Uber's Foodpanda Taiwan Acquisition Fails Amidst Regulatory Challenges

Table of Contents
Antitrust Concerns and Competition Issues in the Taiwanese Food Delivery Market
The primary reason for the acquisition's failure stems from significant antitrust concerns and competition issues within the Taiwanese food delivery market.
Dominant Market Share
Foodpanda held a substantial market share in Taiwan before the proposed acquisition. While precise figures are not publicly available, industry analysts estimate Foodpanda's dominance to be significantly higher than its competitors, including Uber Eats. The acquisition would have further consolidated Uber's already considerable presence, creating a near-monopoly.
- Existing market dominance of Foodpanda: Foodpanda's extensive network of restaurants and delivery drivers gave it a commanding lead.
- Uber Eats' presence in the market: Uber Eats, although a significant player, held a considerably smaller market share compared to Foodpanda.
- Potential impact on competition post-merger: The combined entity would have likely controlled a disproportionate share of the market, potentially stifling competition.
- Concerns about reduced consumer choice and potentially higher prices: A lack of competition often leads to reduced consumer choice and potentially inflated prices for food delivery services.
Fair Trade Commission Scrutiny
The Taiwanese Fair Trade Commission (FTC) played a crucial role in blocking the merger. The FTC launched a thorough investigation into the potential anti-competitive effects of the acquisition. Their primary concern centered on the significant increase in market concentration and the potential for monopolistic practices.
- FTC investigation timeline: The FTC's investigation spanned several months, involving detailed analysis of market data and extensive consultations with stakeholders.
- Key objections raised by the FTC: The FTC highlighted concerns about reduced competition, potential price increases, and the limitation of choices for both consumers and restaurants.
- Evidence presented by the FTC regarding market concentration: The FTC likely presented evidence demonstrating Foodpanda's already dominant position and the significant further concentration that the merger would have created.
- Public statements made by the FTC: The FTC released public statements outlining their concerns and ultimately rejecting the proposed acquisition based on their findings.
Responses from Uber and Foodpanda
In response to the FTC's concerns, Uber and Foodpanda likely attempted to address the issues, but their efforts proved insufficient to sway the commission. While specific details of their responses remain largely confidential, it's likely they proposed remedies aimed at mitigating the anti-competitive concerns.
- Public statements from Uber and Foodpanda: Both companies likely issued public statements expressing their disappointment but acknowledging the FTC's decision.
- Proposed remedies or concessions offered: They may have offered concessions such as divesting certain assets or agreeing to specific operational restrictions to address the FTC's concerns.
- Any legal challenges initiated by Uber or Foodpanda: It's possible, though not confirmed, that legal challenges were considered or initiated, but these were ultimately unsuccessful.
Regulatory Landscape in Taiwan and its Impact on Mergers and Acquisitions
Taiwan boasts a relatively stringent regulatory environment for mergers and acquisitions, particularly in sectors deemed crucial for consumer welfare, such as food delivery.
Stringent Regulations
Compared to some other jurisdictions, Taiwan's regulatory framework places a significant emphasis on preventing monopolies and protecting fair competition. This is reflected in the rigorous review process undertaken by the FTC.
- Specific laws and regulations impacting the deal: The Fair Trade Act is the primary legislation governing mergers and acquisitions in Taiwan.
- Comparison with regulatory environments in other countries (e.g., US, EU): While the US and EU also have antitrust regulations, the Taiwanese approach may be considered more stringent in certain aspects.
- Role of government oversight in preventing monopolies: The Taiwanese government actively intervenes to prevent the formation of monopolies that could harm consumers and businesses.
Protection of Consumers and Businesses
The Taiwanese government's focus on protecting consumers and ensuring a level playing field for businesses underpins its stringent merger regulations. This reflects a broader societal commitment to fair competition and consumer welfare.
- Importance of fair competition for consumers: Fair competition ensures consumers benefit from lower prices, greater choice, and improved service quality.
- Government's commitment to maintaining a level playing field for businesses: Preventing monopolies ensures that smaller businesses have a fair chance to compete and thrive.
- Public opinion and consumer advocacy groups' role: Public opinion and consumer advocacy groups often play a significant role in shaping regulatory decisions concerning mergers and acquisitions.
Implications of the Failed Acquisition for the Future of the Taiwanese Food Delivery Market
The failed acquisition has significant implications for the future of Taiwan's food delivery market.
Increased Competition
The failed merger could lead to increased competition, benefiting consumers and fostering innovation. Existing players like Uber Eats and other smaller players might now have an opportunity to expand their market share.
- Potential for new entrants into the market: The absence of a dominant player might incentivize new players to enter the market.
- Opportunities for existing competitors to gain market share: Uber Eats and other competitors can now aggressively compete for customers and restaurants.
- Long-term outlook for consumer prices and service quality: Increased competition could lead to lower prices and improved service quality for consumers.
Lessons Learned for Future Mergers
The failed Uber-Foodpanda acquisition provides valuable lessons for future mergers and acquisitions in Taiwan. Companies must now conduct more thorough due diligence and carefully consider the potential regulatory hurdles.
