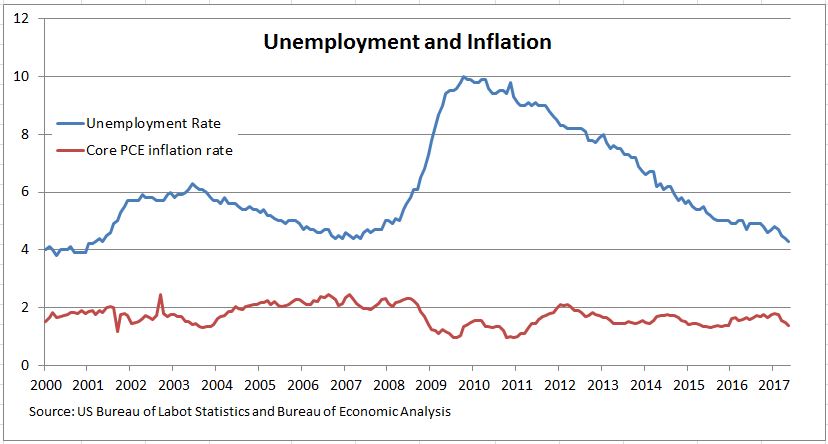
Table of Contents
Inflationary Pressures Remain a Key Concern
Inflation remains a significant headwind for the U.S. economy. The Consumer Price Index (CPI) and Producer Price Index (PPI) continue to reflect elevated price levels, although recent data suggests a potential slowing in the rate of increase. The Fed's target inflation rate is 2%, and while the current figures are showing signs of easing, they remain significantly above this goal. Several factors contribute to this persistent inflation:
- Supply chain disruptions: Ongoing global supply chain bottlenecks continue to constrain the availability of goods, driving up prices.
- Energy prices: Fluctuations in energy prices, particularly oil and natural gas, significantly impact overall inflation.
- Wage growth: While a healthy economy requires wage growth, rapid increases can contribute to inflationary pressures if not matched by productivity gains.
The Fed is closely monitoring these factors, as sustained high inflation erodes purchasing power and can destabilize the economy. The core inflation rate (excluding volatile food and energy prices) also remains a key indicator for the central bank's policy decisions. The persistence of core inflation suggests that underlying price pressures are still present.
Unemployment Rates and Labor Market Dynamics
The labor market presents a mixed picture. While the unemployment rate has fallen to historically low levels, signifying strong job growth, the situation is complicated by persistent labor shortages in certain sectors. This tight labor market contributes to upward pressure on wages, which, as discussed above, can fuel inflation.
- Low unemployment figures: The recent employment reports indicate remarkably low unemployment numbers, suggesting a robust job market.
- Strong job growth: Job creation across various sectors remains strong, further supporting the idea of a healthy, albeit tight, labor market.
- Wage growth implications: Rapid wage growth in some sectors is partly a response to labor shortages, but it presents a challenge for the Fed in balancing employment with inflation control.
The Fed's Balancing Act: Growth vs. Inflation
The Fed faces the difficult task of balancing its dual mandate: promoting maximum employment and price stability. Raising interest rates is a traditional tool to combat inflation, as it makes borrowing more expensive and slows economic activity. However, aggressive rate hikes risk triggering a recession by stifling economic growth and increasing unemployment. The Fed is therefore carefully navigating this tightrope, attempting to cool inflation without causing significant economic harm. Quantitative easing and other monetary policies are also considered alongside interest rate adjustments.
Market Reactions and Investor Sentiment
The Fed's decision to hold rates has been met with varied reactions in the market. While some investors welcomed the pause, others expressed concern about the persistence of inflation. Stock market performance following the announcement was mixed, reflecting this uncertainty.
- Stock market response: Stock market indices showed relatively modest changes, suggesting a degree of market anticipation.
- Bond yields: Changes in bond yields provide further insights into investor expectations regarding future interest rate movements.
- Investor confidence: Investor confidence indicators, such as the consumer confidence index, offer a valuable gauge of overall market sentiment.
Future Outlook and Potential Next Steps
The Fed's forward guidance provides some clues about its future intentions, but significant uncertainty remains. The path of future interest rates hinges on several key factors, including the evolution of inflation, the strength of the labor market, and global economic conditions.
- Fed's forward guidance: The Fed's communication to the public concerning their policy intentions will provide insight into upcoming decisions.
- Potential rate adjustments: Future rate increases or decreases will depend on evolving economic data.
- Economic forecasts: Economists' forecasts and projections vary, suggesting a range of possible scenarios.
Conclusion:
The U.S. Federal Reserve's decision to hold interest rates reflects the delicate balancing act between controlling inflation and supporting economic growth. While recent data shows some progress in curbing inflation, persistent inflationary pressures and a tight labor market remain significant concerns. The path forward remains uncertain, and the Fed's future decisions will depend critically on upcoming economic data. Stay updated on the latest developments concerning U.S. Fed interest rate decisions and their impact on the economy. Continue to monitor credible sources for economic analysis and updates to stay informed.

Featured Posts
-
 Analysis Of Wireless Mesh Networks Market 9 8 Cagr And Beyond
May 09, 2025
Analysis Of Wireless Mesh Networks Market 9 8 Cagr And Beyond
May 09, 2025 -
 Ftcs Appeal Challenges Judges Decision On Microsoft Activision Merger
May 09, 2025
Ftcs Appeal Challenges Judges Decision On Microsoft Activision Merger
May 09, 2025 -
 Palantir Stock Analyzing The Potential For A 40 Rise By 2025
May 09, 2025
Palantir Stock Analyzing The Potential For A 40 Rise By 2025
May 09, 2025 -
 Young Thug Vows Fidelity To Mariah The Scientist In Leaked Snippet
May 09, 2025
Young Thug Vows Fidelity To Mariah The Scientist In Leaked Snippet
May 09, 2025 -
 Strategicheskoe Partnerstvo Frantsiya I Polsha Ukreplyayut Oboronu Otvet Trampu I Putinu
May 09, 2025
Strategicheskoe Partnerstvo Frantsiya I Polsha Ukreplyayut Oboronu Otvet Trampu I Putinu
May 09, 2025
