Understanding Dangerous Climate Whiplash: Impacts And Responses In Cities
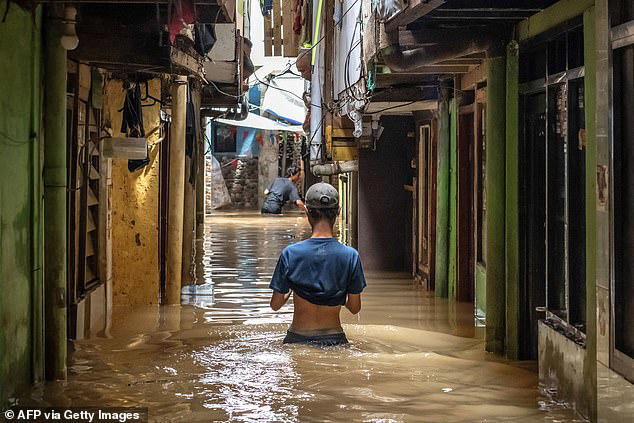

Table of Contents
Defining Climate Whiplash and its Urban Impacts
Climate whiplash refers to the rapid and unpredictable transitions between extreme weather conditions. Unlike gradual climate change, which involves a slow shift in average temperatures and precipitation, climate whiplash involves sudden and dramatic swings, creating cascading effects on urban systems. This unpredictability makes planning and adaptation incredibly challenging. The difference lies in the speed and intensity of the changes. Gradual change allows for slower adaptation, whereas climate whiplash demands immediate and flexible responses.
- Increased frequency of heatwaves followed by intense cold snaps: This creates significant stress on infrastructure and public health, demanding systems capable of handling both extremes.
- Rapid shifts from drought to flooding, impacting water resources: Cities face the dual challenge of managing water scarcity during droughts and preventing catastrophic flooding during subsequent intense rainfall.
- Severe storms interspersed with periods of unusual calm: This unpredictable pattern makes it difficult to predict and prepare for infrastructure damage and potential public safety threats.
- The cumulative effect on infrastructure and public health: Repeated exposure to these extreme weather swings weakens infrastructure and increases the strain on public health systems, leading to more significant damage and higher costs over time.
Vulnerable urban populations, including low-income communities and marginalized groups, are disproportionately affected by climate whiplash. They often lack access to resources that would help them cope with extreme weather events and recover from their impacts.
Infrastructure Vulnerability to Climate Whiplash
Existing urban infrastructure is largely designed for predictable weather patterns, making it ill-equipped to handle the rapid shifts characteristic of climate whiplash. This vulnerability is evident across various urban systems:
Water Management Systems
Sudden shifts from drought to flooding overwhelm water management systems. Existing infrastructure may struggle to handle the volume of water during floods, while drought periods expose vulnerabilities in water supply and storage. This necessitates robust water management strategies including improved drainage systems, water storage solutions, and efficient water reuse programs.
Transportation Networks
Extreme weather events—from flash floods to heavy snowfalls—frequently disrupt transportation networks. Roads, bridges, and public transportation systems face damage and closures, impacting commutes, emergency services, and the overall economy. Investing in resilient transportation infrastructure and implementing contingency plans are critical.
Energy Grids
Extreme temperature swings place significant strain on energy grids. Heatwaves can lead to increased energy demand and potentially power outages, while extreme cold can damage power lines and other components. Investing in smart grids and energy storage solutions is key to building resilience.
Building Resilience: The Need for Adaptable and Robust Infrastructure
To address these challenges, cities must invest in adaptable and robust infrastructure. This includes:
- Case studies of cities affected by climate whiplash-related infrastructure failures: Examining these instances helps identify weaknesses and inform future infrastructure development.
- Technological solutions for improved infrastructure resilience: Smart sensors, advanced forecasting models, and resilient building materials play a key role.
- Financial considerations for upgrading infrastructure: Securing adequate funding is crucial for implementing necessary improvements and upgrading existing systems.
Public Health Consequences of Climate Whiplash
The rapid shifts in weather conditions associated with climate whiplash have significant implications for public health:
- Increased risk of heatstroke and hypothermia: Rapid temperature fluctuations expose populations to both heat-related illnesses and hypothermia.
- Spread of infectious diseases due to flooding and changing water conditions: Flooding can contaminate water sources and create breeding grounds for disease vectors.
- Mental health impacts of repeated extreme weather events: The stress and trauma associated with repeated exposure to extreme weather can have significant mental health consequences.
- Air quality deterioration from wildfires and dust storms: Extreme weather events can exacerbate air pollution, increasing respiratory illnesses.
Effective public health preparedness, including robust early warning systems and community outreach programs, is crucial for mitigating these risks.
Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies for Cities
Cities must implement comprehensive mitigation and adaptation strategies to address the challenges of climate whiplash:
- Investing in green infrastructure (green roofs, urban forests): These features can help regulate temperatures, reduce flooding, and improve air quality.
- Implementing water-sensitive urban design: This approach focuses on managing stormwater runoff and reducing the impact of flooding.
- Improving early warning systems for extreme weather: Advanced weather forecasting and communication systems are vital for timely alerts and evacuations.
- Strengthening community resilience through preparedness programs: Educating communities on how to prepare for and respond to extreme weather events is essential.
- Promoting sustainable urban planning and development: This involves integrating climate considerations into all aspects of urban planning.
Effective implementation requires strong policy support, collaborative partnerships between government, businesses, and communities, and active community engagement.
Conclusion
Understanding the multifaceted impacts of climate whiplash is crucial for ensuring the safety and resilience of our cities. From infrastructure vulnerability to public health consequences, the effects are far-reaching and require comprehensive strategies. By investing in resilient infrastructure, implementing effective adaptation measures, and fostering community resilience, cities can better prepare for and mitigate the risks associated with climate whiplash. Let's work together to build more climate-resilient urban environments and reduce the impact of dangerous climate whiplash. Learn more about developing effective climate whiplash response strategies for your city today.

Featured Posts
-
 Selena Gomez And Miley Cyrus Akhiri Perseteruan Siap Untuk Kencan Berempat
May 31, 2025
Selena Gomez And Miley Cyrus Akhiri Perseteruan Siap Untuk Kencan Berempat
May 31, 2025 -
 Sanofi Et Ses Rejets Toxiques Analyse D Une Controverse
May 31, 2025
Sanofi Et Ses Rejets Toxiques Analyse D Une Controverse
May 31, 2025 -
 Analyzing Provincial Influence On Residential Construction Speed
May 31, 2025
Analyzing Provincial Influence On Residential Construction Speed
May 31, 2025 -
 Zverevs Indian Wells Campaign Ends Early Griekspoor Upsets Top Seed
May 31, 2025
Zverevs Indian Wells Campaign Ends Early Griekspoor Upsets Top Seed
May 31, 2025 -
 Federal Probe Into Impersonation Of White House Chief Of Staff Susie Wiles
May 31, 2025
Federal Probe Into Impersonation Of White House Chief Of Staff Susie Wiles
May 31, 2025