- Increased due diligence requirements for future mergers: Companies will need to conduct extensive antitrust analysis and engage with the FTC early in the process.
- More rigorous regulatory review processes: The FTC's scrutiny will likely intensify, leading to longer review periods and more demanding requirements for approval.
- Greater emphasis on anti-competitive analysis: Companies will need to demonstrate that their proposed mergers will not harm competition.
Conclusion
The failure of Uber's Foodpanda Taiwan acquisition underscores the significant role of regulatory challenges and antitrust concerns in shaping the food delivery landscape. The Taiwanese FTC's decision reflects a strong commitment to preventing monopolies and protecting consumer welfare. This case serves as a stark reminder of the complexities involved in navigating mergers and acquisitions in Taiwan's dynamic food delivery market. Understanding the intricacies of Taiwanese antitrust laws and the Fair Trade Commission's scrutiny is crucial for any company considering a similar venture in the future. Businesses must carefully consider the potential implications before pursuing any mergers and acquisitions related to the food delivery market in Taiwan.

Featured Posts
-
 Gazze De Cadirda Kuran Ezberleyen Cocuklar Bir Gerceklik
May 19, 2025
Gazze De Cadirda Kuran Ezberleyen Cocuklar Bir Gerceklik
May 19, 2025 -
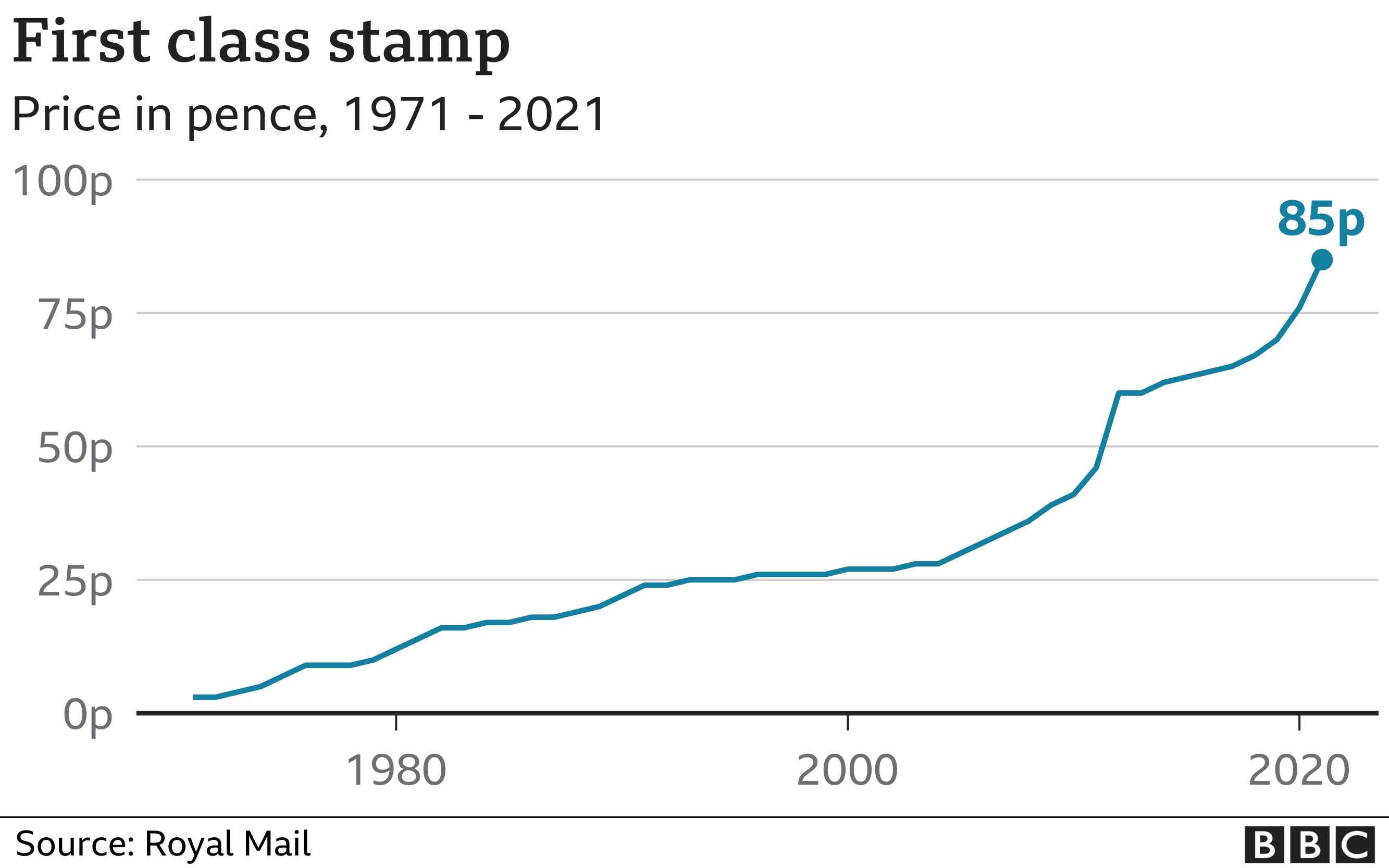 Uk First Class Stamp Price Increase 1 70 From Date
May 19, 2025
Uk First Class Stamp Price Increase 1 70 From Date
May 19, 2025 -
 El Cne Segun Ana Paola Hall Independencia Y Naturaleza Colegiada
May 19, 2025
El Cne Segun Ana Paola Hall Independencia Y Naturaleza Colegiada
May 19, 2025 -
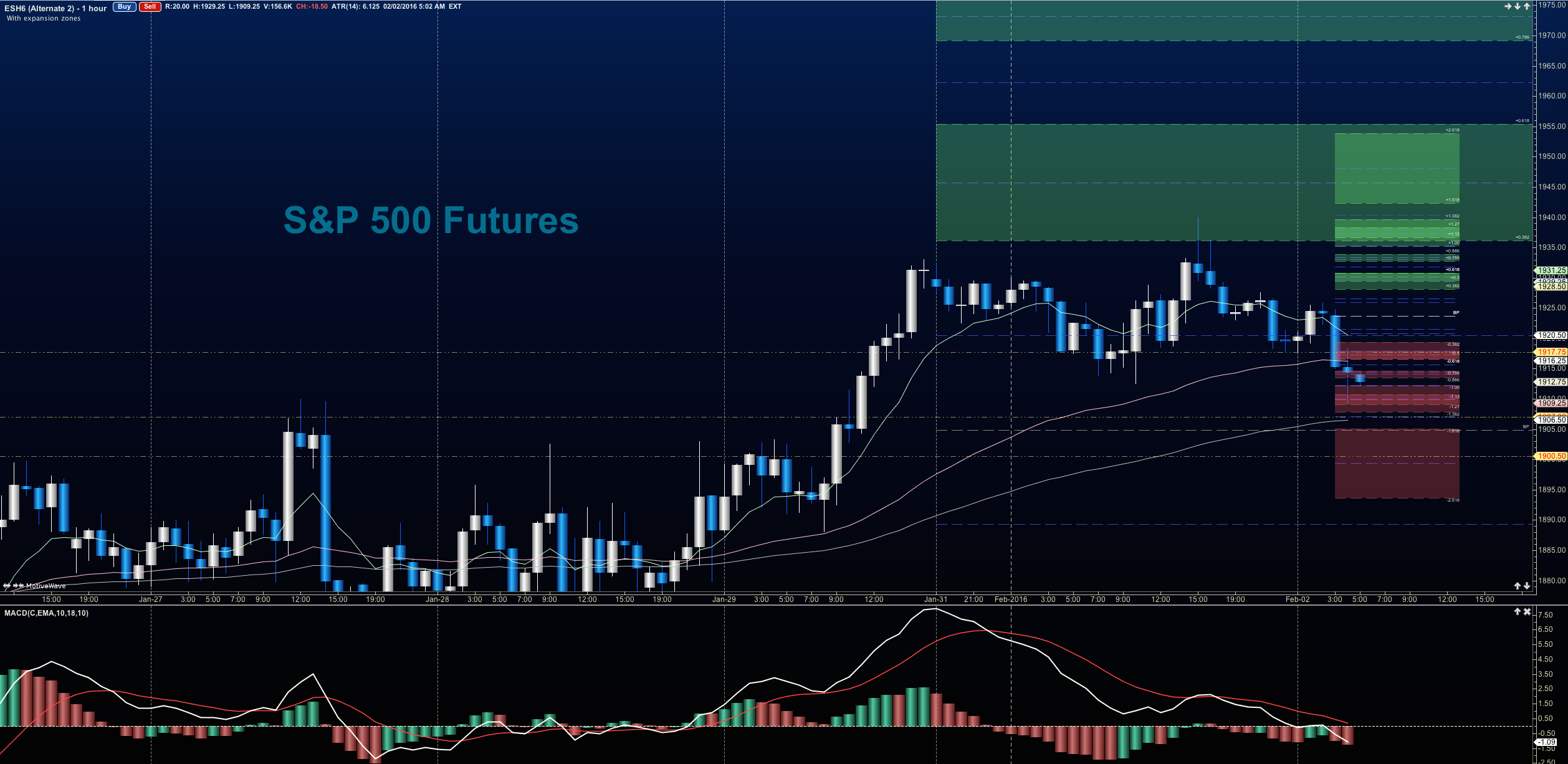 Euro And European Futures Surge On Swissquote Bank Usd Futures Decline
May 19, 2025
Euro And European Futures Surge On Swissquote Bank Usd Futures Decline
May 19, 2025 -
 Analyzing Red Carpet Rule Violations Insights From Cnn
May 19, 2025
Analyzing Red Carpet Rule Violations Insights From Cnn
May 19, 2025
